Abstract
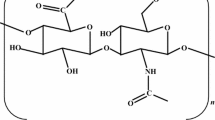
Hyaluronic acid is an evolutionarily ancient molecule commonly found in vertebrate tissues and capsules of some bacteria. Here we review modern data regarding structure, properties, and biological functions of hyaluronic acid in mammals and Streptococcus spp. bacteria. Various aspects of biogenesis and degradation of hyaluronic acid are discussed, biosynthesis and degradation metabolic pathways for glycosaminoglycan together with involved enzymes are described, and vertebrate and bacterial hyaluronan synthase genes are characterized. Special attention is given to the mechanisms underlying the biological action of hyaluronic acid as well as the interaction between polysaccharide and various proteins. In addition, all known signaling pathways involving hyaluronic acid are outlined. Impaired hyaluronic acid metabolism, changes in biopolymer molecular weight, hyaluronidase activity, and enzyme isoforms often accompany carcinogenesis. The interaction between cells and hyaluronic acid from extracellular matrix that may be important during malignant change is discussed. An expected role for high molecular weight hyaluronic acid in resistance of naked mole rat to oncologic diseases and the protective role of hyaluronic acid in bacteria are discussed.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- CAP:
-
catabolite activator protein (or cAMP receptor protein)
- CDS:
-
carbohydrate deficiency shock
- HA:
-
hyaluronic acid
- HAS:
-
bacterial hyaluronan synthase
- HAS(13):
-
vertebrate hyaluronan synthases
- has(1-3) :
-
vertebrate hyaluronan synthase genes
- hasABC :
-
bacterial hyaluronan synthase operon
- HYAL-(1-4):
-
HYAL-P1, and PH20 are human hyaluronidases
- hylA :
-
streptococcal hyaluronan lyase gene
References
Meyer, K., and Palmer, J. (1934) The polysaccharide of the vitreous humor, J. Biol. Chem., 107, 629–634.
Linker, A., and Meyer, K. (1954) Production of unsaturated uronides by bacterial hyaluronidases, Nature, 174, 1192–1194.
Radaeva, I. F., Kostina, G. A., and Zmievskiy, A. V. (1997) Hyaluronic acid: biological role, structure, synthesis, isolation, purification and use, Prikl. Biokhim. Mikrobiol., 33, 133–137.
Armstrong, D. C., and Johns, M. R. (1995) Improved molecular weight analysis of streptococcal hyaluronic acid by size exclusion chromatography, Biotechnol. Techniq., 9, 491–496.
Armstrong, D. C., and Johns, M. R. (1997) Effect of culture conditions on molecular weight of hyaluronic acid produced by Streptococcus zooepidemicus, Appl. Environ. Microbiol., 63, 2759–2764.
Scott, J. E., Cummings, C., Brass, A., and Chen, Y. (1991) Secondary and tertiary structures of hyaluronan in aqueous solution, investigated by rotary shadowing-electron microscopy and computer simulation. Hyaluronan is a very efficient network-forming polymer, Biochem. J., 274, 699–705.
Atkins, E. D., Phelps, C. F., and Sheehan, J. K. (1972) The conformation of the mucopolysaccharides. Hyaluronates, Biochem. J., 128, 1255–1263.
Sheehan, J. K., Arundel, C., and Phelps, C. F. (1983) Effects of the cations sodium, potassium and calcium on the interaction of hyaluronate chains–a light-scattering and viscosimetric study, Int. J. Biol. Macromol., 5, 222–228.
Sheehan, J. K., Gardner, K. H., and Atkins, E. D. (1977) Hyaluronic acid: a double helix structure in the presence of potassium at low pH and found also with the cations ammonium, rubidium and calcium, J. Mol. Biol., 117, 113–135.
Atkins, E. D., and Sheehan, J. K. (1973) Hyaluronates: relation between molecular conformations, Science, 179, 562–564.
Dea, I. C., and Moorhouse, M. R. (1973) Hyaluronic acid: a novel, double helical molecule, Science, 179, 560–562.
Guss, J. M., Hukins, D. W., Smith, P. J., Winter, W. T., and Arnott, S. (1975) Hyaluronic acid: molecular conformations and interactions in two sodium salts, J. Mol. Biol., 95, 359–384.
Winter, W. T., and Arnott, S. (1977) Hyaluronic acid: the role of divalent cations in conformation and packing, J. Mol. Biol., 117, 761–784.
Cleland, R. L., and Wang, J. L. (1970) Ionic polysaccharides. III. Dilute solution properties of hyaluronic acid fractions, Biopolymers, 9, 799–810.
Cleland, R. L. (1977) The persistence length of hyaluronic acid: an estimate from small-angle X-ray scattering and intrinsic viscosity, Arch. Biochem. Biophys., 180, 57–68.
Cleland, R. L. (1968) Ionic polysaccharides. II. Comparison of polyelectrolyte behavior of hyaluronate with that of carboxymethyl cellulose, Biopolymers, 6, 1519–1529.
Darke, A., Finer, E. G., Moorhouse, R., and Rees, D. A. (1975) Studies of hyaluronate solutions by nuclear magnetic relaxation measurements. Detection of covalentlydefined, stiff segments within the flexible chains, J. Mol. Biol., 99, 477–486.
Ribitsch, G., Schurz, J., and Ribitsch, V. (1980) Investigation of the solution structure of hyaluronic acid by light-scattering, SAXS and viscosity measurements, Colloid Polym. Sci., 258, 1322–1334.
Cowman, M. K., Spagnoli, C., Kudasheva, D., Li, M., Dyal, A., Kanai, S., and Balazs, E. A. (2005) Extended, relaxed, and condensed conformations of hyaluronan, Biophys. J., 88, 590–602.
