Abstract
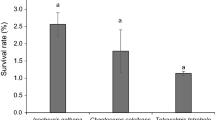
The feeding behavior and growth of post-larval Haliotis diversicolor with initial shell lengths (SL) of approximately 500 μm (Exp. 1–1 and 1–2), 800 μm (Exp. 2), and 1200 μm (Exp. 3) were studied in a laboratory setting while they fed on four species of benthic diatom Achnanthes longipes, Cocconeis sublittoralis, Cylindrotheca closterium, and Navicula ramosissima. Exp. 1–1 and 1–2 revealed no marked differences in post-larval growth rates (mean 24–39 μm SL/day) among the diatom species. However, marked differences in growth rates among the species were revealed in Exp. 2 and 3. Three species, A. longipe, Co. sublittoralis, and Cy. closterium, produced faster growth (Exp. 2 mean 29–51 μm/day, Exp. 3 mean 36–44 μm/day) than N. ramosissima (Exp. 2 mean 18 μm/day, Exp. 3 mean 23 μm/day). Post-larvae fed N. ramosissima had lower digestion efficiency (42.8%) than those fed other diatom species (90.7–100%). Diatom extracellular substances appeared to be principally used from post-settlement to 800 μm SL, and diatom cell contents were required to produce rapid growth of larger post-larvae (>800 μm SL). It is likely that the availability of each diatom for post-larvae was affected by diatom morphology, attachment strength, frustule strength, and post-larval size.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Geiger DL. A total evidence cladistic analysis of the Haliotidae (Gastropoda: Vetigastropoda). PhD Thesis. University of Southern California, Los Angeles, CA. 1999.
Lee YC, Kuo HH, Chen YG. Discrimination and abundance estimation of wild and released abalone Haliotis diversicolor using stable carbon and oxygen isotope analysis in north-eastern Taiwan. Fish, Sci. 2002; 68: 1020–1028.
Kawamura T, Roberts RD, Takami H. A review of the feeding and growth of postlarval abalone. J. Shellfish Res. 1998; 17: 615–625.
Roberts RD, Kawamura T, Nicholson CM. Growth and survival of post-larval abalone (Haliotis iris) in relation to development and diatom diet. J. Shellfish Res. 1999; 18: 243–250.
Kawamura T, Takami H, Saido T. Early life ecology of abalone Haliotis discus hannai in relation to recruitment fluctuations. Fish. Sci. 2002; 68 (Suppl. 1): 230–233.
Takami H. Studies on the feeding, growth and survival in early life stages of an abalone Haliotis discus hannai. PhD Thesis. University of Tokyo, Tokyo, 2002 (in Japanese).
Kawamura T, Saido T, Takami H, Yamashita Y. Dietary value of benthic diatoms for the growth of post-larval abalone Haliotis discus hannai. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 1995; 194: 189–199.
Kawamura T, Roberts RD, Nicholson CM. Factors affecting the food value of diatom strains for post-larval abalone Haliotis iris. Aquaculture 1998; 160: 81–88.
Takami H, Kawamura T. Dietary changes in the abalone, Haliotis discus hannai, and relationship with the development of the digestive organ. JARQ 2003; 37: 89–98.
Takami H, Muraoka D, Kawamura T, Yamashita Y. When is the abalone Haliotis discus hannai Ino 1953 first able to use brown macroalgae? J. Shellfish Res. 2003; 22: 795–800.
Kawamura T, Takami H, Robertss RD, Yamashita Y. Radula development in abalone Haliotis discus hannai from larva to adult in relation to feeding transitions. Fish. Sci. 2001; 67: 596–605.
Takami H, Kawamura T, Yamashita Y. Development of polysaccharide degradation activity in postlarval abalone Haliotis discus hannai. J. Shell fish Res. 1998; 17: 723–727.
Onitsuka T, Kawamura T, Ohashi S, Horii T, Watanabe Y. Morphological changes in the radula of abalone Haliotis diversicolor aquatilis from post-larva to adult. J. Shellfish Res. 2004; 23: 1079–1085.
Roberts RD, Kawamura T, Takami H. Morphological changes in the radula of abalone (Haliotis iris) during postlarval development. J. Shell fish Res. 1999; 18: 637–644.
Okutani T. Marine Mollusks in Japan. Tokai University Press, Tokyo. 2000.
Onitsuka T. Studies on the reproduction and early life ecology of Haliotis diversicolor at nagai in Sagami Bay. PhD Thesis. University of Tokyo, Tokyo. 2006 (in Japanese).
Jørgensen EG. Antibiotic substances from cells and solution of unicellular algae with special reference to some chlorophyll derivatives. Physiol. Plant. 1962; 15: 530–545.
Kawamura T, Hirano R. Seasonal changes in benthic diatom communities colonizing glass slides in Aburatsubo Bay, Japan. Diatom Res. 1992; 7: 227–239.
Kawamura T, Takami H. Analysis of feeding and growth rate of newly metamorphosed abalone Haliotis discus hannai fed on four species of benthic diatom. Fish. Sci. 1995; 61: 357–358.
Takami H, Kawamura T, Yamashita Y. Survival and growth rates of post-larval abalone Haliotis discus hannai fed conspecific trail mucus and/or benthic diatom Cocconeis scutellum var. parva. Aquaculture 1997; 152: 129–138.
Daume S, Brand S, Woelkerling WJ. Effects of post-larval abalone (Haliotis rubra) grazing on the epiphytic diatom assemblage of coralline red algae. Moll. Res. 1997; 18: 119–130.
Lee YH, Vacquier VD. Evolution and systematics in Haliotidae (Mollusca: Gastropoda): inferences from DNA sequences of sperm lysine. Mar. Biol. 1995; 124: 267–278.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Onitsuka, T., Kawamura, T., Ohashi, S. et al. Dietary value of benthic diatoms for post-larval abalone Haliotis diversicolor associated with feeding transitions. Fish Sci 73, 295–302 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1444-2906.2007.01335.x
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1444-2906.2007.01335.x