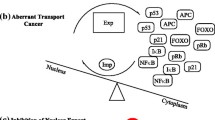
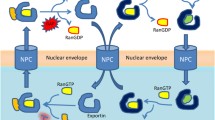
Abstract
Nucleocytoplasmic transport of macromolecules is tightly regulated in eukaryotic cells. XPO1 is a transport factor responsible for the nuclear export of several hundred protein and RNA substrates. Elevated levels of XPO1 and recurrent mutations have been reported in multiple cancers and linked to advanced disease stage and poor survival. In recent years, several novel small-molecule inhibitors of XPO1 were developed and extensively tested in preclinical cancer models and eventually in clinical trials. In this brief review, we summarize the functions of XPO1, its role in cancer, and the latest results of clinical trials of XPO1 inhibitors.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- AML:
-
acute myeloid leukemia
- CLL:
-
chronic lymphocytic leukemia
- CR:
-
complete response
- DLBCL:
-
diffuse large B-cell lymphoma
- MCL:
-
mantle cell lymphoma
- MM:
-
multiple myeloma
- NES:
-
nuclear export signal
- R/R:
-
relapsed or refractory
References
Beck, M., and Hurt, E. (2017) The nuclear pore complex: understanding its function through structural insight, Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol., 18, 73-89, https://doi.org/10.1038/nrm.2016.147.
Timney, B. L., Raveh, B., Mironska, R., Trivedi, J. M., Kim, S. J., et al. (2016) Simple rules for passive diffusion through the nuclear pore complex, J. Cell Biol., 215, 57-76, https://doi.org/10.1083/jcb.201601004.
Cagatay, T., and Chook, Y. M. (2018) Karyopherins in cancer, Curr. Opin. Cell. Biol., 52, 30-42, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceb.2018.01.006.
Sorokin, A. V., Kim, E. R., and Ovchinnikov, L. P. (2007) Nucleocytoplasmic transport of proteins, Biochemistry (Moscow), 72, 1439-1457, https://doi.org/10.1134/s0006297907130032.
Adachi, Y., and Yanagida, M. (1989) Higher order chromosome structure is affected by cold-sensitive mutations in a Schizosaccharomyces pombe gene crm1+ which encodes a 115-kDa protein preferentially localized in the nucleus and its periphery, J. Cell Biol., 108, 1195-1207, https://doi.org/10.1083/jcb.108.4.1195.
Fornerod, M., Ohno, M., Yoshida, M., and Mattaj, I. W. (1997) CRM1 is an export receptor for leucine-rich nuclear export signals, Cell, 90, 1051-1060, https://doi.org/10.1016/s0092-8674(00)80371-2.
Fukuda, M., Asano, S., Nakamura, T., Adachi, M., Yoshida, M., et al. (1997) CRM1 is responsible for intracellular transport mediated by the nuclear export signal, Nature, 390, 308-311, https://doi.org/10.1038/36894.
Ossareh-Nazari, B., Bachelerie, F., and Dargemont, C. (1997) Evidence for a role of CRM1 in signal-mediated nuclear protein export, Science, 278, 141-144, https://doi.org/10.1126/science.278.5335.141.
Stade, K., Ford, C. S., Guthrie, C., and Weis, K. (1997) Exportin 1 (Crm1p) is an essential nuclear export factor, Cell, 90, 1041-1050, https://doi.org/10.1016/s0092-8674(00)80370-0.
Lee, Y., Pei, J., Baumhardt, J. M., Chook, Y. M., and Grishin, N. V. (2019) Structural prerequisites for CRM1-dependent nuclear export signaling peptides: accessibility, adapting conformation, and the stability at the binding site, Sci. Rep., 9, 6627, https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-019-43004-0.
Fung, H. Y., Fu, S. C., Brautigam, C. A., and Chook, Y. M. (2015) Structural determinants of nuclear export signal orientation in binding to exportin CRM1, Elife, 4, e10034, https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.10034.
Kosugi, S., Hasebe, M., Tomita, M., and Yanagawa, H. (2008) Nuclear export signal consensus sequences defined using a localization-based yeast selection system, Traffic, 9, 2053-2062, https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-0854.2008.00825.x.
Hutten, S., and Kehlenbach, R. H. (2007) CRM1-mediated nuclear export: to the pore and beyond, Trends Cell Biol., 17, 193-201, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tcb.2007.02.003.
Fu, S. C., Huang, H. C., Horton, P., and Juan, H. F. (2013) ValidNESs: a database of validated leucine-rich nuclear export signals, Nucleic Acids Res., 41, D338-D343, https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gks936.
Xu, D., Grishin, N. V., and Chook, Y. M. (2012) NESdb: a database of NES-containing CRM1 cargoes, Mol.Biol. Cell, 23, 3673-3676, https://doi.org/10.1091/mbc.E12-01-0045.
Thakar, K., Karaca, S., Port, S. A., Urlaub, H., and Kehlenbach, R. H. (2013) Identification of CRM1-dependent nuclear export cargos using quantitative mass spectrometry, Mol. Cell. Proteomics, 12, 664-678, https://doi.org/10.1074/mcp.M112.024877.
Kirli, K., Karaca, S., Dehne, H. J., Samwer, M., Pan, K. T., et al. (2015) A deep proteomics perspective on CRM1-mediated nuclear export and nucleocytoplasmic partitioning, Elife, 4, e11466, https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.11466.
Wuhr, M., Guttler, T., Peshkin, L., McAlister, G. C., Sonnett, M., et al. (2015) The nuclear proteome of a vertebrate, Curr. Biol., 25, 2663-2671, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cub.2015.08.047.