Kogan, G., Soltes, L., Stern, R., and Gemeiner, P. (2007) Hyaluronic acid: a natural biopolymer with a broad range of biomedical and industrial applications, Biotechnol. Lett., 29, 17–25.
Asari, A., Miyauchi, S., Kuriyama, S., Machida, A., Kohno, K., and Uchiyama, Y. (1994) Localization of hyaluronic acid in human articular cartilage, J. Histochem. Cytochem., 42, 513–522.
Cleland, R. L., and Sherblom, A. P. (1977) Isolation and physical characterization of hyaluronic acid prepared from bovine nasal septum by cetylpyridinium chloride precipitation, J. Biol. Chem., 252, 420–426.
Levy, P., Picard, J., and Bruel, A. (1981) Glycosaminoglycan biosynthesis in arterial wall sulfation of heparan sulfate in cell membrane of aortic media-intima, Eur. J. Biochem., 115, 397–404.
Nardinia, M., Oria, M., Vigettid, D., Gornatid, R., Nardia, I., and Perris, R. (2004) Regulated gene expression of hyaluronan synthases during Xenopus laevis development, Gene Exp. Patterns, 4, 303–308.
Schmidt, A., Prager, M., Selmke, P., and Buddecke, E. (1982) Isolation and properties of proteoglycans from bovine aorta, Eur. J. Biochem., 125, 95–101.
Itano, N., and Kimata, K. (1996) Expression cloning and molecular characterization of HAS protein, a eukaryotic hyaluronan synthase, J. Biol. Chem., 271, 9875–9878.
Shyjan, A. M., Heldin, P., Butcher, E. C., Yoshino, T., and Briskin, M. J. (1996) Functional cloning of the cDNA for a human hyaluronan synthase, J. Biol. Chem., 271, 23395–23399.
Spicer, A. P., Augustine, M. L., and McDonald, J. A. (1996) Molecular cloning and characterization of a putative mouse hyaluronan synthase, J. Biol. Chem., 271, 23400–23406.
Watanabe, K., and Yamaguchi, Y. (1996) Molecular identification of a putative human hyaluronan synthase, J. Biol. Chem., 271, 22945–22948.
Giji, S., and Arumugam, M. (2014) Isolation and characterization of hyaluronic acid from marine organisms, Adv. Food Nutr. Res., 72, 61–77.
Volpi, N., and Maccari, F. (2003) Purification and characterization of hyaluronic acid from the mollusk bivalve Mytilus galloprovincialis, Biochimie, 85, 619–625.
DeAngelis, P. L., Jing, W., Graves, M. V., Burbank, D. E., and Van Etten, J. L. (1997) Hyaluronan synthase of chlorella virus PBCV-1, Science, 278, 1800–1803.
Graves, M. V., Burbank, D. E., Roth, R., Heuser, J., DeAngelis, P. L., and Van Etten, J. L. (1999) Hyaluronan synthesis in virus PBCV-1-infected chlorella-like green algae, Virology, 257, 15–23.
Kendall, F. E., Heidelberger, M., and Dawson, M. H. (1937) A serologically inactive polysaccharide elaborated by mucoid strains of group A hemolytic Streptococcus, J. Biol. Chem., 118, 61–69.
Seastone, C. V. (1939) The virulence of group C hemolytic streptococci of animal origin, J. Exp. Med., 70, 361–378.
Topper, Y. J., and Lipton, M. M. (1953) The biosynthesis of a streptococcal capsular polysaccharide, J. Biol. Chem., 203, 135–142.
Stoolmiller, A. C., and Dorfman, A. (1969) The biosynthesis of hyaluronic acid by Streptococcus, J. Biol. Chem., 244, 236–246.
Kass, E. H., and Seastone, C. V. (1944) The role of the mucoid polysaccharide (hyaluronic acid) in the virulence of group A streptococci, J. Exp. Med., 79, 319–330.
Carter, G. R., and Annau, E. (1953) Isolation of capsular polysaccharides from colonial variants of Pasteurella multocida, Am. J. Vet. Res., 14, 475–478.
DeAngelis, P. L., Jing, W., Drake, R. R., and Achyuthan, A. M. (1998) Identification and molecular cloning of a unique hyaluronan synthase from Pasteurella multocida, J. Biol. Chem., 273, 8454–8458.
Evanko, S. P., and Wight, T. N. (1999) Intracellular localization of hyaluronan in proliferating cells, J. Histochem. Cytochem., 47, 1331–1342.
Huang, L., Grammatikakis, N., Yoneda, M., Banerjee, S. D., and Toole, B. P. (2000) Molecular characterization of a novel intracellular hyaluronan-binding protein, J. Biol. Chem., 275, 29829–29839.
Kreil, G. (1995) Hyaluronidases — a group of neglected enzymes, Protein Sci., 4, 1666–1669.
Toole, B. P. (1991) Proteoglycans and hyaluronan in morphogenesis and differentiation, in Cell Biology of Extracellular Matrix (Hay, E. D., ed.) Plenum Press, NY, pp. 305–341.
Toole, B. P. (1997) Hyaluronan in morphogenesis, J. Intern. Med., 242, 35–40.
Camenisch, T. D., Spicer, A. P., Brehm-Gibson, T., Biesterfeldt, J., Augustine, M. L., Calabro, A., ffixJr., Kubalak, S., Klewer, S. E., and McDonald, J. A. (2000) Disruption of hyaluronan synthase-2 abrogates normal cardiac morphogenesis and hyaluronan-mediated transformation of epithelium to mesenchyme, J. Clin. Investig., 106, 349–360.
Juhlin, L. (1997) Hyaluronan in skin, J. Intern. Med., 242, 61–66.
Prehm, P. (2000) Hyaluronan, in Biopolymers. Vol. 5. Polysaccharides. I. Polysaccharides from prokaryotes (Vandamme, E. J., DeBaets, S., and Steinbuchel, A.-W., eds.) Wiley-VCH, NY, pp. 379–404.
