Abstract
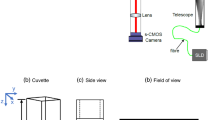
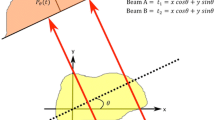
This paper presents the results of two-line OH planar laser-induced fluorescence (PLIF) thermometry in a laminar conical flame of a gas–droplet mixture of ethanol and air. Laminar flow of a droplet-laden ethanol–air uniform mixture was produced by an ultrasonic atomizer in a vessel filled with liquid ethanol. The properties of the two-phase flow at the nozzle exit without combustion were controlled by a time-shift optical sensor. The temperature field was estimated based on the excitation of the \(Q_{1}\)(5) and \(Q_{1}\)(14) lines of the (1–0) band of the \(A^{2}\Sigma ^{ + }\)–\(X^{2}\Pi\)electronic system. The spatial nonuniformity of the energy distribution in the laser light sheet illuminating the central plane of the flame cone and the change in the pulse energy from frame to frame were compensated using an additional camera recording the laser light intensity distribution in the calibration cuvette.












Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
W. A. Sirignano, “Fuel Droplet Vaporization and Spray Combustion Theory," Prog. Energy Combust. Sci. 9 (4), 291–322 (1983); DOI: 10.1016/0360-1285(83)90011-4.
S. C. Li, “Spray Stagnation Flames," Prog. Energy Combust. Sci. 23 (4), 303–347 (1997); DOI: 10.1016/S0360-1285(96)00013-5.
P. Jenny, D. Roekaerts, and N. N. Beishuize, “Modeling of Turbulent Dilute Spray Combustion," Prog. Energy Combust. Sci. 38 (6), 846–887 (2012); DOI: 10.1016/j.pecs.2012.07.001.
A. R. Masri, “Turbulent Combustion of Sprays: from Dilute to Dense," Combust. Sci. Technol. 188 (10), 1619–1639 (2016); DOI: 10.1080/00102202.2016.1198788.
D. R. Ballal and A. H. Lefebvre, “Ignition and Flame Quenching of Flowing Heterogeneous Fuel–Air Mixtures," Combust. Flame 35, 155–168 (1979); DOI: 10.1016/0010-2180(79)90019-1.
A. M. Danis, I. Namer, and N. P Cernansky, “Droplet Size and Equivalence Ratio Effects on Spark Ignition of Monodisperse n-Heptane and Methanol Sprays," Combust. Flame 74 (3), 285–294 (1988); DOI: 10.1016/0010-2180(88)90074-0.
P. M. De Oliveira, P. M. Allison, and E. Mastorakos, “Ignition of Uniform Droplet-Laden Weakly Turbulent Flows Following a Laser Spark," Combust. Flame 199, 387–400 (2019); DOI: 10.1016/j.Combustflame.2018.10.009.
P. M. De Oliveira and E. Mastorakos, “Mechanisms of Flame Propagation in Jet Fuel Sprays As Revealed by OH/Fuel Planar Laser-Induced Fluorescence and OH* Chemiluminescence," Combust. Flame 206, 308–321 (2019); DOI: 10.1016/j.combustflame.2019.05.005.
S. Hayashi, S. Kumagai, and T. Sakai, “Propagation Velocity and Structure of Flames in Droplet–Vapor–Air Mixtures," Combust. Sci. Technol. 15 (5/6), 169–177 (1977); DOI: 10.1080/00102207708946782.
G. A. Richards and A. H. Lefebvre, “Turbulent Flame Speeds of Hydrocarbon Fuel Droplets in Air," Combust. Flame 78 (3/4), 299–307 (1989); DOI: 10.1016/0010-2180(89)90019-9.
H. Nomura, I. Kawasumi, Y. Ujiie, and J. I. Sato, “Effects of Pressure on Flame Propagation in a Premixture Containing Fine Fuel Droplets," Proc. Combust. Inst. 31 (2), 2133–2140 (2007); DOI: 10.1016/j.proci.2006.07.036.
D. Bradley, M. Lawes, S. Liao, and A. Saat, “Laminar Mass Burning and Entrainment Velocities and Flame Instabilities of i-Octane, Ethanol and Hydrous Ethanol/Air Aerosols," Combust. Flame 161 (6), 1620–1632 (2014); DOI: 10.1016/j.Combustflame.2013.12.011.
J. H. Burgoyne and L. Cohen, “The Effect of Drop Size on Flame Propagation in Liquid Aerosols," Proc. R. Soc. A 225 (1162), 375–392 (1954); DOI: 10.1098/rspa.1954.0210.
G. Chen and A. Gomez, “Counterflow Diffusion Flames of Quasi-Monodisperse Electrostatic Sprays," Proc. Combust. Inst. 24 (1), 1531–1539 (1992); DOI: 10.1016/S0082-0784(06)80178-5.
N. Darabiha, F. Lacas, J.C. Rolon, and S. Candel, “Laminar Counterflow Spray Diffusion Flames: A Comparison between Experimental Results and Complex Chemistry Calculations," Combust. Flame 95 (3), 261–275 (1993); DOI: 10.1016/0010-2180(93)90131-L.