Mackmull, M. T., Klaus, B., Heinze, I., Chokkalingam, M., Beyer, A., et al. (2017) Landscape of nuclear transport receptor cargo specificity, Mol. Syst. Biol., 13, 962, https://doi.org/10.15252/msb.20177608.
Hill, R., Cautain, B., de Pedro, N., and Link, W. (2014) Targeting nucleocytoplasmic transport in cancer therapy, Oncotarget, 5, 11-28, https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.1457.
Johnson, A. W., Lund, E., and Dahlberg, J. (2002) Nuclear export of ribosomal subunits, Trends Biochem. Sci., 27, 580-585, https://doi.org/10.1016/s0968-0004(02)02208-9.
Wild, T., Horvath, P., Wyler, E., Widmann, B., Badertscher, L., Zemp, I., et al. (2010) A protein inventory of human ribosome biogenesis reveals an essential function of exportin 5 in 60S subunit export, PLoS Biol., 8, e1000522, https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pbio.1000522.
Muqbil, I., Bao, B., Abou-Samra, A. B., Mohammad, R. M., and Azmi, A. S. (2013) Nuclear export mediated regulation of microRNAs: potential target for drug intervention, Curr. Drug Targets, 14, 1094-1100, https://doi.org/10.2174/1389450111314100002.
Volpon, L., Culjkovic-Kraljacic, B., Sohn, H. S., Blanchet-Cohen, A., Osborne, M. J., et al. (2017) A biochemical framework for eIF4E-dependent mRNA export and nuclear recycling of the export machinery, RNA, 23, 927-937, https://doi.org/10.1261/rna.060137.116.
Topisirovic, I., Siddiqui, N., Lapointe, V. L., Trost, M., Thibault, P., et al. (2009) Molecular dissection of the eukaryotic initiation factor 4E (eIF4E) export-competent RNP, EMBO J., 28, 1087-1098, https://doi.org/10.1038/emboj.2009.53.
Ohno, M., Segref, A., Bachi, A., Wilm, M., and Mattaj, I. W. (2000) PHAX, a mediator of U snRNA nuclear export whose activity is regulated by phosphorylation, Cell, 101, 187-198, https://doi.org/10.1016/S0092-8674(00)80829-6.
Izaurralde, E., Lewis, J., Gamberi, C., Jarmolowski, A., McGuigan, C., et al. (1995) A cap-binding protein complex mediating U snRNA export, Nature, 376, 709-712, https://doi.org/10.1038/376709a0.
Forbes, D. J., Travesa, A., Nord, M. S., and Bernis, C. (2015) Nuclear transport factors: Global regulation of mitosis, Curr. Opin. Cell Biol., 35, 78-90, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceb.2015.04.012.
Yao, Y., Dong, Y., Lin, F., Zhao, H., Shen, Z., et al. (2009) The expression of CRM1 is associated with prognosis in human osteosarcoma, Oncol. Rep., 21, 229-235, https://doi.org/10.3892/or_00000213.
Noske, A., Weichert, W., Niesporek, S., Roske, A., Buckendahl, A. C., et al. (2008) Expression of the nuclear export protein chromosomal region maintenance/exportin 1/Xpo1 is a prognostic factor in human ovarian cancer, Cancer, 112, 1733-1743, https://doi.org/10.1002/cncr.23354.
Huang, W. Y., Yue, L., Qiu, W. S., Wang, L. W., Zhou, X. H., et al. (2009) Prognostic value of CRM1 in pancreas cancer, Clin. Invest. Med., 32, E315.
Shen, A., Wang, Y., Zhao, Y., Zou, L., Sun, L., et al. (2009) Expression of CRM1 in human gliomas and its significance in p27 expression and clinical prognosis, Neurosurgery, 65, 153-160, https://doi.org/10.1227/01.NEU.0000348550.47441.4B.
Van der Watt, P. J., Maske, C. P., Hendricks, D. T., Parker, M. I., Denny, L., et al. (2009) The Karyopherin proteins, Crm1 and Karyopherin beta1, are overexpressed in cervical cancer and are critical for cancer cell survival and proliferation, Int. J. Cancer, 124, 1829-1840, https://doi.org/10.1002/ijc.24146.
Sexton, R., Mahdi, Z., Chaudhury, R., Beydoun, R., Aboukameel, A., et al. (2019) Targeting nuclear exporter protein XPO1/CRM1 in gastric cancer, Int. J. Mol. Sci., 20, 4826, https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20194826.
Zhou, F., Qiu, W., Yao, R., Xiang, J., Sun, X., et al. (2013) CRM1 is a novel independent prognostic factor for the poor prognosis of gastric carcinomas, Med. Oncol., 30, 726, https://doi.org/10.1007/s12032-013-0726-1.
Inoue, H., Kauffman, M., Shacham, S., Landesman, Y., Yang, J., et al. (2013) CRM1 blockade by selective inhibitors of nuclear export attenuates kidney cancer growth, J. Urol., 189, 2317-2326, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.juro.2012.10.018.
Van der Watt, P. J., Zemanay, W., Govender, D., Hendricks, D. T., Parker, M. I., et al. (2014) Elevated expression of the nuclear export protein, Crm1 (exportin 1), associates with human oesophageal squamous cell carcinoma, Oncol. Rep., 32, 730-738, https://doi.org/10.3892/or.2014.3231.