Schiller, J., Fuchs, B., Arnhold, J., and Arnold, K. (2003) Contribution of reactive oxygen species to cartilage degradation in rheumatic diseases: molecular pathways, diagnosis and potential therapeutic strategies, Curr. Med. Chem., 10, 2123–2145.
Soltes, L., Mendichi, R., Kogan, G., Schiller, J., Stankovska, M., and Arnhold, J. (2006) Degradative action of reactive oxygen species on hyaluronan, Biomacromolecules, 7, 659–668.
Tammi, M. I., Day, A. J., and Turley, E. A. (2002) Hyaluronan and homeostasis: a balancing act, J. Biol. Chem., 277, 4581–4584.
Kogan, G., Soltes, L., Stern, R., Schiller, J., and Mendichi, R. (2008) Hyaluronic acid: its function and degradation in in vivo systems, in Studies in Natural Products Chemistry (Atta-ur-Rahman, ed.) Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp. 131–143.
Noble, P. W., Lake, F. R., Henson, P. M., and Riches, D. W. (1993) Hyaluronate activation of CD-44 induces insulin-like growth factor-1 expression by a tumor necrosis factor-α1-dependent mechanism in murine macrophages, J. Clin. Invest., 91, 2368–2377.
Hodge-Dufour, J., Horton, M. R., Burdick, M. D., Strieter, R. M., Noble, P. W., Hunter, C., Trinchieri, G., and Pure, E. (1997) Induction of IL-12 and chemokines by hyaluronan requires adhesion-dependent priming of resident but not elicited macrophages, J. Immunol., 159, 2492–2500.
Horton, M. R., Shapiro, S., Lowenstein, C. J., and Noble, P. W. (1999) Induction and regulation of macrophage metalloelastase by hyaluronan fragments in mouse macrophages, J. Immunol., 162, 4171–4176.
West, D. C., and Kumar, S. (1989) The effect of hyaluronate and its oligosaccharides on endothelial cell proliferation and monolayer integrity, Exp. Cell Res., 183, 179–196.
Rooney, P., Kumar, S., Ponting, J., and Wang, M. (1995) The role of hyaluronan in tumor neovascularization, Int. J. Cancer, 60, 632–636.
Ohkawara, Y., Tamura, G., Iwasaki, T., Tanaka, A., Kikuchi, T., and Shirato, K. (2000) Activation and transforming growth factor-ß production in eosinophils by hyaluronan, Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol., 23, 444–451.
West, D. C., Hampson, I. N., Arnold, F., and Kumar, S. (1985) Angiogenesis induced by degradation products of hyaluronic acid, Science, 228, 1324–1326.
Feinberg, R. N., and Beebe, D. C. (1983) Hyaluronate in vasculogenesis, Science, 220, 1177–1179.
Termeer, C. C., Hennies, J., Voith, U., Ahrens, T., Weiss, J. M., Prehm, P., and Simon, J. C. (2000) Oligosaccharides of hyaluronan are potent activators of dendritic cells, J. Immunol., 165, 1863–1870.
Xu, H., Ito, T., Tawada, A., Maeda, H., Yamanokuchi, H., Isahara, K., Yoshida, K., Uchiyama, Y., and Asari, A. (2002) Effect of hyaluronan oligosaccharides on the expression of heat shock protein 72, J. Biol. Chem., 277, 17308–17314.
Stern, R., Asari, A. A., and Sugahara, K. N. (2006) Hyaluronan fragments: an information-rich system, Eur. J. Cell Biol., 85, 699–715.
Heldermon, C., DeAngelis, P. L., and Weigel, P. H. (2001) Topological organization of the hyaluronan synthase from Streptococcus pyogenes, J. Biol. Chem., 276, 2037–2046.
Philipson, L. H., and Schwartz, N. B. (1984) Subcellular localization of hyaluronate synthetase in oligodendroglioma cells, J. Biol. Chem., 259, 5017–5023.
Appel, A., Horwitz, A. L., and Dorfman, A. (1979) Cellfree synthesis of hyaluronic acid in Marfan syndrome, J. Biol. Chem., 254, 12199–12203.
Philipson, L. H., Westley, J., and Schwartz, N. B. (1985) Effect of hyaluronidase treatment of intact cells on hyaluronate synthetase activity, Biochemistry, 24, 899–906.
Prehm, P. (1983) Synthesis of hyaluronate in differentiated teratocarcinoma cells: characterization of the synthase, Biochem. J., 211, 181–189.
Weigel, P. H., Hascall, V. C., and Tammi, M. (1997) Hyaluronan synthases, J. Biol. Chem., 272, 13997–14000.
Kumari, K., and Weigel, P. H. (1997) Molecular cloning, expression, and characterization of the authentic hyaluronan synthase from group C Streptococcus equisimilis, J. Biol. Chem., 272, 32539–32546.
DeAngelis, P. L., Papaconstantinou, J., and Weigel, P. H. (1993) Molecular cloning, identification and sequence of the hyaluronic acid synthase gene from group A Streptococcus pyogenes, J. Biol. Chem., 268, 19181–19184.
DeAngelis, P. L., and Weigel, P. H. (1994) Immunochemical confirmation of the primary structure of streptococcal hyaluronan synthase and synthesis of high molecular weight product by the recombinant enzyme, Biochemistry, 33, 9033–9039.
Prehm, P. (1983) Synthesis of hyaluronate in differentiated teratocarcinoma cells. Mechanism of chain growth, Biochem. J., 211, 191–198.
Asplund, T., Brinck, J., Suzuki, M., Briskin, M. J., and Heldin, P. (1998) Characterization of hyaluronan synthase from a human glioma cell line, Biochim. Biophys. Acta, 1380, 377–388.
