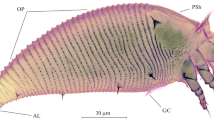
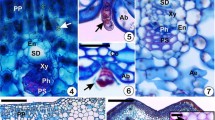
Abstract
A review of the latest data on the problem of gall formation on plants under the influence of eryophyoid mites of the superfamily Eriophyoidea is given. Gall formation is induced in epidermal cells and includes a complicated growth reaction appearing as a response to the injection of mite saliva. The nature of gall-inducing agents is unknown. The role of such agents could be played by specific mite saliva factors affecting plant cell proliferation (e.g., plant hormones, probably secreted by mites) and microbial plant pathogens. Differences in the external gall structure are primarily determined by the mite species. Variability of galls is limited to several basic shapes that had probably appeared as convergent structures in phylogenetically remote plant hosts. A new renovated classification of types of damage caused by eryophyoid mites on plants is assumed on the basis of the following characters: the number of plant organs involved in the pathological process, duration of the existence of the damage and of the mite colony inside it, and localization of damage on the plant (topography). A step-by-step program for further studies of gall formation is substantiated.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amrine, J.W.Jr., Stasny, T.A., and Flechtmann, Ch.W., Revised Keys to World Genera of Eriophyoidea (Acari: Prostigmata) (Michigan, Indira Publ., 2003).
Bird, D.M. and Koltai, H., “Plant Parasitic Nematodes: Habitats, Hormones, and Horizontally-Acquired Genes,” J. Plant Growth Regulation 19 (19), 183–194 (2000).
Choi, J., Choi, K.D., Lee, S., Ryu, C.M., and Hwang, I., “Cytokinins and Plant Immunity: Old Foes or New Friends?,” Trends in Plant Science 16 (16), 388–394 (2011).
Cvrkovic, T., Chetverikov, P., Vidovic, B., and Petanovic, R., “Molecular Analysis of COI mtDNA in Phytoptus (Phytoptidae) and Eriophyes (Eriophyidae) Species Associated with Galls of Tilia spp. (Tiliaceae): Preliminary Results,” in Proceedings of the International Symposium on Current Trends in Plant Protection, Belgrade, Serbia, 25–28th September, 2012 (2012), pp. 483–488.
De Lillo, E. and Monfreda, R., “Salivary Secretions of Eriophyoids (Acari: Eriophyoidea): First Results of an Experimental Model,” Experimental and Applied Acarology, 34 (3–4), 291–306 (2004).
Dodueva, I.E., Frolova, N.V., and Lutova, L.A., “Plant Tumorigenesis: Different Ways for Shifting Systemic Control of Plant Cell Division and Differentiation,” Transgenic Plant J. 1, 3–24 (2007).
Dodueva, I.E., Yurlova, E.V., Osipova, M.A., and Lutova, L.A., “CLE Peptides are Universal Regulators of Meristem Development,” Russ. J. Plant Physiol. 59 (59), 14–27 (2012).
Dodueva, I., Kiryushkin, A., Yurlova, E., Osipova, M., Buzovkina, I., and Lutova, L., “The Influence of Cytokinins on the Expression of Genes CLE of the Reddish,” Physiologiya Rastenii, No. 3, 399 (2013).
Erb, M., Meldau, S., and Howe, G.A., “The Role of Phytohormones in Insect-Specific Plant Reactions,” Trends in Plant Science 17 (17), 250–259 (2012).
Farmer, E.E., “Potent Mitogenic Lipids from Gall- Inducing Insects,” Trends in Plant Science 5 (5), 359–360 (2000).
Galinha, C., Bilsborough, G., and Tsiantis, M., “Hormonal Input in Plant Meristems: A Bbalancing Act,” Seminars in Cell & Developmental Biology 20 (20), 1149–1156 (2009).
Hartig, K. and Beck, E., “Crosstalk between Auxin, Cytokinins, and Sugars in the Plant Cell Cycle,” Plant Biology 8 (8), 389–396 (2006).
Kane, N.A., Jones, C.S., and Vuorisalo, T., “Development of Galls on Leaves of Alnus glutinosa and Alnus incana (Betulaceae) Caused by the Eriophyid Mite Eriophyes laevis (Nalepa),” Intern. J. Plant Sci. 158 (158), 13–23 (1997).
Keifer, H.H., “Eriophyoidea Nalepa,” in Mites Injurious to Economic Plants (Univ. California, Berkeley, Los Angeles, London, 1975), pp. 327–533.
Lutova, L.A. and Dodueva, I.E., “The Role of Meristem-Specific Genes of Plants in Formation of Genetic Tumors,” Russ. J. Developmental Biology 38 (38), 350–362 (2007).
Mitchum, M.G., Xiaohong, W., and Davis, E.L., “Diverse and Conserved Roles of CLE Peptides,” Current Opinion in Plant Biology 11 (11), 75–81 (2008).