Zheng, Y., Gery, S., Sun, H., Shacham, S., Kauffman, M., et al. (2014) KPT-330 inhibitor of XPO1-mediated nuclear export has anti-proliferative activity in hepatocellular carcinoma, Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol., 74, 487-495, https://doi.org/10.1007/s00280-014-2495-8.
Kojima, K., Kornblau, S. M., Ruvolo, V., Dilip, A., Duvvuri, S., et al. (2013) Prognostic impact and targeting of CRM1 in acute myeloid leukemia, Blood, 121, 4166-4174, https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2012-08-447581.
Lapalombella, R., Sun, Q., Williams, K., Tangeman, L., Jha, S., Zhong, Y., et al. (2012) Selective inhibitors of nuclear export show that CRM1/XPO1 is a target in chronic lymphocytic leukemia, Blood, 120, 4621-4634, https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2012-05-429506.
Yoshimura, M., Ishizawa, J., Ruvolo, V., Dilip, A., Quintas-Cardama, A., et al. (2014) Induction of p53-mediated transcription and apoptosis by exportin-1 (XPO1) inhibition in mantle cell lymphoma, Cancer Sci., 105, 795-801, https://doi.org/10.1111/cas.12430.
Zhang, K., Wang, M., Tamayo, A. T., Shacham, S., Kauffman, M., et al. (2013) Novel selective inhibitors of nuclear export CRM1 antagonists for therapy in mantle cell lymphoma, Exp. Hematol., 41, 67-78.e64, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.exphem.2012.09.002.
Schmidt, J., Braggio, E., Kortuem, K. M., Egan, J. B., Zhu, Y. X., et al. (2013) Genome-wide studies in multiple myeloma identify XPO1/CRM1 as a critical target validated using the selective nuclear export inhibitor KPT-276, Leukemia, 27, 2357-2365, https://doi.org/10.1038/leu.2013.172.
Tai, Y. T., Landesman, Y., Acharya, C., Calle, Y., Zhong, M. Y., et al. (2014) CRM1 inhibition induces tumor cell cytotoxicity and impairs osteoclastogenesis in multiple myeloma: molecular mechanisms and therapeutic implications, Leukemia, 28, 155-165, https://doi.org/10.1038/leu.2013.115.
Luo, B., Huang, L., Gu, Y., Li, C., Lu, H., et al. (2018) Expression of exportin-1 in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma: Immunohistochemistry and TCGA analyses, Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol., 11, 5547-5560.
Aladhraei, M., Kassem Al-Thobhani, A., Poungvarin, N., and Suwannalert, P. (2019) Association of XPO1 overexpression with NF-kappaB and Ki67 in colorectal cancer, Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev., 20, 3747-3754, https://doi.org/10.31557/APJCP.2019.20.12.3747.
Walker, C. J., Oaks, J. J., Santhanam, R., Neviani, P., Harb, J. G., et al. (2013) Preclinical and clinical efficacy of XPO1/CRM1 inhibition by the karyopherin inhibitor KPT-330 in Ph+ leukemias, Blood, 122, 3034-3044, https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2013-04-495374.
Yang, J., Bill, M. A., Young, G. S., La Perle, K., Landesman, Y., et al. (2014) Novel small molecule XPO1/CRM1 inhibitors induce nuclear accumulation of TP53, phosphorylated MAPK and apoptosis in human melanoma cells, PLoS One, 9, e102983, https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0102983.
Gravina, G. L., Mancini, A., Sanita, P., Vitale, F., Marampon, F., et al. (2015) KPT-330, a potent and selective exportin-1 (XPO-1) inhibitor, shows antitumor effects modulating the expression of cyclin D1 and survivin [corrected] in prostate cancer models, BMC Cancer, 15, 941, https://doi.org/10.1186/s12885-015-1936-z.
Deng, M., Zhang, M., Xu-Monette, Z. Y., Pham, L. V., Tzankov, A., et al. (2020) XPO1 expression worsens the prognosis of unfavorable DLBCL that can be effectively targeted by selinexor in the absence of mutant p53, J. Hematol. Oncol., 13, 148, https://doi.org/10.1186/s13045-020-00982-3.
Galinski, B., Luxemburg, M., Landesman, Y., Pawel, B., Johnson, K. J., et al. (2021) XPO1 inhibition with selinexor synergizes with proteasome inhibition in neuroblastoma by targeting nuclear export of IkB, Transl. Oncol., 14, 101114, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tranon.2021.101114.
Chen, Y., Camacho, S. C., Silvers, T. R., Razak, A. R., Gabrail, N. Y., et al. (2017) Inhibition of the nuclear export receptor XPO1 as a therapeutic target for platinum-resistant ovarian cancer, Clin. Cancer Res., 23, 1552-1563, https://doi.org/10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-16-1333.
Turner, J. G., Kashyap, T., Dawson, J. L., Gomez, J., Bauer, A. A., et al. (2016) XPO1 inhibitor combination therapy with bortezomib or carfilzomib induces nuclear localization of IkappaBalpha and overcomes acquired proteasome inhibitor resistance in human multiple myeloma, Oncotarget, 7, 78896-78909, https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.12969.
Turner, J. G., Dawson, J. L., Grant, S., Shain, K. H., Dalton, W. S., et al. (2016) Treatment of acquired drug resistance in multiple myeloma by combination therapy with XPO1 and topoisomerase II inhibitors, J. Hematol. Oncol., 9, 73, https://doi.org/10.1186/s13045-016-0304-z.