Jing, W., and DeAngelis, P. L. (2003) Analysis of the two active sites of the hyaluronan synthase and the chondroitin synthase of Pasteurella multocida, Glycobiology, 13, 661–671.
DeAngelis, P. L. (2002) Evolution of glycosaminoglycans and their glycosyltransferases: implications for the extracellular matrices of animals and the capsules of pathogenic bacteria, Anat. Rec., 268, 317–326.
Toyoda, H., Kinoshita-Toyoda, A., and Selleck, S. B. (2000) Structural analysis of glycosaminoglycans in Drosophila and Caenorhabditis elegans and demonstration that tout-velu, a Drosophila gene related to EXT tumor suppressors, affects heparan sulfate in vivo, J. Biol. Chem., 275, 2269–2275.
Spicer, A. P., and McDonald, J. A. (1998) Characterization and molecular evolution of a vertebrate hyaluronan synthase gene family, J. Biol. Chem., 273, 1923–1932.
Itano, N., and Kimata, K. (1996) Molecular cloning of human hyaluronan synthase, Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun., 222, 816–820.
Martin, J., Han, C., Gordon, L. A., Terry, A., Prabhakar, S., She, X., Xie, G., Hellsten, U. Chan, Y. M., Altherr, M., Couronne, O., Aerts, A., Bajorek, E., Black, S., Blumer, H., Branscomb, E., Brown, N. C., Bruno, W. J., Buckingham, J. M., Callen, D. F., Campbell, C. S., Campbell, M. L., Campbell, E. W., Caoile, C., Challacombe, J. F., Chasteen, L. A., Chertkov, O., Chi, H. C., Christensen, M., Clark, L. M., Cohn, J. D., Denys, M., Detter, J. C., Dickson, M., Dimitrijevic-Bussod, M., Escobar, J., Fawcett, J. J., Flowers, D., Fotopulos, D., Glavina, T., Gomez, M., Gonzales, E., Goodstein, D., Goodwin, L. A., Grady, D. L., Grigoriev, I., Groza, M., Hammon, N., Hawkins, T., Haydu, L., Hildebrand, C. E., Huang, W., Israni, S., Jett, J., Jewett, P. B., Kadner, K., Kimball, H., Kobayashi, A., Krawczyk, M. C., Leyba, T., Longmire, J. L., Lopez, F., Lou, Y., Lowry, S., Ludeman, T., Manohar, C. F., Mark, G. A., Mc Murray, K. L., Meincke, L. J., Morgan, J., Moyzis, R. K., Mundt, M. O., Munk, A. C., Nandkeshwar, R. D., Pitluck, S., Pollard, M., Predki, P., Parson-Quintana, B., Ramirez, L., Rash, S., Retterer, J., Ricke, D. O., Robinson, D. L., Rodriguez, A., Salamov, A., Saunders, E. H., Scott, D., Shough, T., Stallings, R. L., Stalvey, M., Sutherland, R. D., Tapia, R., Tesmer, J. G., Thayer, N., Thompson, L. S., Tice, H., Torney, D. C., Tran-Gyamfi, M., Tsai, M., Ulanovsky, L. E., Ustaszewska, A., Vo, N., White, P. S., Williams, A. L., Wills, P. L., Wu, J. R., Wu, K., Yang, J., Dejong, P., Bruce, D., Doggett, N. A., Deaven, L., Schmutz, J., Grimwood, J., Richardson, P., Rokhsar, D. S., Eichler, E. E., Gilna, P., Lucas, S. M., Myers, R. M., Rubin, E. M., and Pennacchio, L. A. (2004) The sequence and analysis of duplication-rich human chromosome 16, Nature, 432, 988–994.
Toole, B. P. (2000) Hyaluronan is not just a goo! J. Clin. Invest., 106, 335–336.
Lee, J. Y., and Spicer, A. P. (2000) Hyaluronan: a multifunctional, megaDalton, stealth molecule, Curr. Opin. Cell Biol., 12, 581–586.
Sattar, A., Rooney, P., Kumar, S., Pye, D., West, D. C., Scott, I., and Ledger, P. (1994) Application of angiogenic oligosaccharides of hyaluronan increase blood vessel numbers in skin, J. Invest. Dermatol., 103, 573–579.
Lees, V. C., Fan, T. P., and West, D. C. (1995) Angiogenesis in a delayed revascularization model is accelerated by angiogenic oligosaccharides of hyaluronan, Lab. Invest., 73, 259–266.
Deed, R., Rooney, P., Kumar, P., Norton, J. D., Smith, J., Freemont, A. J., and Kumar, S. (1997) Early-response gene signaling is induced by angiogenic oligosaccharides of hyaluronan in endothelial cells, Int. J. Cancer, 71, 251–256.
Slevin, M., Krupinski, J., Kumar, S., and Gaffney, J. (1998) Angiogenic oligosaccharides of hyaluronan induce protein tyrosine kinase activity in endothelial cells and activate a cytoplasmic signal transduction pathway resulting in proliferation, Lab. Invest., 78, 987–1003.
Lokeshwar, V. B., and Selzer, M. G. (2000) Differences in hyaluronic acid-mediated functions and signaling in arterial, microvessel, and vein-derived human endothelial cells, J. Biol. Chem., 275, 27641–27649.
Slevin, M., Kumar, S., and Gaffney, J. (2002) Angiogenic oligosaccharides of hyaluronan induce multiple signaling pathways affecting vascular endothelial cell mitogenic and wound healing responses, J. Biol. Chem., 277, 41046–41059.
Suzuki, M., Kobayashi, H., Kanayama, N., Nishida, T., Takigawa, M., and Terao, T. (2002) CD44 stimulation by fragmented hyaluronic acid induces upregulation and tyrosine phosphorylation of c-Met receptor protein in human chondrosarcoma cells, Biochim. Biophys. Acta, 1591, 37–44.
