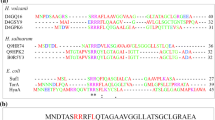
Abstract
Neurotrophic factors, including neurturin, increase the life span of the neurons and prevent neuronal destruction. As recombinant expression of neurturin with 3 disulfide bonds in Escherichia coli leads to the formation of inclusion bodies in the cytoplasm, periplasmic production of it is preferred. Signal peptides naturally exist at the N-terminus of the most newly synthesized proteins and are responsible for determining the final destination of the proteins. In the present study for the first time a novel signal peptide was designed de novo to secret recombinant neurturin to the periplasmic space of E. coli through the Sec pathway. Also the efficiency of de novo designed signal peptide (D.D.SP) was compared with that of pelB signal peptide. Designing process was performed using experiences from previous optimization studies and several bioinformatics tools such as BioEdit 7.2 software and SignalP-5.0 server. The quantitative analysis of Western blotting bands by ImageJ software showed that about 82% of expressed neurturin was secreted to the periplasmic space by D.D.SP while only 44% of expressed neurturin was obtained in the periplasmic space when PelB was used as a signal peptide. Moreover, CD spectroscopy analysis showed that the structure of secreted recombinant neurturin has high similarity to the commercial one.




Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Chen, R., Biotechnol. Adv., 2012, vol. 30, no. 5, pp. 1102–1107.
Demain, A.L. and Vaishnav, P., Biotechnol. Adv., 2009, vol. 27, no. 3, pp. 297–306.
Huang, C-J., Lin, H., and Yang, X., J. Ind. Microbiol. Biotechnol., 2012, vol. 39, no. 3, pp. 383–399.
Costa, T.R., Felisberto-Rodrigues, C., Meir, A., Prevost, M.S., Redzej, A., Trokter, M., et al., Nat. Rev. Microbiol., 2015, vol. 13, no. 6, pp. 343–359.
Green, E.R. and Mecsas, J., Microbiol. Spectr., 2016, vol. 4, pp. 213–239.
Bensing, B.A., Siboo, I.R., and Sullam, P.M., J. Bacteriol., 2007, vol. 189, no. 10, pp. 3846–3854.
Low, K.O., Mahadi, N.M., and Illias, R.M., Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol., 2013, vol. 97, no. 9, pp. 3811–3826.
Yoon, S.H., Kim, S.K., and Kim, J.F., Recent. Pat. Biotechnol., 2010, vol. 4, no. 1, pp. 23–29.
Walker, M.J. and Xu, X-M., Brain Sci., 2018, vol. 8, no. 6, pp. 109.
Airaksinen, M.S. and Saarma, M., Nat. Rev. Neurosci., 2002, vol. 3, no. 5, pp. 383–394.
Sambrook, J., Fritsch, E.F., and Maniatis, T., Molecular Cloning: A Laboratory Manual, Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory, New York: Cold Spring Harbor Press, 1989.
Brown, T.A., Gene Cloning and DNA Analysis: An Introduction, New York: Wiley, 2016.
Hajihassan, Z., Sohrabi, M., Rajabi Bazl, M., and Eftekhary, H., Rom. Biotechnol. Lett., 2016, vol. 21, no. 5, pp. 11850–11856.
Bradford, M.M., Anal. Biochem., 1976, vol. 72, no. 1–2, pp. 248–254.
Laemmli, U.K., Nature, 1970, vol. 227, no. 5259, pp. 680–685.
Protein Blotting. A Practical Approach, Dunbar, B.S., Ed., New York: IRL Press, 1994.
Schneider, C.A., Rasband, W.S., and Eliceiri, K.W., Nat. Methods, 2012, vol. 9, no. 7, pp. 671–675.
Hajihassan, Z., Abdi, M., Roshani Yasaghi, E., and Rabbani-Chadegani, A., Minerva Biotecnol., 2017, vol. 29, no. 3, pp. 126–132.
Inouye, M., Halegoua, S., and Beckwith, J., Crit. Rev. Biochem. Mol. Biol., 1980, vol. 7, no. 4, pp. 339–371.
Zalucki, Y.M., Power, P.M., and Jennings, M.P., Nucleic Acids Res., 2007, vol. 35, no. 17, pp. 5748–5754.
Puziss, J.W., Harvey, R., and Bassford, P., J. Bacteriol., 1992, vol. 174, no. 20, pp. 6488–6497.
Chou, Y-T. and Gierasch, L.M., J. Biol. Chem., 2005, vol. 280, no. 38, pp. 32753–32760.
Kebir, M.O. and Kendall, D.A., Biochemistry, 2002, vol. 41, no. 17, pp. 5573–5580.
Suominen, I., Meyer, P., Tilgmann, C., Glumoff, T., Glumoff, V., Käpylä, J., et al., Microbiology, 1995, vol. 141, no. 3, pp. 649–654.
Rusch, S.L., Chen, H., Izard, J.W., and Kendall, D.A., J. Cell Biochem., 1994, vol. 55, no. 2, pp. 209–217.
Adams, H., Scotti, P.A., de Cock, H., Luirink, J., and Tommassen, J., Eur. J. Biochem., 2002, vol. 269, no. 22, pp. 5564–5571.
Jonet, M.A., Mahadi, N.M., Murad, A.M.A., Rabu, A., Bakar, F.D.A., Rahim, R.A., et al., J. Mol. Microb. Biotech., 2012, vol. 22, no. 1, pp. 48–58.
Geukens, N., Frederix, F., Reekmans, G., Lammertyn, E., Van Mellaert, L., Dehaen, W. et al., Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun., 2004, vol. 314, no. 2, pp. 459–467.
Malten, M., Nahrstedt, H., Meinhardt, F., and Jahn, D., Biotechnol. Bioeng., 2005, vol. 91, no. 5, pp. 616–621.
Karamyshev, A.L., Karamysheva, Z.N., Kajava, A.V., Ksenzenko, V.N., and Nesmeyanova, M.A., J. Mol. Biol., 1998, vol. 277, no. 4, pp. 859–870.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
We thank also M.P. Naghshbandi for help in drawing figures.
Funding
The authors would like to acknowledge the financial support of University of Tehran (Iran) for this research under Grant no. 28669/06/11.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest. This article does not contain any studies involving animals or human participants performed by any of the authors.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Maleki, M., Hajihassan, Z. De Novo Designing a Novel Signal Peptide for Secretion of Neurturin to the Periplasmic Space of Escherichia coli. Appl Biochem Microbiol 57 (Suppl 1), S54–S63 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0003683821100057
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S0003683821100057