Cosson, A., Chapiro, E., Bougacha, N., Lambert, J., Herbi, L., et al. (2017) Gain in the short arm of chromosome 2 (2p+) induces gene overexpression and drug resistance in chronic lymphocytic leukemia: Analysis of the central role of XPO1, Leukemia, 31, 1625-1629, https://doi.org/10.1038/leu.2017.100.
Chanukuppa, V., Paul, D., Taunk, K., Chatterjee, T., Sharma, S., et al. (2019) XPO1 is a critical player for bortezomib resistance in multiple myeloma: A quantitative proteomic approach, J. Proteomics, 209, 103504, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jprot.2019.103504.
Kulkoyluoglu-Cotul, E., Smith, B. P., Wrobel, K., Zhao, Y. C., Chen, K. L. A., et al. (2019) Combined targeting of estrogen receptor alpha and XPO1 prevent Akt activation, remodel metabolic pathways and induce autophagy to overcome tamoxifen resistance, Cancers (Basel), 11, 479, https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers11040479.
Jardin, F., Pujals, A., Pelletier, L., Bohers, E., Camus, V., et al. (2016) Recurrent mutations of the exportin 1 gene (XPO1) and their impact on selective inhibitor of nuclear export compounds sensitivity in primary mediastinal B-cell lymphoma, Am. J. Hematol., 91, 923-930, https://doi.org/10.1002/ajh.24451.
Mehmood, R., Jibiki, K., Shibazaki, N., and Yasuhara, N. (2021) Molecular profiling of nucleocytoplasmic transport factor genes in breast cancer, Heliyon, 7, e06039, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2021.e06039.
Dong, Y., Tu, R., Liu, H., and Qing, G. (2020) Regulation of cancer cell metabolism: oncogenic MYC in the driver’s seat, Signal. Transduct. Target Ther., 5, 124, https://doi.org/10.1038/s41392-020-00235-2.
Golomb, L., Bublik, D. R., Wilder, S., Nevo, R., Kiss, V., et al. (2012) Importin 7 and exportin 1 link c-Myc and p53 to regulation of ribosomal biogenesis, Mol. Cell, 45, 222-232, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcel.2011.11.022.
Kandoth, C., McLellan, M. D., Vandin, F., Ye, K., Niu, B., et al. (2013) Mutational landscape and significance across 12 major cancer types, Nature, 502, 333-339, https://doi.org/10.1038/nature12634.
Taylor, J., Sendino, M., Gorelick, A. N., Pastore, A., Chang, M. T., et al. (2019) Altered nuclear export signal recognition as a driver of oncogenesis, Cancer Discov., 9, 1452-1467, https://doi.org/10.1158/2159-8290.CD-19-0298.
Jain, P., Kanagal-Shamanna, R., Wierda, W., Keating, M., Sarwari, N., et al. (2016) Clinical and molecular characteristics of XPO1 mutations in patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia, Am. J. Hematol., 91, E478-E479, https://doi.org/10.1002/ajh.24496.
Puente, X. S., Pinyol, M., Quesada, V., Conde, L., Ordonez, G. R., et al. (2011) Whole-genome sequencing identifies recurrent mutations in chronic lymphocytic leukaemia, Nature, 475, 101-105, https://doi.org/10.1038/nature10113.
Landau, D. A., Carter, S. L., Stojanov, P., McKenna, A., Stevenson, K., et al. (2013) Evolution and impact of subclonal mutations in chronic lymphocytic leukemia, Cell, 152, 714-726, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2013.01.019.
Baumhardt, J. M., Walker, J. S., Lee, Y., Shakya, B., Brautigam, C. A., et al. (2020) Recognition of nuclear export signals by CRM1 carrying the oncogenic E571K mutation, Mol. Biol. Cell, 31, 1879-1891, https://doi.org/10.1091/mbc.E20-04-0233.
Garcia-Santisteban, I., Arregi, I., Alonso-Marino, M., Urbaneja, M. A., Garcia-Vallejo, J. J., et al. (2016) A cellular reporter to evaluate CRM1 nuclear export activity: Functional analysis of the cancer-related mutant E571K, Cell. Mol. Life Sci., 73, 4685-4699, https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-016-2292-0.
Miloudi, H., Bohers, E., Guillonneau, F., Taly, A., Gibouin, V. C., et al. (2020) XPO1(E571K) mutation modifies exportin 1 localisation and Interactome in B-cell lymphoma, Cancers (Basel), 12, 2829, https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12102829.
Gao, W., Lu, C., Chen, L., and Keohavong, P. (2015) Overexpression of CRM1: A characteristic feature in a transformed phenotype of lung carcinogenesis and a molecular target for lung cancer adjuvant therapy, J. Thorac. Oncol., 10, 815-825, https://doi.org/10.1097/JTO.0000000000000485.
Tiedemann, R. E., Zhu, Y. X., Schmidt, J., Shi, C. X., Sereduk, C., et al. (2012) Identification of molecular vulnerabilities in human multiple myeloma cells by RNA interference lethality screening of the druggable genome, Cancer Res., 72, 757-768, https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-11-2781.
Hong, A. L., Tseng, Y. Y., Cowley, G. S., Jonas, O., Cheah, J. H., et al. (2016) Integrated genetic and pharmacologic interrogation of rare cancers, Nat. Commun., 7, 11987, https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms11987.
Kim, J., McMillan, E., Kim, H. S., Venkateswaran, N., Makkar, G., et al. (2016) XPO1-dependent nuclear export is a druggable vulnerability in KRAS-mutant lung cancer, Nature, 538, 114-117, https://doi.org/10.1038/nature19771.