Kobayashi, H., Suzuki, M., Kanayama, N., Nishida, T., Takigawa, M., and Terao, T. (2002) CD44 stimulation by fragmented hyaluronic acid induces upregulation of urokinase-type plasminogen activator and its receptor and subsequently facilitates invasion of human chondrosarcoma cells, Int. J. Cancer, 102, 379–389.
Nasreen, N., Mohammed, K. A., Hardwick, J., Van Horn, R. D., Sanders, K., Kathuria, H., Loghmani, F., and Antony, V. B. (2002) Low molecular weight hyaluronan induces malignant mesothelioma cell (MMC) proliferation and haptotaxis: role of CD44 receptor in MMC proliferation and haptotaxis, Oncol. Res., 13, 71–78.
Fujita, Y., Kitagawa, M., Nakamura, S., Azuma, K., Ishii, G., Higashi, M., Kishi, H., Hiwasa, T., Koda, K., Nakajima, N., and Harigaya, K. (2002) CD44 signaling through focal adhesion kinase and its anti-apoptotic effect, FEBS Lett., 528, 101–108.
Zimmerman, E., Geiger, B., and Addadi, L. (2002) Initial stages of cell-matrix adhesion can be mediated and modulated by cell-surface hyaluronan, Biophys. J., 82, 1848–1857.
Ichikawa, T., Itano, N., Sawai, T., Kimata, K., Koganehira, Y., Saida, T., and Taniguchi, S. (1999) Increased synthesis of hyaluronate enhances motility of human melanoma cells, J. Invest. Dermatol., 113, 935–939.
Itano, N., Sawai, T., Miyaishi, O., and Kimata, K. (1999) Relationship between hyaluronan production and metastatic potential of mouse mammary carcinoma cells, Cancer Res., 59, 2499–2504.
Kosaki, R., Watanabe, K., and Yamaguchi, Y. (1999) Overproduction of hyaluronan by expression of the hyaluronan synthase Has2 enhances anchorage-independent growth and tumorigenicity, Cancer Res., 59, 1141–1145.
Liu, N., Lapcevich, R. K., Underhill, C. B., Han, Z., Gao, F., Swartz, G., Plum, S. M., Zhang, L., and Gree, S. J. (2001) Metastatin: a hyaluronan-binding complex from cartilage that inhibits tumor growth, Cancer Res., 61, 1022–1028.
Itano, N., Atsumi, F., Sawai, T., Yamada, Y., Miyaishi, O., Senga, T., Hamaguchi, M., and Kimata, K. (2002) Abnormal accumulation of hyaluronan matrix diminishes contact inhibition of cell growth and promotes cell migration, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 99, 3609–3614.
Itano, N., Sawai, T., Yoshida, M., Lenas, P., and Yamada, Y. (1999) Three isoforms of mammalian hyaluronan synthases have distinct enzymatic properties, J. Biol. Chem., 274, 25085–25092.
Adamia, S., Maxwell, C. A., and Pilarski, L. M. (2005) Hyaluronan and hyaluronan synthases: potential therapeutic targets in cancer, Curr. Drug Targets Cardiovasc. Haematol. Disord., 5, 3–14.
Meyer, K. (1971) Hyaluronidases, in The Enzymes (Boyer, P. D., ed.) Academic Press, NY, pp. 307–320.
Chain, E., and Duthie, E. S. (1940) Identity of hyaluronidase and spreading factor, Br. J. Expl. Path., 21, 324–338.
De Salegui, M., and Pigman, W. (1967) The existence of an acid-active hyaluronidase in serum, Arch. Biochem. Biophys., 120, 60–67.
Afify, A. M., Stern, M., Guntenhoener, M., and Stern, R. (1993) Purification and characterization of human serum hyaluronidase, Arch. Biochem. Biophys., 305, 434–441.
Frost, G. I., Csoka, T., and Stern, R. (1996) The hyaluronidases: a chemical, biological and clinical overview, Trends Glycosci. Glycotech., 8, 419–434.
Hovingh, P., and Linker, A. (1999) Hyaluronidase activity in leeches (Hirudinea), Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Biochem. Mol. Biol., 124, 319–326.
Yuki, H., and Fishman, W. H. (1963) Purification and characterization of leech hyaluronic acid-endo-P-glucuronidase, J. Biol. Chem., 238, 1877–1879.
Karlstam, B., Vincent, J., Johansson, B., and Bryno, C. (1991) A simple purification method of squeezed krill for obtaining high levels of hydrolytic enzymes, Prep. Biochem., 21, 237–256.
Karlstam, B., and Ljungloef, A. (1991) Purification and partial characterization of a novel hyaluronic acid-degrading enzyme from Antarctic krill, Polar Biol., 11, 501–507.
Stern, R., and Jedrzejas, M. J. (2006) Hyaluronidases: their genomics, structures, and mechanisms of action, Chem. Rev., 106, 818–839.
Stern, R. (2005) Hyaluronan metabolism: a major paradox in cancer biology, Pathol. Biol., 53, 372–382.
Csoka, A. B., Frost, G. I., and Stern, R. (2001) The six hyaluronidase-like genes in the human and mouse genomes, Matrix Biol., 20, 499–508.
Lokeshwar, V. B., Schroeder, G. L., Carey, R. I., Soloway, M. S., and Iida, N. (2002) Regulation of hyaluronidase activity by alternative mRNA splicing, J. Biol. Chem., 277, 33654–33663.
Lokeshwar, V. B., Obek, C., Pham, H. T., Wei, D., Young, M. J., Duncan, R. C., Soloway, M. S., and Block, M. L. (2000) Urinary hyaluronic acid and hyaluronidase: markers for bladder cancer detection and evaluation of grade, J. Urol., 163, 348–356.