C. T. Chong and S. Hochgreb, “Measurements of Laminar Flame Speeds of Acetone/Methane/Air Mixtures," Combust. Flame 158 (3), 490–500 (2011); DOI: 10.1016/j.Combustflame.2010.09.019.
L. Fan, B. Tian, C. T. Chong, et al., “The Effect of Fine Droplets on Laminar Propagation Speed of a Strained Acetone–Methane Flame: Experiment and Simulations," Combust. Flame 229, 111377 (2021); DOI: 10.1016/j.Combustflame.2021.02.023.
R. Giezendanner-Thoben, U. Meier, W. Meier, and M. Aigner, “Phase-Locked Temperature Measurements by Two-Line OH PLIF Thermometry of a Self-Excited Combustion Instability in a Gas Turbine Model Combustor," Flow Turbul. Combust. 75 (1–4) 317–333 (2005); DOI: 10.1007/s10494-005-8587-0.
B. Ayoola, G. Hartung, C. A. Armitage, et al., “Temperature Response of Turbulent Premixed Flames to Inlet Velocity Oscillations," Exp. Fluids 46 (1) 27–41 (2009); DOI: 10.1007/s00348-008-0534-0.
Z. Yang, X. Yu, J. Peng, et al., “Effects of N2, CO2 and H2O Dilutions on Temperature and Concentration Fields of OH in Methane Bunsen Flames by Using PLIF Thermometry and Bi-Directional PLIF," Exp. Therm. Fluid Sci. 81, 209–222 (2017); DOI: 10.1016/j.Expthermflusci.2016.10.017.
B. R. Halls, P. S. Hsu, S. Roy, T. R. Meyer, and J. R. Gord, “Two-Color Volumetric Laser-Induced Fluorescence for 3D OH and Temperature Fields in Turbulent Reacting Flows," Opt. Lett. 43 (12), 2961–2964 (2018); DOI: 10.1364/OL.43.002961.
J. M. Seitzman, R. K. Hanson, P. A. DeBarber, and C. F. Hess, “Application of Quantitative Two-Line OH Planar Laser-Induced Fluorescence for Temporally Resolved Planar Thermometry in Reacting Flows," Appl. Opt. 33 (18), 4000–4012 (1994); DOI: 10.1364/AO.33.004000.
E. J. Welle, W. L. Roberts, C. D. Carter, and J. M. Donbar, “The Response of a Propane–Air Counter-Flow Diffusion Flame Subjected to a Transient Flow Field," Combust. Flame 135 (3), 285–297 (2003); DOI: 10.1016/S0010-2180(03)00167-6.
R. Devillers, G. Bruneaux, and C. Schulz, “Development of a Two-Line OH-Laser-Induced Fluorescence Thermometry Diagnostics Strategy for Gas-Phase Temperature Measurements in Engines," Appl. Opt. 47 (31) 5871–5885 (2008); DOI: 10.1364/AO.47.005871.
S. Kostka et al., “Comparison of Line-Peak and Line-Scanning Excitation in Two-Color Laser-Induced-Fluorescence Thermometry of OH," Appl. Opt. 48 (32), 6332–6343 (2009); DOI: 10.1364/AO.48.006332.
A. S. Lobasov, R. V. Tolstoguzov, D. K. Sharaborin, L. M. Chikishev, and V. M. Dulin, “On the Efficiency of Using Different Excitation Lines of (1–0) Two-Line OH Fluorescence for Planar Thermometry," Teplofiz. Aeromekh. 28 (5), 793–797 (2021) [Thermophys. Aeromech. 28 (5), 751–755 (2021); https://doi.org/10.1134/S0869864321050176].
W. Schäfer and C. Tropea, “Time-Shift Technique for Simultaneous Measurement of Size, Velocity, and Relative Refractive Index of Transparent Droplets or Particles in a Flow," Appl. Opt. 53 (4), 588–597 (2014); DOI: 10.1364/AO.53.000588.
A. S. Lobasov, S. V. Alekseenko, D. M. Markovich, and V. M. Dulin, “Mass and Momentum Transport in the near Field of Swirling Turbulent Jets. Effect of Swirl Rate," Int. J. Heat Fluid Flow 83, 108539 (V); DOI: 10.1016/j.ijheatfluidflow.2020.108539.
J. Luque and D. Crosley, “Lifbase: Database and Spectral Simulation (Version 1.5)," SRI Int. Report No. MP 99-009 (1999).
S. M. Soloff, R. J. Adrian, and Z. C. Liu, “Distortion Compensation for Generalized Stereoscopic Particle Image Velocimetry," Meas. Sci. Technol. 8 (12), 1441–1454 (1997).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Translated from Fizika Goreniya i Vzryva, 2022, Vol. 58, No. 5, pp. 3-11.https://doi.org/10.15372/FGV20220501.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sharaborin, D.K., Lobasov, A.S., Tolstoguzov, R.V. et al. Temperature Measurement in a Bunsen Gas–Droplet Flame of Ethanol Using OH PLIF. Combust Explos Shock Waves 58, 507–515 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1134/S001050822205001X
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S001050822205001X