Reddy, A., Zhang, J., Davis, N. S., Moffitt, A. B., Love, C. L., et al. (2017) Genetic and functional drivers of diffuse large B cell lymphoma, Cell, 171, 481-494.e415, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2017.09.027.
Inoue, A., Robinson, F. S., Minelli, R., Tomihara, H., Rizi, B. S., et al. (2021) Sequential administration of XPO1 and ATR inhibitors enhances therapeutic response in TP53-mutated colorectal cancer, Gastroenterology, 161, 196-210, https://doi.org/10.1053/j.gastro.2021.03.022.
Dickmanns, A., Monecke, T., and Ficner, R. (2015) Structural basis of targeting the exportin CRM1 in cancer, Cells, 4, 538-568, https://doi.org/10.3390/cells4030538.
Gravina, G. L., Senapedis, W., McCauley, D., Baloglu, E., Shacham, S., et al. (2014) Nucleo-cytoplasmic transport as a therapeutic target of cancer, J. Hematol. Oncol., 7, 85, https://doi.org/10.1186/s13045-014-0085-1.
Freedman, D. A., and Levine, A. J. (1998) Nuclear export is required for degradation of endogenous p53 by MDM2 and human papillomavirus E6, Mol. Cell Biol., 18, 7288-7293, https://doi.org/10.1128/MCB.18.12.7288.
Subhash, V. V., Yeo, M. S., Wang, L., Tan, S. H., Wong, F. Y., et al. (2018) Anti-tumor efficacy of Selinexor (KPT-330) in gastric cancer is dependent on nuclear accumulation of p53 tumor suppressor, Sci. Rep., 8, 12248, https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-30686-1.
Boons, E., Nogueira, T. C., Dierckx, T., Menezes, S. M., Jacquemyn, M., et al. (2021) XPO1 inhibitors represent a novel therapeutic option in adult T-cell leukemia, triggering p53-mediated caspase-dependent apoptosis, Blood Cancer J., 11, 27, https://doi.org/10.1038/s41408-021-00409-3.
Stommel, J. M., Marchenko, N. D., Jimenez, G. S., Moll, U. M., Hope, T. J., et al. (1999) A leucine-rich nuclear export signal in the p53 tetramerization domain: regulation of subcellular localization and p53 activity by NES masking, EMBO J., 18, 1660-1672, https://doi.org/10.1093/emboj/18.6.1660.
Foo, R. S., Nam, Y. J., Ostreicher, M. J., Metzl, M. D., Whelan, R. S., et al. (2007) Regulation of p53 tetramerization and nuclear export by ARC, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 104, 20826-20831, https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0710017104.
Azmi, A. S., Al-Katib, A., Aboukameel, A., McCauley, D., Kauffman, M., et al. (2013) Selective inhibitors of nuclear export for the treatment of non-Hodgkin’s lymphomas, Haematologica, 98, 1098-1106, https://doi.org/10.3324/haematol.2012.074781.
Azmi, A. S., Aboukameel, A., Bao, B., Sarkar, F. H., Philip, P. A., et al. (2013) Selective inhibitors of nuclear export block pancreatic cancer cell proliferation and reduce tumor growth in mice, Gastroenterology, 144, 447-456, https://doi.org/10.1053/j.gastro.2012.10.036.
Nakayama, R., Zhang, Y. X., Czaplinski, J. T., Anatone, A. J., Sicinska, E. T., et al. (2016) Preclinical activity of selinexor, an inhibitor of XPO1, in sarcoma, Oncotarget, 7, 16581-16592, https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.7667.
Miyake, T., Pradeep, S., Wu, S. Y., Rupaimoole, R., Zand, B., et al. (2015) XPO1/CRM1 inhibition causes antitumor effects by mitochondrial accumulation of eIF5A, Clin. Cancer Res., 21, 3286-3297, https://doi.org/10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-14-1953.
Kashyap, T., Argueta, C., Aboukameel, A., Unger, T. J., Klebanov, B., et al. (2016) Selinexor, a Selective Inhibitor of Nuclear Export (SINE) compound, acts through NF-kappaB deactivation and combines with proteasome inhibitors to synergistically induce tumor cell death, Oncotarget, 7, 78883-78895, https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.12428.
Nair, J. S., Musi, E., and Schwartz, G. K. (2017) Selinexor (KPT-330) induces tumor suppression through nuclear sequestration of IkappaB and downregulation of survivin, Clin. Cancer Res., 23, 4301-4311, https://doi.org/10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-16-2632.
Han, X., Wang, J., Shen, Y., Zhang, N., Wang, S., et al. (2015) CRM1 as a new therapeutic target for non-Hodgkin lymphoma, Leuk. Res., 39, 38-46, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.leukres.2014.10.003.
Ahmed, M. M., Sheldon, D., Fruitwala, M. A., Venkatasubbarao, K., Lee, E. Y., et al. (2008) Downregulation of PAR-4, a pro-apoptotic gene, in pancreatic tumors harboring K-ras mutation, Int. J. Cancer, 122, 63-70, https://doi.org/10.1002/ijc.23019.
Azmi, A. S., Wang, Z., Burikhanov, R., Rangnekar, V. M., Wang, G., et al. (2008) Critical role of prostate apoptosis response-4 in determining the sensitivity of pancreatic cancer cells to small-molecule inhibitor-induced apoptosis, Mol. Cancer Ther., 7, 2884-2893, https://doi.org/10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-08-0438.