Muravnik, L.E., and Shavarda, A.L., “Leaf Glandular Trichomes in Empetrum nigrum: Morphology, Histochemistry, Ultrastructure and Secondary Metabolites,” Nordic J. Botany 30 (4), 470–481 (2012).
Oldfield, G.N. and Proeseler, G., “Chaper 1.4.9. Eriophyoid Mites as Vectors of Plant Pathogens,” Eriophyoid Mites. Their Biology, Natural Enemies and Control. World Crop Pests, Ed. by Lindquist, E.E., Sabelis, M.W., and Bruin, J. (Elsevier, Amsterdam, 1996), issue 6, pp. 259–276.
Petanovic, R. and Kielkiewicz, M., “Plant—Eriophyoid Mite Interactions: Cellular Biochemistry and Metabolic Responses Induced in Mite-Injured Plants. Part I.” Experimental and Applied Acarology 51 (1–3), 61–80 (2010a).
Petanovic, R. and Kielkiewicz, M., “Plant—Eriophyoid Mite Interactions: Specific and Unspecific Morphological Alterations. Part II,” Experimental and Applied Acarology 51, 81–91 (2010b).
Raman, A., “Gall Induction by Hemipteroid Insects,” J. Plant Interactions 7 (1), 29–44. (2012).
Raman, A., “Morphogenesis of Insect-Induced Plant Galls: Facts and Questions,” Flora 206 (206), 517–533 (2011).
Roivainen, H., “Contributions to the Knowledge of the Eriophyids of Finland,” Acta Entomol. Fennica 8, 1–72 (1951).
Shevchenko, V.G. and Rupais, A.A., “Eryophyoid mites (Acarina, Eriophyoidea)—Pests of Park Plants in Latvia,” in Fauna of Latvian SSR and Adjacent Territories, No. 4, 203–239. (1964).
Soika, G. and Kozak, M., “Eriophyes Species (Acari: Eriophyoidea) Inhabiting Lime Trees (Tilia spp.: Tiliaceae)— Supplementary Description and Morphological Variability Related to Host Plants and Female Forms,” Zootaxa 3646 (3646), 349–385 (2013).
Sopow, S.L., Shorthouse, J.D., Strong, W., and Quiring, D.T., “Evidence for Long-Distance, Chemical Gall Induction by an Insect,” Ecology Letters 6 (6), 102–105 (2003).
Sukhareva, S.I., Eryophyoid mites on Cereals (St. Petersburg, St. Petersburg Univ., 1992) [In Russian].
Sukhareva, S.I. and Chetverikov, Ph.E. “Morphological Transformations Associated with Passing from Protogynous to Deutogynous Females in Eryophyoid Mites (Acari: Eriophyoidea),” Vestnik SpbGU 3 (3), 3–15 (2015).
Suzuki, H., Yokokura, J., Ito, T., Arai, R., Yokoyama, C., Toshima, H., Nagata, S., Asami, T., and Suzuki, Y., “Biosynthetic Pathway of the Phytohormone Auxin in Insects and Screening of its Inhibitors,” Insect Biochemistry and Molecular Biology 53, 66–72 (2014).
Testone, G., Bruno, L., Condello, E., Chiappetta, A., Bruno, A., Mele, G., Tartarini, A., Spano, L., Innocenti, A.M., Mariotti, D., Bitonti, M.B., and Giannino, D., “Peach [Prunus persica (L.) Batsch] KNOPE1, a Class 1 KNOX Orthologue to Arabidopsis BREVIPEDICELLUS/ KNAT1, is Misexpressed During Hyperplasia of Leaf Curl Disease,” J. Experimental Botany 59 (59), 389–402 (2008).
Tooker, J.F. and Helms, A.M., “Phytohormone Dynamics Associated with Gall Insects, and Their Potential Role in the Evolution of the Gall-Inducing Habit,” J. Chemical Ecology 40 (40), 742–753 (2014).
Westphal, E., “Cecidogenesis and Resistance Phenomena in Mite-Induced Galls,” in Biology of Insectinduced Galls, Ed. by Shorthouse, J. and Rohfritsch, O. (Oxford Univ., New York, 1992), pp. 141–156.
Westphal, E. and Manson, D.C.M., “1.4.6 Feeding Effects on Host Plants: Gall Formation and Other Distortions,” in Eriophyoid Mites. Their Biology, Natural Enemies and Control, World Crop Pests, Ed. by Lindquist, E.E., Sabelis, M.W., and Bruin, J. (Elsevier, Amsterdam, 1996), pp. 231–242.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Original Russian Text © P.E. Chetverikov, A.E. Vishyakov, I.T. Dodueva, M.A. Osipova, S.I. Sukhareva, A.L. Shavarda, 2015, published in Parazitologiya, 2015, Vol. 49, No. 5, pp. 365–375.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chetverikov, P.E., Vishyakov, A.E., Dodueva, I.T. et al. Gallogenesis induced by eryophyoid mites (Acariformes: Eriophyoidea). Entmol. Rev. 95, 1137–1143 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0013873815080217
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S0013873815080217