Abstract
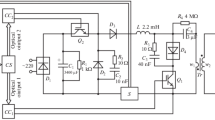
Control systems of high-voltage transistor switches are described. Possible ways to develop these systems are considered. A control system of the transistors of a high-voltage switch on the basis of a current loop is considered in detail. Signals for turning the transistors on and off arrive to their control boards from their common conductor with bipolar current pulses. A positive pulse turns the transistors on, while a negative pulse turns them off. The time interval between these pulses sets the time during which the switch is in the conducting state. The minimum duration of the conducting state is several microseconds, while the maximum duration is not limited. The results of tests of a switch prototype with an operating voltage of up to 4 kV are presented. The operation of the switch was demonstrated when obtaining rectangular pulses in the microsecond range across a resistive load. We also verified the possibility of forming pulses of damped oscillations at a frequency of 1 MHz by this device. The positive test results make it possible to develop switches for operating voltages of tens of kilovolts using the considered approach.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Vasiliev, P.V., Lyubutin, S.K., Pedos, M.S., Ponomarev, A.V., Rukin, S.N., Slovikovskii, B.G., Timoshenkov, S.P., and Cholakh, S.O., Instrum. Exp. Tech., 2010, vol. 53, no. 6, p. 830. doi 10.1134/ S0020441210060114
Baek, J.W., Yoo, D.-W., and Kim, H.-G., IEEE Trans. Ind. Applic., 2001, vol. 37, no. 6, p. 1832. doi 10.1109/28.968198
Arntz, F., Casey, J., Kempkes, M., Butler, N., and Gaudreau, M., Proc. of EPAC, Edinburgh, Scotland, 2006, p. 3136.
Moshkunov, S.I., Rebrov, I.E., and Khomich, V.Yu., Uspekhi Prikladn. Fiz., 2013, vol. 1, no. 5, p. 630.
Jiang, J., Ma, G.M., Luo, D.P., Li, C.R., Li, Q.M., and Wang, W., Rev. Sci. Instrum., 2014, vol. 85, no. 2, p. 024706. doi 10.1063/1.4866654
Kazantsev, V.I. and Platonov, S.A., Naukoemkie Tekhnol., 2014, vol. 15, no. 11, p. 71.
Vinod, J., Bum-Seok, S., and Lipo, T.A., IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl., 1999, vol. 35, no. 5, p. 1108. doi 10.1109/ 28.793372
Ponomarev, A.V., Gusev, A.I., Pedos, M.S., and Mamontov, Yu.I., Izv. Vyssh. Uchebn. Zaved. Fiz., 2014, vol. 57, no. 12/2, p. 250.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Original Russian Text © A.V. Ponomarev, Yu.I. Mamontov, 2017, published in Pribory i Tekhnika Eksperimenta, 2017, No. 6, pp. 42–50.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ponomarev, A.V., Mamontov, Y.I. Control systems of high-voltage transistor switches. Instrum Exp Tech 60, 818–825 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0020441217060082
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S0020441217060082