Tabe, Y., Kojima, K., Yamamoto, S., Sekihara, K., Matsushita, H., et al. (2015) Ribosomal biogenesis and translational flux inhibition by the Selective Inhibitor of Nuclear Export (SINE) XPO1 antagonist KPT-185, PLoS One, 10, e0137210, https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0137210.
Hamamoto, T., Seto, H., and Beppu, T. (1983) Leptomycins A and B, new antifungal antibiotics. II. Structure elucidation, J. Antibiot. (Tokyo), 36, 646-650, https://doi.org/10.7164/antibiotics.36.646.
Nishi, K., Yoshida, M., Fujiwara, D., Nishikawa, M., Horinouchi, S., et al. (1994) Leptomycin B targets a regulatory cascade of crm1, a fission yeast nuclear protein, involved in control of higher order chromosome structure and gene expression, J. Biol. Chem., 269, 6320-6324.
Kudo, N., Matsumori, N., Taoka, H., Fujiwara, D., Schreiner, E. P., et al. (1999) Leptomycin B inactivates CRM1/exportin 1 by covalent modification at a cysteine residue in the central conserved region, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 96, 9112-9117, https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.96.16.9112.
Sun, Q., Carrasco, Y. P., Hu, Y., Guo, X., Mirzaei, H., et al. (2013) Nuclear export inhibition through covalent conjugation and hydrolysis of Leptomycin B by CRM1, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 110, 1303-1308, https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1217203110.
Leopold, W. R., Shillis, J. L., Mertus, A. E., Nelson, J. M., Roberts, B. J., et al. (1984) Anticancer activity of the structurally novel antibiotic Cl-920 and its analogues, Cancer Res., 44, 1928-1932.
Newlands, E. S., Rustin, G. J., and Brampton, M. H. (1996) Phase I trial of elactocin, Br. J. Cancer, 74, 648-649, https://doi.org/10.1038/bjc.1996.415.
Ferreira, B. I., Cautain, B., Grenho, I., and Link, W. (2020) Small Molecule Inhibitors of CRM1, Front. Pharmacol., 11, 625, https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2020.00625.
Kalid, O., Toledo Warshaviak, D., Shechter, S., Sherman, W., and Shacham, S. (2012) Consensus Induced Fit Docking (cIFD): Methodology, validation, and application to the discovery of novel Crm1 inhibitors, J. Comput. Aided Mol. Des., 26, 1217-1228, https://doi.org/10.1007/s10822-012-9611-9.
Parikh, K., Cang, S., Sekhri, A., and Liu, D. (2014) Selective inhibitors of nuclear export (SINE) – a novel class of anti-cancer agents, J. Hematol. Oncol., 7, 78, https://doi.org/10.1186/s13045-014-0078-0.
Etchin, J., Sun, Q., Kentsis, A., Farmer, A., Zhang, Z. C., et al. (2013) Antileukemic activity of nuclear export inhibitors that spare normal hematopoietic cells, Leukemia, 27, 66-74, https://doi.org/10.1038/leu.2012.219.
Ranganathan, P., Yu, X., Na, C., Santhanam, R., Shacham, S., et al. (2012) Preclinical activity of a novel CRM1 inhibitor in acute myeloid leukemia, Blood, 120, 1765-1773, https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2012-04-423160.
Etchin, J., Sanda, T., Mansour, M. R., Kentsis, A., Montero, J., et al. (2013) KPT-330 inhibitor of CRM1 (XPO1)-mediated nuclear export has selective anti-leukaemic activity in preclinical models of T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukaemia and acute myeloid leukaemia, Br. J. Haematol., 161, 117-127, https://doi.org/10.1111/bjh.12231.
Etchin, J., Berezovskaya, A., Conway, A. S., Galinsky, I. A., Stone, R. M., et al. (2017) KPT-8602, a second-generation inhibitor of XPO1-mediated nuclear export, is well tolerated and highly active against AML blasts and leukemia-initiating cells, Leukemia, 31, 143-150, https://doi.org/10.1038/leu.2016.145.
Hing, Z. A., Fung, H. Y., Ranganathan, P., Mitchell, S., El-Gamal, D., et al. (2016) Next-generation XPO1 inhibitor shows improved efficacy and in vivo tolerability in hematological malignancies, Leukemia, 30, 2364-2372, https://doi.org/10.1038/leu.2016.136.
Cheng, Y., Holloway, M. P., Nguyen, K., McCauley, D., Landesman, Y., et al. (2014) XPO1 (CRM1) inhibition represses STAT3 activation to drive a survivin-dependent oncogenic switch in triple-negative breast cancer, Mol. Cancer Ther., 13, 675-686, https://doi.org/10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-13-0416.
Hing, Z. A., Mantel, R., Beckwith, K. A., Guinn, D., Williams, E., et al. (2015) Selinexor is effective in acquired resistance to ibrutinib and synergizes with ibrutinib in chronic lymphocytic leukemia, Blood, 125, 3128-3132, https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2015-01-621391.
Green, A. L., Ramkissoon, S. H., McCauley, D., Jones, K., Perry, J. A., et al. (2015) Preclinical antitumor efficacy of selective exportin 1 inhibitors in glioblastoma, Neuro Oncol., 17, 697-707, https://doi.org/10.1093/neuonc/nou303.
Wahba, A., Rath, B. H., O’Neill, J. W., Camphausen, K., and Tofilon, P. J. (2018) The XPO1 inhibitor selinexor inhibits translation and enhances the radiosensitivity of glioblastoma cells grown in vitro and in vivo, Mol. Cancer Ther., 17, 1717-1726, https://doi.org/10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-17-1303.
