Abstract
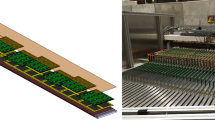
A calorimeter for detecting hadrons in the energy range 10–100 GeV is described. It is used at CERN in the NA58 (COMPASS) experiment aimed at studying the nucleon structure and spectroscopy measurements of charmed particles. The calorimeter is composed of 480 modules with a cross section of 15×15 cm2, assembled in a matrix with dimensions of 4.2×3 m2 and a central window of area 1.2×0.6 m2. In each module are 40 iron and scintillator layers of a total thickness of 4.8 interaction lengths. The energy resolution of the calorimeter for hadrons (pions) and electrons and the spatial resolution, determined on the test beams, are \(\frac{{\sigma _\pi (E)}}{{E[GeV]}} = \frac{{59.4 \pm 2.9}}{{\sqrt E }} \oplus (7.6 \pm 0.4)\% ;\frac{{\sigma _e (E)}}{{E[GeV]}} = \frac{{24.6 \pm 0.7}}{{\sqrt E }} \oplus (0.7 \pm 0.4)\% \), and σ x,y ≈ 15 mm, respectively. The average value of the e/π ratio that characterizes the amplitude responses of the calorimeter to electrons and pions with equal energies from the above range is 1.2 ± 0.1. This study was performed at the JINR Laboratory for Particle Physics.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
The COMPASS Collaboration (Common Muon and Proton Apparatus for Structure and Spectroscopy). Proposal to the CERN, SPSLC (CERN/S PSLC 96-14, SPSC/P297. March 1, 1996) and Addendum (CERN/S PSLC/96-30, SPSLC/P297 Add.1. May 20, 1996).
Brun, R. and Gartminati, F., GEANT 3.21, CERN, Program Library.
Gabriel, T.A., Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res., Sect. A, 1991, vol. 319, p. 106.
Wigmans, R., Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res., Sect. A, 1987, vol. 259, p. 389.
Leroy, C. and Rancoita, P.G., Rep. Prog. Phys., 2000, vol. 63, pp. 505–606.
Aleev, A.N., Aleksandrov, L., Balandin, V.P., et al., Preprint of Joint Instit. for Nucl. Res., Dubna, 1989, no. R1-89-434.
Aref’ev, V.A., Astakhov, V.I., Batyunya, B.V., et al., Kratk. Soobshch. OIYaI, Dubna, 1996, no. 5[79]-96, p. 15.
Kadykov, M.G., Semenov, V.K., and Suzdalev, V.I., Preprint of Joint Inst. for Nucl. Res., Dubna, 1990, no. 13-90-16.
Hubbeling, L., CERN/ECP, Geneva, 1992, no. 92-10.
http://wwwcompass.cern.ch/compass/detector/trigger/muon-trigger/welcome.html.
/afs/cern.ch/user/e/emk/public/trigger.ps.gz; Hannapel J., Klein F., Ostrick M., et al., The COMPASS Trigger System for Muon Scattering, submitted to Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res., Sect. A.
http://wwwcompass.cern.ch/compass/detector/daq/welcome.html.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Original Russian Text © N.V. Vlasov, O.P. Gavrishchuk, N.A. Kuz’min, V.V. Kukhtin, A.N. Maksimov, P.K. Man’yakov, Yu.V. Mikhailov, I.A. Savin, V.K. Semenov, A.B. Shalygin, A.I. Yukaev, 2006, published in Pribory i Tekhnika Eksperimenta, 2006, No. 1, pp. 47–61.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vlasov, N.V., Gavrishchuk, O.P., Kuz’min, N.A. et al. A calorimeter for detecting hadrons with energies of 10–100 GeV. Instrum Exp Tech 49, 41–55 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0020441206010040
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S0020441206010040