Lepperdinger, G., Strobl, B., and Kreil, G. (1998) HYAL2, a human gene expressed in many cells, encodes a lysosomal hyaluronidase with a novel type of specificity, J. Biol. Chem., 273, 22466–22470.
Frost, G. I., Csoka, A. B., Wong, T., and Stern, R. (1997) Purification, cloning, and expression of human plasma hyaluronidase, Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun., 236, 10–15.
Lesley, J., Hyman, R., and Kincade, P. (1993) CD44 and its interaction with extracellular matrix, Adv. Immunol., 54, 271–335.
Bourguignon, L. Y. (1996) Chap. 14. Interactions between the membrane-cytoskeleton and CD44 during lymphocyte signal transduction and cell adhesion, Curr. Top. Membr., 43, 293–312.
Bourguignon, L. Y., Lokeshwar, V. B., He, J., Chen, X., and Bourguignon, G. J. (1992) A CD44-like endothelial cell transmembrane glycoprotein (GP116) interacts with extracellular matrix and ankyrin, Mol. Cell. Biol., 12, 4464–4471.
Screaton, G. R., Bell, M. V., Jackson, D. G., Cornelis, F. B., Gerth, U., and Bell, J. I. (1992) Genomic structure of DNA encoding the lymphocyte homing receptor CD44 reveals at least 12 alternatively spliced exons, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 89, 12160–12164.
Bourguignon, L. Y., Zhu, H. B., Chu, A., Zhang, L., and Hung, M. C. (1997) Interaction between the adhesion receptor, CD44, and the oncogene product, p185HER2, promotes human ovarian tumor cell activation, J. Biol. Chem., 272, 27913–27918.
Bourguignon, L. Y., Zhu, D., and Zhu, H. (1998) CD44 isoform–cytoskeleton interaction in oncogenic signaling and tumor progression, Front. Biosci., 3, 637–649.
Oliferenko, S., Kaverina, I., Small, J. V., and Huber, L. A. (2000) Hyaluronic acid (HA) binding to CD44 activates Rac1 and induces lamellipodia outgrowth, J. Cell Biol., 148, 1159–1164.
Bretscher, A. (1999) Regulation of cortical structure by the ezrin-radixin-moesin protein family, Curr. Opin. Cell Biol., 11, 109–116.
Bourguignon, L. Y., Zhu, H., Shao, L., and Chen, Y. W. (2000) CD44 interaction with tiaml promotes Rac1 signaling and hyaluronic acid-mediated breast tumor cell migration, J. Biol. Chem., 275, 1829–1838.
Bourguignon, L. Y., Zhu, H., Shao, L., and Chen, Y. W. (2000) Ankyrin–Tiam1 interaction promotes Rac1 signaling and metastatic breast tumor cell invasion and migration, J. Cell Biol., 150, 177–191.
Bourguignon, L. Y., Zhu, H., Zhou, B., Diedrich, F., Singleton, P. A., and Hung, M. C. (2001) Hyaluronan (HA) promotes CD44v3-Vav2 interaction with Grb2p185HER2 and induces Rac1 & Ras signaling during ovarian tumor cell migration and growth, J. Biol. Chem., 277, 48679–48692.
Assmann, V., Jenkinson, D., Marshall, J. F., and Hart, I. R. (1999) The intracellular hyaluronan receptor RHAMM/IHABP interacts with microtubules and actin filaments, J. Cell Sci., 112, 3943–3954.
Lynn, B. D., Turley, E. A., and Nagy, J. I. (2001) Subcellular distribution, calmodulin interaction and mitochondrial association of the hyaluronan-binding protein RHAMM in rat brain, J. Neurosci. Res., 65, 6–16.
Entwistle, J., Hall, C. L., and Turley, E. A. (1996) Hyaluronan receptors: regulators of signaling to the cytoskeleton, J. Cell. Biochem., 61, 569–577.
Zhang, S., Chang, M. C., Zylka, D., Turley, S., Harrison, R., and Turley, E. A. (1998) The hyaluronan receptor RHAMM regulates extracellular-regulated kinase, J. Biol. Chem., 273, 11342–11348.
Hall, C. L., Lange, L. A., Prober, D. A., Zhang, S., and Turley, E. A. (1996) pp60(c-src) is required for cell locomotion regulated by the hyaluronan receptor RHAMM, Oncogene, 13, 2213–2224.
Hall, C. L., Collis, L., Lange, L., Mc Nicol, A., Gerrard, J. M., and Turley, E. A. (2001) Fibroblasts require protein kinase C activation to respond to hyaluronan with increased locomotion, Matrix Biol., 20, 183–192.
Hall, C. L., Yang, B., Yang, X., Zhang, S., Turley, M., Samuel, S., Lange, L. A., Wang, C., Curpen, G. D., Savani, R. C., Greenberg, A. H., and Turley, E. A. (1995) Overexpression of the hyaluronan receptor RHAMM is transforming and is also required for H-ras transformation, Cell, 82, 19–26.
Hall, C. L., Wang, C., Lange, L. A., and Turley, E. A. (1994) Hyaluronan and the hyaluronan receptor RHAMM promote focal adhesion turnover and transient tyrosine kinase activity, J. Cell Biol., 126, 575–588.
Masellis-Smith, A., Belch, A. R., Mant, M. J., Turley, E. A., and Pilarski, L. M. (1996) Hyaluronan-dependent motility of ß cells and leukemic plasma cells in multiple myeloma: alternative usage of RHAMM and CD44, Blood, 87, 1891–1899.
Ahrens, T., Assmann, V., Fieber, C., Termeer, C., Herrlich, P., Hofmann, M., and Simon, J. C. (2001) CD44 is the principal mediator of hyaluronic-acid-induced melanoma cell proliferation, J. Invest. Dermatol., 116, 93–101.
