Abstract
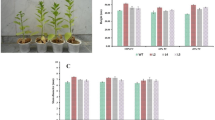
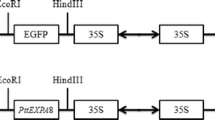
Expansins are non-enzymatic plant proteins breaking hydrogen bonds between cellulose microfibrils and hemicellulose polymer matrix. Each plant has many expansin genes, whose protein products participate in the regulation of plant growth and development mainly by regulating cell expansion. To analyze the effects of elevated expansin expression on the plant organ sizes, we cloned the AtEXPA10 gene from Arabidopsis thaliana and PnEXPA1 gene from Populus nigra. Transgenic tobacco plants expressing the target genes were obtained. The obtained transgenic tobacco plants were shown to have significantly larger leaves and longer stems compared to control plants. The flowers were quite insignificantly larger, but at the same time transgenic plants had more flowers. The microscopic studies showed that the organs of AtEXPA10-carrying plants were larger mainly due to stimulated cell proliferation, whereas the overexpression of the PnEXPA1 gene activated cell expansion.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- BA:
-
benzyladenine
- Hyg:
-
hygromycin
- MS:
-
Murashige and Skoog nutrient medium
References
Sharova, E.I., Expansins: Proteins Involved in Cell Wall Softening during Plant Growth and Morphogenesis, Russ. J. Plant Physiol., 2007, vol. 54, pp. 713–727.
McQueen-Mason, S., Durachko, D.M., and Cosgrove, D.J., Two Endogenous Proteins That Induce Cell Wall Extension in Plants, Plant Cell, 1992, vol. 4, pp. 1425–1433.
Li, Z.-C., Durachko, D.M., and Cosgrove, D.J., An Oat Coleoptile Wall Protein That Induces Wall Extension In Vitro and That Is Antigenically Related to a Similar Protein from Cucumber Hypocotyls, Planta, 1993, vol. 191, pp. 349–356.
Cosgrove, D.J., Bedinger, P., and Durachko, D.M., Group 1 Allergens of Grass Pollen as Cell Wall-Loosening Agents, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 1997, vol. 94, pp. 6559–6564.
Gao, X., Liu, K., and Lu, Y.T., Specific Roles of AtEXPA1 in Plant Growth and Stress Adaptation, Russ. J. Plant Physiol., 2010, vol. 57, pp. 241–246.
Cho, H.T. and Cosgrove, D.J., Altered Expression of Expansin Modulates Leaf Growth and Pedicel Abscission in Arabidopsis thaliana, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 2000, vol. 97, pp. 9783–9788.
Gray-Mitsumune, M., Blomquist, K., McQueen-Mason, S., Teeri, T.T., Sundberg, B., and Mellerowicz, E.J., Ectopic Expression of a Wood-Abundant Expansin PttEXPA1 Promotes Cell Expansion in Primary and Secondary Tissues in Aspen, Plant Biotechnol. J., 2008, vol. 6, pp. 62–72.
Aljanabi, S.M. and Martinez, I., Universal and Rapid Salt-Extraction of High Quality Genomic DNA for PCR-Based Techniques, Nucleic Acids Res., 1997, vol. 25, pp. 4692–4693.
Gallois, P. and Marinho, P., Leaf Disk Transformation Using Agrobacterium tumefaciens-Expression of Heterologous Genes in Tobacco, Methods Molecular Biology, vol. 49, Plant Gene Transfer and Expression Protocols, Jones, H., Ed., Totowa (NJ): Humana Press, 1994, pp. 39–48.
Murashige, T. and Skoog, F., A Revised Medium for Rapid Growth and Bioassays with Tobacco Tissue Cultures, Physiol. Plant., 1962, vol. 15, pp. 473–497.
Jefferson, R.A., Assaying Chimeric Genes in Plants: The GUS Gene Fusion System, Plant Mol. Biol. Rep., 1987, vol. 5, pp. 387–405.
Stomp, A.M., Histochemical Localization of β-Glucuronidase, S.R. Gallagher GUS Protocols: Using the GUS Gene as a Reporter of Gene Expression, San Diego: Academic, 1992, pp. 103–113.
Kuluev, B.R., Knyazev, A.V., Iljassowa, A.A., and Chemeris, A.V., Constitutive Expression of the ARGOS Gene Driven by Dahlia Mosaic Virus Promoter in Tobacco Plants, Russ. J. Plant Physiol., 2011, vol. 58, pp. 507–515.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Original Russian Text © B.R. Kuluev, A.B. Knyazev, Ya.P. Lebedev, A.V. Chemeris, 2012, published in Fiziologiya Rastenii, 2012, Vol. 59, No. 1, pp. 108–117.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kuluev, B.R., Knyazev, A.B., Lebedev, Y.P. et al. Morphological and physiological characteristics of transgenic tobacco plants expressing expansin genes: AtEXP10 from Arabidopsis and PnEXPA1 from poplar. Russ J Plant Physiol 59, 97–104 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1134/S1021443712010128
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S1021443712010128