Azmi, A. S., Khan, H. Y., Muqbil, I., Aboukameel, A., Neggers, J. E., et al. (2020) Preclinical assessment with clinical validation of selinexor with gemcitabine and Nab-paclitaxel for the treatment of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma, Clin. Cancer Res., 26, 1338-1348, https://doi.org/10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-19-1728.
Gravina, G. L., Mancini, A., Colapietro, A., Marampon, F., Sferra, R., et al. (2017) Pharmacological treatment with inhibitors of nuclear export enhances the antitumor activity of docetaxel in human prostate cancer, Oncotarget, 8, 111225-111245, https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.22760.
Alexander, T. B., Lacayo, N. J., Choi, J. K., Ribeiro, R. C., Pui, C. H., et al. (2016) Phase I study of selinexor, a selective inhibitor of nuclear export, in combination with fludarabine and cytarabine, in pediatric relapsed or refractory acute leukemia, J. Clin. Oncol., 34, 4094-4101, https://doi.org/10.1200/JCO.2016.67.5066.
Garzon, R., Savona, M., Baz, R., Andreeff, M., Gabrail, N., et al. (2017) A phase 1 clinical trial of single-agent selinexor in acute myeloid leukemia, Blood, 129, 3165-3174, https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2016-11-750158.
Wang, A. Y., Weiner, H., Green, M., Chang, H., Fulton, N., et al. (2018) A phase I study of selinexor in combination with high-dose cytarabine and mitoxantrone for remission induction in patients with acute myeloid leukemia, J. Hematol. Oncol., 11, 4, https://doi.org/10.1186/s13045-017-0550-8.
Zhang, W., Ly, C., Ishizawa, J., Mu, H., Ruvolo, V., et al. (2018) Combinatorial targeting of XPO1 and FLT3 exerts synergistic anti-leukemia effects through induction of differentiation and apoptosis in FLT3-mutated acute myeloid leukemias: from concept to clinical trial, Haematologica, 103, 1642-1653, https://doi.org/10.3324/haematol.2017.185082.
Abboud, R., Chendamarai, E., Rettig, M. P., Trinkaus, K. M., Riedell, P. A., et al. (2020) Selinexor combined with cladribine, cytarabine, and filgrastim in relapsed or refractory acute myeloid leukemia, Haematologica, 105, e404-e407, https://doi.org/10.3324/haematol.2019.236810.
Sweet, K., Komrokji, R., Padron, E., Cubitt, C. L., Turner, J. G., et al. (2020) Phase I clinical trial of selinexor in combination with daunorubicin and cytarabine in previously untreated poor-risk acute myeloid leukemia, Clin. Cancer Res., 26, 54-60, https://doi.org/10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-19-2169.
Martinez Sanchez, M. P., Megias-Vericat, J. E., Rodriguez-Veiga, R., Vives, S., Bergua, J. M., et al. (2021) A phase I trial of selinexor plus FLAG-Ida for the treatment of refractory/relapsed adult acute myeloid leukemia patients, Ann. Hematol., 100, 1497-1508, https://doi.org/10.1007/s00277-021-04542-8.
Fiedler, W., Chromik, J., Amberg, S., Kebenko, M., Thol, F., et al. (2020) A Phase II study of selinexor plus cytarabine and idarubicin in patients with relapsed/refractory acute myeloid leukaemia, Br. J. Haematol., 190, e169-e173, https://doi.org/10.1111/bjh.16804.
Taylor, J., Mi, X., Penson, A. V., Paffenholz, S. V., Alvarez, K., Sigler, A., et al. (2020) Safety and activity of selinexor in patients with myelodysplastic syndromes or oligoblastic acute myeloid leukaemia refractory to hypomethylating agents: a single-centre, single-arm, phase 2 trial, Lancet Haematol., 7, e566-e574, https://doi.org/10.1016/S2352-3026(20)30209-X.
Chen, C., Siegel, D., Gutierrez, M., Jacoby, M., Hofmeister, C. C., et al. (2018) Safety and efficacy of selinexor in relapsed or refractory multiple myeloma and Waldenstrom macroglobulinemia, Blood, 131, 855-863, https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2017-08-797886.
Vogl, D. T., Dingli, D., Cornell, R. F., Huff, C. A., Jagannath, S., et al. (2018) Selective inhibition of nuclear export with oral selinexor for treatment of relapsed or refractory multiple myeloma, J. Clin. Oncol., 36, 859-866, https://doi.org/10.1200/JCO.2017.75.5207.
Chari, A., Vogl, D. T., Gavriatopoulou, M., Nooka, A. K., Yee, A. J., et al. (2019) Oral selinexor-dexamethasone for triple-class refractory multiple myeloma, N. Engl. J. Med., 381, 727-738, https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa1903455.
Bahlis, N. J., Sutherland, H., White, D., Sebag, M., Lentzsch, S., et al. (2018) Selinexor plus low-dose bortezomib and dexamethasone for patients with relapsed or refractory multiple myeloma, Blood, 132, 2546-2554, https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2018-06-858852.
Jakubowiak, A. J., Jasielec, J. K., Rosenbaum, C. A., Cole, C. E., Chari, A., et al. (2019) Phase 1 study of selinexor plus carfilzomib and dexamethasone for the treatment of relapsed/refractory multiple myeloma, Br. J. Haematol., 186, 549-560, https://doi.org/10.1111/bjh.15969.