Savani, R. C., Cao, G., Pooler, P. M., Zaman, A., Zhou, Z., and DeLisser, H. M. (2001) Differential involvement of the hyaluronan (HA) receptors CD44 and receptor for HA-mediated motility in endothelial cell function and angiogenesis, J. Biol. Chem., 276, 36770–36778.
Toole, B. P. (2001) Hyaluronan in morphogenesis, Semin. Cell Dev. Biol., 12, 79–87.
Auvinen, P., Tammi, R., Parkkinen, J., Tammi, M., Agren, U., Johansson, R., Hirvikoski, P., Eskelinen, M., and Kosma, V. M. (2000) Hyaluronan in peritumoral stroma and malignant cells associates with breast cancer spreading and predicts survival, Am. J. Pathol., 156, 529–536.
Anttila, M. A., Tammi, R. H., Tammi, M. I., Syrjanen, K. J., Saarikoski, S. V., and Kosma, V. M. (2000) High levels of stromal hyaluronan predict poor disease outcome in epithelial ovarian cancer, Cancer Res., 60, 150–155.
Liu, N., Gao, F., Han, Z., Xu, X., Underhill, C. B., and Zhang, L. (2001) Hyaluronan synthase 3 overexpression promotes the growth of TSU prostate cancer cells, Cancer Res., 61, 5207–5214.
Peterson, R. M., Yu, Q., Stamenkovic, I., and Toole, B. P. (2000) Perturbation of hyaluronan interactions by soluble CD44 inhibits growth of murine mammary carcinoma cells in ascites, Am. J. Pathol., 156, 2159–2167.
Yu, Q., Toole, B. P., and Stamenkovic, I. (1997) Induction of apoptosis of metastatic mammary carcinoma cells in vivo by disruption of tumor cell surface CD44 function, J. Exp. Med., 186, 1985–1996.
Yu, Q., and Stamenkovic, I. (1999) Localization of matrix metalloproteinase 9 to the cell surface provides a mechanism for CD44-mediated tumor invasion, Genes Dev., 13, 35–48.
Yu, Q., and Stamenkovic, I. (2000) Cell surface-localized matrix metalloproteinase-9 proteolytically activates TGFbeta and promotes tumor invasion and angiogenesis, Genes Dev., 14, 163–176.
Ahrens, T., Sleeman, J. P., Schempp, C. M., Howells, M., Hofmann, M., Ponta, H., Herrlich, P., and Simon, J. C. (2001) Soluble CD44 inhibits melanoma tumor growth by blocking cell surface CD44 binding to hyaluronic acid, Oncogene, 20, 3399–3408.
Zeng, C., Toole, B. P., Kinney, S. D., Kuo, J. W., and Stamenkovic, I. (1998) Inhibition of tumor growth in vivo by hyaluronan oligomers, Int. J. Cancer, 77, 396–401.
Nara, Y., Kato, Y., Torii, Y., Tsuji, Y., Nakagaki, S., Goto, S., Isobe, H., Nakashima, N., and Takeuchi, J. (1997) Immunohistochemical localization of extracellular matrix components in human breast tumors with special reference to PG-M/versican, Histochem. J., 29, 21–30.
Toole, B. P., Wight, T. N., and Tammi, M. I. (2002) Hyaluronan–cell interactions in cancer and vascular disease, J. Biol. Chem., 277, 4593–4596.
Ropponen, K., Tammi, M., Parkkinen, J., Eskelinen, M., Tammi, R., Lipponen, P., Egren, U., Alhava, E., and Kosma, V. M. (1998) Tumor cell associated hyaluronan as an unfavorable prognostic factor in colorectal cancer, Cancer Res., 58, 342–347.
Setala, L. P., Tammi, M. I., Tammi, R. H., Eskelinen, M. J., Lipponen, P. K., Egren, U. M., Parkkinen, J., Alhava, E. M., and Kosma, V. M. (1999) Hyaluronan expression in gastric cancer cells is associated with local and nodal spread and reduced survival rate, Br. J. Cancer, 79, 1133–1138.
Turley, E. A., Noble, P. W., and Bourguignon, L. Y. (2002) Signaling properties of hyaluronan receptors, J. Biol. Chem., 277, 4589–4592.
Csoka, A. B., Frost, G. I., Wong, T., and Stern, R. (1997) Purification and microsequencing of hyaluronidase isozymes from human urine, FEBS Lett., 417, 307–310.
Schroeder, G. L., Lorenzo-Gomez, M. F., Hautmann, S. H., Friedrich, M. G., Ekici, S., Huland, H., and Lokeshwar, V. (2004) A side by side comparison of cytology and biomarkers for bladder cancer detection, J. Urol., 172, 1123–1126.
Hautmann, S. H., Lokeshwar, V. B., Schroeder, G. L., Civantos, F., Duncan, R. C., Gnann, R., Friedrich, M. G., and Soloway, M. S. (2001) Elevated tissue expression of hyaluronic acid and hyaluronidase validates the HA–HAase urine test for bladder cancer, J. Urol., 165, 2068–2074.
Aboughalia, A. H. (2006) Elevation of hyaluronidase-1 and soluble intercellular adhesion molecule-1 helps select bladder cancer patients at risk of invasion, Arch. Med. Res., 37, 109–116.
Eissa, S., Kassim, S. K., Labib, R. A., El-Khouly, I. M., Ghaffer, T. M., Sadek, M., Razek, O. A., and El-Ahmady, O. (2005) Detection of bladder carcinoma by combined testing of urine for hyaluronidase and cytokeratin 20 RNAs, Cancer, 103, 1356–1362.
Posey, J. T., Soloway, M. S., Ekici, S., Sofer, M., Civantos, F., Duncan, R. C., and Lokeshwar, V. B. (2003) Evaluation of the prognostic potential of hyaluronic acid and hyaluronidase (HYAL1) for prostate cancer, Cancer Res., 63, 2638–2644.
