Abstract
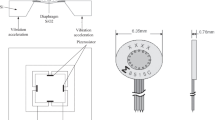
The measured wall pressure of high-speed train will be affected by train vibration due to the complex test environment. This paper is devoted to the investigation of the influence of vibration acceleration on the wall pressure measurement of high-speed trains. Aiming at the vibration-induced effect of piezoresistive pressure sensors, a vibration-pressure coupling laboratory platform is established. The output of the piezoresistive pressure sensor under different frequency vibration loads is obtained from the platform. The vibration and pressure sensor output signals are separated through an EEMD-based method. By the analysis of different vibration loads and the pressure sensor output signal, their internal relations are obtained. Moreover, the results provide theoretical guidance for measuring high-speed train wall pressure and the pressure under other acceleration loading environments.





















Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Raghu, S., Kim, H.D., and Setoguchi, T., Prog. Aerosp. Sci., 2002, vol. 38, p. 469. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0376-0421(02)00029-5
Zhiyun Shen, J. China Railw. Soc., 2006, vol. 28, no. 4, p. 12.
Suzuki, M. and Tanemoto, K., J. Wind Eng. Ind. Aerodyn., 2003, vol. 91, no. 1, p. 209. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0167-6105(02)00346-X
Jiali Liu, Jiye Zhang, and Weihua Zhang, J. China Railw. Soc., 2011, vol. 33, no. 9, p. 19.
Junhao Peng, Qing Jiang, Jianbin Tang, and Qianjun Zhou, Intstrum. Tech. Sens., 2014, vol. 8, no. 1, p. 9.
Chunjun Chen, Hongyang He, and Yunlong Shao, J. Southwest Jiaotong Univ., 2015, vol. 50, no. 3, p. 472.
Gradolph, C., Freidberger, A., Müller, G., and Wilde, J., Sens. Actuators, A, 2009, vol. 150, p. 69. https://doi-org-s.era.lib.swjtu.edu.cn/10.1016/j.sna.2008.12.007
Yupeng Zhai, Zhijie Zhang, and Hao Zhang, J. Meas. Sci. Instrum., 2019, vol. 10, no. 2, p. 176.
Zhongliang Yu, Yulong Zhao, Lili Li, Bian Tian, Rongjun Cheng, and Cun Li, Micro Nano Lett., 2014, vol. 9, p. 680.
Chao Deng, Chunjun Chen, Qi Sun, Dongwei Wang, and Zhiying He, Fluctuation Noise Lett., 2020, vol. 19, no. 2, p. 2050020. https://doi.org/10.1142/S0219477520500200
Chunjun Chen, Chao Deng, and Dongwei Wang, Measurement, 2021, vol. 168, p. 108442. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.measurement.2020.108442
Maliha Farhath, and Mst. Fateha Samad, J. Comput. Electron., 2020, vol. 19, p. 310. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10825-019-01429-w
Clark, S.K. and Wise, K.D., IEEE Trans. Electron Devices, 1979, vol. 16, no. 12, p. 1887. https://doi.org/10.1109/T-ED.1979.19792
Herrera-May, A.L., Soto-Cruz, B.S., Lopez-Huerta, F., and Aguilera Cortes, L.A., Rev. Mex. Fis., 2009, vol. 55, no. 1, p. 14.
Fiorillo, A.S., Critello, C.D., and Pullano, S.A., Sens. Actuators, A, 2018, vol. 281, p. 156. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sna.2018.07.006
Leger, P., Ide, I.M., and Paulter, P., Comput. Struct., 1990, vol. 36, p. 1153. https://doi.org/10.1002/smll.201800819
Fei He, Hongqiang Liao, Jihong Zhu, and Zhongze Guo, Chin. J. Aeronaut., 2019, vol. 32, no. 6, p. 1416. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cja.2019.03.031
Stanii, M.M., Q. Appl. Math., 1955, vol. 12, no. 4, p. 361. https://doi.org/10.1090/qam/65382
Huang, N., Shen, Z., Long, S., Wu, M., Shih, H., Zheng, Q., Yen, N., Tung, C., and Liu, H., Proc. R. Soc. A, 1998, vol. 454, no. 1971, p. 903. https://doi.org/10.1098/rspa.1998.0193
Wu, Z.H. and Huang, N.E., Adv. Adapt. Data Anal., 2009, vol. 1, no. 1, p. 1. https://doi.org/10.1142/S1793536909000047
Hongyang He, Chunjun Chen, Xiaolang Miao, and Fasheng He, J. Vib. Shock, 2015, vol. 34, no. 19, p. 71.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (grants nos. 51975487 and 51475387).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yuxiao, C., Chunjun, C. & Chao, D. Research on Vibration Effect of Piezoresistive Pressure Sensor. Instrum Exp Tech 65, 653–667 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0020441222040170
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S0020441222040170