Salcedo, M., Lendvai, N., Mastey, D., Schlossman, J., Hultcrantz, M., et al. (2020) Phase I study of selinexor, ixazomib, and low-dose dexamethasone in patients with relapsed or refractory multiple myeloma, Clin. Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk., 20, 198-200, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clml.2019.12.013.
Grosicki, S., Simonova, M., Spicka, I., Pour, L., Kriachok, I., et al. (2020) Once-per-week selinexor, bortezomib, and dexamethasone versus twice-per-week bortezomib and dexamethasone in patients with multiple myeloma (BOSTON): A randomised, open-label, phase 3 trial, Lancet, 396, 1563-1573, https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(20)32292-3.
Kuruvilla, J., Savona, M., Baz, R., Mau-Sorensen, P. M., Gabrail, N., et al. (2017) Selective inhibition of nuclear export with selinexor in patients with non-Hodgkin lymphoma, Blood, 129, 3175-3183, https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2016-11-750174.
Kalakonda, N., Maerevoet, M., Cavallo, F., Follows, G., Goy, A., et al. (2020) Selinexor in patients with relapsed or refractory diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (SADAL): a single-arm, multinational, multicentre, open-label, phase 2 trial, Lancet Haematol., 7, e511-e522, https://doi.org/10.1016/S2352-3026(20)30120-4.
Tang, T., Martin, P., Somasundaram, N., Lim, C., Tao, M., et al. (2020) Phase I study of selinexor in combination with dexamethasone, ifosfamide, carboplatin, etoposide chemotherapy in patients with relapsed or refractory peripheral T-cell or naturalkiller/T-cell lymphoma, Haematologica, 6, 3170-3175, https://doi.org/10.3324/haematol.2020.251454.
Abdul Razak, A. R., Mau-Soerensen, M., Gabrail, N. Y., Gerecitano, J. F., Shields, A. F., et al. (2016) First-in-class, first-in-human phase I study of selinexor, a selective inhibitor of nuclear export, in patients with advanced solid tumors, J. Clin. Oncol., 34, 4142-4150, https://doi.org/10.1200/JCO.2015.65.3949.
Wei, X. X., Siegel, A. P., Aggarwal, R., Lin, A. M., Friedlander, T. W., et al. (2018) A phase II trial of selinexor, an oral selective inhibitor of nuclear export compound, in abiraterone- and/or enzalutamide-refractory Metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer, Oncologist, 23, 656-e664, https://doi.org/10.1634/theoncologist.2017-0624.
Shafique, M., Ismail-Khan, R., Extermann, M., Sullivan, D., Goodridge, D., et al. (2019) A phase II trial of selinexor (KPT-330) for metastatic triple-negative breast cancer, Oncologist, 24, 887-e416, https://doi.org/10.1634/theoncologist.2019-0231.
Vergote, I. B., Lund, B., Peen, U., Umajuridze, Z., Mau-Sorensen, M., et al. (2020) Phase 2 study of the exportin 1 inhibitor selinexor in patients with recurrent gynecological malignancies, Gynecol. Oncol., 156, 308-314, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ygyno.2019.11.012.
Rubinstein, M. M., Grisham, R. N., Cadoo, K., Kyi, C., Tew, W. P., et al. (2021) A phase I open-label study of selinexor with paclitaxel and carboplatin in patients with advanced ovarian or endometrial cancers, Gynecol. Oncol., 160, 71-76, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ygyno.2020.10.019.
Gounder, M. M., Zer, A., Tap, W. D., Salah, S., Dickson, M. A., et al. (2016) Phase IB study of selinexor, a first-in-class inhibitor of nuclear export, in patients with advanced refractory bone or soft tissue sarcoma, J. Clin. Oncol., 34, 3166-3174, https://doi.org/10.1200/JCO.2016.67.6346.
Nilsson, S., Stein, A., Rolfo, C., Kranich, A. L., Mann, J., et al. (2020) Selinexor (KPT-330), an oral Selective Inhibitor of Nuclear Export (SINE) compound, in combination with FOLFOX in patients with metastatic colorectal cancer (mCRC) – final results of the phase I trial SENTINEL, Curr. Cancer Drug Targets, 20, 811-817, https://doi.org/10.2174/1568009620666200628105727.
(2019) XPO1 inhibitor approved for multiple myeloma, Cancer Discov., 9, 1150-1151, https://doi.org/10.1158/2159-8290.CD-NB2019-085.
Cornell, R., Hari, P., Tang, S., Biran, N., Callander, N., et al. (2021) Overall survival of patients with triple-class refractory multiple myeloma treated with selinexor plus dexamethasone vs standard of care in MAMMOTH, Am. J. Hematol., 96, E5-E8, https://doi.org/10.1002/ajh.26010.
Machlus, K. R., Wu, S. K., Vijey, P., Soussou, T. S., Liu, Z. J., et al. (2017) Selinexor-induced thrombocytopenia results from inhibition of thrombopoietin signaling in early megakaryopoiesis, Blood, 130, 1132-1143, https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2016-11-752840.
Acknowledgments
The authors dedicate this work to their dear teacher Lev Ovchinnikov, an exceptional mentor who helped shape their scientific careers.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The authors declare no conflicts of interest. This article does not contain description of studies with the involvement of humans or animal subjects performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Translated from Uspekhi Biologicheskoi Khimii, 2022, Vol. 62, pp. 391-420.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, E., Mordovkina, D.A. & Sorokin, A. Targeting XPO1-Dependent Nuclear Export in Cancer. Biochemistry Moscow 87 (Suppl 1), S178–S191 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0006297922140140
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S0006297922140140