Ekici, S., Cerwinka, W. H., Duncan, R., Gomez, P., Civantos, F., Soloway, M. S., and Lokeshwar, V. B. (2004) Comparison of the prognostic potential of hyaluronic acid, hyaluronidase (HYAL-1), CD44v6 and microvessel density for prostate cancer, Int. J. Cancer, 112, 121–129.
Franzmann, E. J., Schroeder, G. L., Goodwin, W. J., Weed, D. T., Fisher, P., and Lokeshwar, V. B. (2003) Expression of tumor markers hyaluronic acid and hyaluronidase (HYAL1) in head and neck tumors, Int. J. Cancer, 106, 438–445.
Pham, H. T., Block, N. L., and Lokeshwar, V. B. (1997) Tumor-derived hyaluronidase: a diagnostic urine marker for high-grade bladder cancer, Cancer Res., 57, 778–783.
Lokeshwar, V. B., Schroeder, G. L., Selzer, M. G., Hautmann, S. H., Posey, J. T., Duncan, R. C., Watson, R., Rose, L., Markowitz, S., and Soloway, M. S. (2002) Bladder tumor markers for monitoring recurrence and screening comparison of hyaluronic acid-hyaluronidase and BTA-stat tests, Cancer, 95, 61–72.
Lokeshwar, V. B., Cerwinka, W. H., and Lokeshwar, B. L. (2005) HYAL1 hyaluronidase in prostate cancer: a tumor promoter and suppressor, Cancer Res., 65, 2243–2250.
Lokeshwar, V. B., Cerwinka, W. H., Isoyama, T., and Lokeshwar, B. L. (2005) HYAL1 hyaluronidase in prostate cancer: a tumor promoter and suppressor, Cancer Res., 65, 7782–7789.
Lokeshwar, V. B., Estrella, V., Lopez, L., Kramer, M., Gomez, P., Soloway, M., and Lokeshwar, B. (2006) Amplification and expression of the Bcl-1 gene in human solid tumor cell lines, Cancer Res., 66, 11219–11227.
Fuchs, K., Hippe, A., Schmaus, A., Homey, B., Sleeman, J. P., and Orian-Rousseau, V. (2013) Opposing effects of highand low-molecular weight hyaluronan on CXCL12induced CXCR4 signaling depend on CD44, Cell Death Dis., 4, e819.
Tian, X., Azpurua, J., Hine, Ch., Vaidya, A., Myakishev-Rempel, M., Ablaeva, J., Mao, Z., Nevo, E., Gorbunova, V., and Seluanov, A. (2013) High-molecular-mass hyaluronan mediates the cancer resistance of the naked mole rat, Nature, 499, 346–349.
Buffenstein, R. (2008) Negligible senescence in the longest living rodent, the naked mole rat: insights from a successfully aging species, J. Comp. Physiol. B, 178, 439–445.
Delaney, M. A., Nagy, L., Kinsel, M. J., and Treuting, P. M. (2013) Spontaneous histologic lesions of the adult naked mole rat (Heterocephalus glaber): a retrospective survey of lesions in a zoo population, Vet. Pathol., 50, 607–621.
Seluanov, A., Hine, C., Azpurua, J., Feigenson, M., Bozzella, M., Mao, Z., Catania, K. C., and Gorbunova, V. (2009) Hypersensitivity to contact inhibition provides a clue to cancer resistance of naked mole rat, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 106, 19352–19357.
Tsepilov, R. N. (2013) Protective role of hyaluronic acid and hyaluronidase in the mechanism of overcoming carbohydrate deficiency shock by the culture of bacterial strain Streptococcus zooepidemicus, FEBS J., 280 (Suppl. 1), 38-th FEBS Congress, St. Petersburg, pp. 104–105.
Tsepilov, R. N., Beloded, A. V., and Samoylenko, I. I. (2013) Optimization of Streptococcus equi subsp. zooepidemicus culture process — a hyaluronic acid producer, Zh. Mikrobiol. Epidemiol. Immunobiol., 2, 12–20.
Holden, M. T., Heather, Z., Paillot, R., Steward, K. F., Webb, K., Ainslie, F., Jourdan, T., Bason, N. C., Holroyd, N. E., Mungall, K., Quail, M. A., Sanders, M., Simmonds, M., Willey, D., Brooks, K., Aanensen, D. M., Spratt, B. G., Jolley, K. A., Maiden, M. C., Kehoe, M., Chanter, N., Bentley, S. D., Robinson, C., Maskell, D. J., Parkhill, J., and Waller, A. S. (2009) Genomic evidence for the evolution of Streptococcus equi: host restriction, increased virulence, and genetic exchange with human pathogens, PLoS Pathog., 5, e1000346.
Koyama, H., Hibi, T., Isogai, Z., Yoneda, M., Fujimori, M., Amano, J., Kawakubo, M., Kannagi, R., Kimata, K., Taniguchi, S., and Itano, N. (2007) Hyperproduction of hyaluronan in neu-induced mammary tumor accelerates angiogenesis through stromal cell recruitment: possible involvement of versican/PG-M, Am. J. Pathol., 170, 1086–1099.
Holmes, M. W., Bayliss, M. T., and Muir, H. (1988) Hyaluronic acid in human articular cartilage: age-related changes in content and size, Biochem. J., 250, 435–441.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Original Russian Text © R. N. Tsepilov, A. V. Beloded, 2015, published in Biokhimiya, 2015, Vol. 80, No. 9, pp. 1315–1333.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tsepilov, R.N., Beloded, A.V. Hyaluronic acid — an “old” molecule with “new” functions: biosynthesis and depolymerization of hyaluronic acid in bacteria and vertebrate tissues including during carcinogenesis. Biochemistry Moscow 80, 1093–1108 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0006297915090011
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S0006297915090011