Abstract—
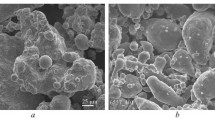
X-ray diffraction, IR spectroscopy, and chemical analysis are used to elucidate the general mechanisms underlying the formation of nanoparticulate solid solutions based on Al2– хFeхO3 and Fe2 –yAlyO3 modified with molybdenum dioxide, zirconium dioxide, and yttrium oxide and prepared by heat-treating ammonium hydroxocarbonate complexes, such as NH4Al2Fe(OH)5(CO3)2. The addition of modifying oxides (within 0.005 mol %) is shown to enhance the polishing ability of the solid solutions for finish polishing of nonferrous metals and alloys (copper and brass) by a factor of 5–7 relative to unmodified aluminum iron oxides, which is attributable to the increased chemical activity of the abrasive material. A modified aluminum iron oxide containing 0.001–0.003 Y2O3 is more effective in polishing titanium. The surface roughness thus achieved is Ra = 0.005–0.006 μm.






Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Artemov, A.S., Polishing nanodiamonds, Phys. Solid State, 2004, vol. 46, no. 4, pp. 687–695.
Jackson, M.J., Mills, B., and Hitchiner, M.P., Controlled wear of vitrified abrasive materials for precision grinding applications, Sadhana, 2003, vol. 28, no. 5, pp. 897–914.
Bakharev, V.P., Dispersion of ceramics and composites in diamond finishing by free abrasive, Russ. Eng. Res., 2009, vol. 29, no. 2, pp. 162–168.
Filatov, Yu.D., Assessing the surface roughness and reflectivity of articles from nonmetallic materials during diamond abrasive finishing, Sverkhtverd. Mater., 2009, no. 5, pp. 70–81.
Storozhenko, P.A., Guseinov, Sh.L., and Malashin, S.I., Nanodispersed powders: synthesis methods and practical applications, Nanotekhnol. Russ., 2009, vol. 4, nos. 5–6, pp. 262–274.
Pokropivnyi, V.V. and Silenko, P.M., Silicon carbide nanotubes and nanotubular fibers: synthesis, stability, structure and classification, Theor. Exp. Chem., 2006, vol. 42, no. 1, pp. 3–15.
Khanra, A.K., Production of boron carbide powder by carbothermal synthesis of gel material, Bull. Mater. Sci., 2007, vol. 30, no. 2, pp. 93–96.
Bogdanov, S.P., Influence of superstoichiometric boron on the synthesis of cubic boron nitride, Glass Phys. Chem., 2008, vol. 34, no. 3, pp. 336–339.
Degtyareva, E.V., Kabakova, I.I., Skorodumova, E.B., and Armyanovskii, V.E., An abrasive-resistant corundum ceramic for drawing microwires, Refract. Ind. Ceram., 1982, vol. 23, nos. 1–2, pp. 82–87.
Garshin, A.P., Gropyanov, V.M., and Lagunov, Yu.V., Abrazivnye materialy (Abrasive Materails), Leningrad: Mashinostroenie, 1983.
Viktorov, V.V., Fotiev, A.A., and Badich, V.D., Abrasive and thermal properties of Al2O3–Cr2O3 solid solutions, Inorg. Mater., 1996., vol. 32, no. 1, pp. 55–57.
Chekhomova, L.F., Abrasive properties of modified chromia, Inorg. Mater., 2001, vol. 37, no. 3, pp. 274–280.
Koroleva, L.F., Modifitsirovannye oksidy, oksogidroksid, shpineli khroma dlya abrazivnykh i pigmentnykh materialov (Modified Chromium Oxides, Oxyhydroxide, and Spinels for Abrasive Materials and Pigments), Yekaterinburg: Ural. Otd. Ross. Akad. Nauk, 2002.
Koroleva, L.F., Abrasive properties of aluminum iron oxide nanoparticles, Inorg. Mater., 2009, vol. 45, no. 10, pp. 1158–1165.
Koroleva, L.F., Tribochemical activity of mixed-oxide abrasive materials in metal polishing, Fiz. Khim. Obrab. Mater., 2006, no. 4, pp. 84–92.
Kotov, Yu.A. and Samatov, O.M., Characteristics of alumina powder prepared by electroexplosion of wire, Poverkhnost, 1994, nos. 10–14, pp. 90–94.
Belousov, V.M., Chertov, V.M., Rozhkova, E.V., Litvin, V.I., and Zazhigalov, V.A., Sol–gel synthesis of porous iron–aluminum oxide materials and control over their physicochemical characteristics, Teor. Eksp. Khim., 1997, vol. 33, no. 2, pp. 120–123.
Nan-Hoon Kim, Jond-Heun Lim, Sang-Yong Kim, and Eui-Goo Chang, Semi-abrasive free slurry with acid colloidal silica for copper chemical mechanical planarization, J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron., 2005, vol. 16, pp. 629–632.
Marchenko, E.A., O prirode razrusheniya poverkhnosti metallov pri trenii (On the Nature of Friction-Induced Metal Surface Fracture), Moscow: Nauka, 1979.
Rebinder, P.A., Importance of physicochemical processes for mechanical fracture and processing of solids in engineering, Vestn. Akad. Nauk SSSR, 1940, no. 8, pp. 5–28.
Koroleva, L.F., Modified nanoparticle oxides for final polishing, Diagnostics, Resource Mech. Mater. Struct., 2016, no. 2, pp. 48–73. https://doi.org/10.17804/2410-9908.2016.2.048-073
Busev, A.I., Analiticheskaya khimiya molibdena (Analytical Chemistry of Molybdenum), Moscow: Akad. Nauk SSSR, 1962.
Nakamoto, K., Infrared Spectra of Inorganic and Coordination Compounds, London: Wiley, 1963.
Koroleva, L.F., Synthesis and abrasive properties of nanoparticulate MoO2-modified Al2 – xFexO3 and Fe2 – yAlyO3 solid solutions, Inorg. Mater., 2010, vol. 46, no. 12, pp. 1330–1336.
Koroleva, L.F., Final polishing of metals to obtain nanoroughened surface, Nanotechnol. Russ., 2012, vol. 7, nos. 1–2, pp. 67–75.
Koroleva, L.F., Nanoparticulate zirconia-modified solid solutions of aluminum–iron oxides for polishing titanium metal, Diagnostics, Resource Mech. Mater. Struct., 2015, no. 1, pp. 90–102. https://doi.org/10.17804/2410-9908
Isasi-Marín, J., Pérez-Estébanez, M., Díaz-Guerra, C., Castillo, J.F., Correcher, V., and Cuervo-Rodríguez, M.R., Structural, magnetic and luminescent characteristics of Pr3+-doped ZrO2 powders synthesized by a sol–gel method, J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys., 2009, vol. 42, no. 7. https://doi.org/10.1088/0022-3727/42/7/075418
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
In our experimental work, we used equipment and instruments at the Plastometriya Shared Research Facilities Center, Institute of Engineering Science, Ural Branch, Russian Academy of Sciences. I am grateful to A.P. Tyutyunnik for determining the phase composition of the samples by X-ray diffraction.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Translated by O. Tsarev
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Koroleva, L.F. Synthesis and Abrasive Properties of Nanoparticulate Modified Solid Solutions of Aluminum and Iron Oxides. Inorg Mater 55, 556–562 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0020168519060074
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S0020168519060074