Abstract
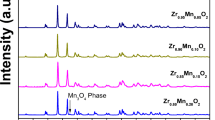
Electrical conductivity of ZrO2 doped with MnO2 has been measured at various temperatures for different molar ratios. The conductivity increases due to hopping of oxygen into neighboring vacancies, created by doping. Increase in temperature increases the rate of hopping, which results in the rise in conductivity and after attaining a maximum the conductivity, decrease due to collapse of the fluorite framework. All compositions show phase transition in ZrO2 from monoclinic to tetragonal at 746 K. The XRD, DTA, and FT-IR studies were carried out for confirming the doping effect and transition in ZrO2.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Steele, B.C.H., Survey of Materials Selection for Ceramic Fuel Cells: II. Cathodes and Anodes, Solid State Ionics, 1996, vols. 86–88, p. 1223.
Boivin, J.C. and Mairesse, G., Recent Material Developments in Fast Oxide Ion Conductors, Chem. Mater., 1998, vol. 10, p. 2870.
Doshi, R., Routbort, J.L., and Alcock, C.B., Diffusion in Mixed Conducting Oxides: A Review, Def. Diff. Forum, 1996, vol. 127, p. 39.
Gellings, P.J. and Bouwmeester, H.J.M., Ion and Mixed Conducting Oxides as Catalysts, Catal. Today, 1992, vol. 1, pp. 1–101.
Solid State Electrochemistry, Bruee, P.G., Ed., Cambridge: CUP, 1997.
Diffusion in Crystalline Solids, Murch, G.E., and Nowick, A.S., Eds., New York: Academic, 1984.
Saiful Islam M., Ionic Transport in ABO3 Perovskite Oxides: A Computer Modelling Tour, J. Mater. Chem., 2000, vol. 10, pp. 1027–1038.
Kilner, J.A., Fast Oxygen Transport in Acceptor Doped Oxides, Solid State Ionics, 2000, vol. 129, pp. 13–23.
Kahlert, H., Fery, F., Boysen, H., and Lassak, K., Defect Structure and Diffuse Scattering of ZrO2 Single Crystals at Elevated Temperatures and Simultaneously Applied Electric Field, J. Appl. Crystallogr., 1995, vol. 28, pp. 812–819.
Haines, J., Leger, J.M., and Atout, A., Crystal Structure and Equation of State of Cotunnite-Type Zirconia, J. Am. Ceram. Soc., 1995, vol. 78, pp. 445–448.
Dravid, V.P., Ravikumar, V., Notis, M.R., et al., Stabilization of Cubic Zircoma with Manganese Oxide, J. Am. Ceram Soc., 1994, vol. 77, no. 10, pp. 2758–2762.
Bondars, B., Heidemane, G., Grabis, J., et al., Powder Diffraction Investigation of Plasma Sprayed Zirconia, J. Mater. Sci., 1995, vol. 30, pp. 1621–1625.
Mukherjee, G.D., Vaidya, S.N., and Karunakaran, C., High Pressure and High Temperature Studies on Manganese Oxide, Phase Transitions, 2002, vol. 75, no. 6, pp. 557–566.
Huang Peng-Nain and Secco, E.A., Tl+ Ion Conductivity in RbxTl(1−x)I for 0 ≤ x ≤ 0.10, Coexistence of Mixed Phases, and Phase Stabilization, J. Solid State Chem., 1993, vol. 103, p. 314.
Nair, S.M., Yahya, A.I., and Ahmad Afaq, Ion Conduction in the Ag2HgI4-Cu2HgI4 Systems Doped with Cd2+, K+, and Na+, J. Solid State Chem., 1996, vol. 122, p. 349.
Kumari, M.S. and Secco, E.A., Phase Transformation Studies on Pure and K-Doped Na2SO4. Can. J. Chem., 1978, vol. 56, p. 2616.
Kumari, M.S. and Secco, E.A., Order-Disorder Transitions: Solid State Kinetics, Thermal Analyses, X-ray Diffraction, and Electrical Conductivity Studies in the Ag2SO4-K2SO4, Can. J. Chem., 1985, vol. 63, p. 324.
Srinivasan, R., Rice, L., and Davis, B.H., Critical Particle Size and Phase Transformation in Zirconia: Transmission Electron Microscopy and X-ray Diffraction Studies, J. Am. Ceram. Soc., 1990, vol. 73, p. 3528.
Cotton, F.A. and Wilkinson, G., Advanced Inorganic Chemistry, New York: Wiley, 1962, p. 681.
Bondioli, F., Leonelli, C., and Manfredini, T., Microwave-Hydrothermal Synthesis and Hyperfine Characterization of Praseodymium-Doped Nanometric Zirconia Powders, J. Am. Ceram. Soc., 2005, vol. 88, p. 633.
Gao, L., Liu, Q., Hong, J.S., Miyamoto, H., et al., Phase Transformation in the Al2O3-ZrO2 System, J. Mater. Sci., 1998, vol. 33, p. 1399.
Powder Diffraction File, Swarthmore: Joint Committee on Powder Diffraction Standards, cards 37-1484, 24-1164.
Powder Diffraction File, Swarthmore: Joint Committee on Powder Diffraction Standards, card 10-69.
Fangxin, L., Jinlong, Y., and Tianpeng, Z., Raman and Fourier-Transform Infrared Photoacoustic Spectra of Granular ZrO2, Phys. Rev. B: Condens. Matter, 1997, vol. 55, p. 8847.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
The text was submitted by the authors in English.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Beg, S., Sarita & Varshney, P. Effect of MnO2 on the electrical conductivity of ZrO2 . Inorg Mater 42, 1083–1087 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0020168506100062
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S0020168506100062