Summary
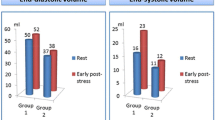
TID is an abnormal finding in stress myocardial perfusion imaging that suggests severe and extensive CAD and signifies a worse prognosis. TID has been reported with exercise and pharmacologic stress testing, planar and SPECT imaging, and Tl-201, Tc-99m, and dual-isotope protocols. Underlying mechanisms include a combination of stress-induced subendocardial hypoperfusion, ischemic systolic dysfunction, and less likely physical LV dilation with severe ischemia. TID appears to represent a significant ischemic burden and, compared with increased pulmonary Tl-201 uptake, suggests less permanent LV dysfunction and more myocardium at risk. Stress-to-rest LV volume ratios of 1.12 (epicardial) and 1.22 (endocardial) have been consistently shown to be highly specific for severe and extensive CAD.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sonnenblick EH, Braunwald E, Williams JF Jr, Glick G. Effects of exercise on myocardial force-velocity relations in intact unanesthetized man: relative roles of changes in heart rate, sympathetic activity, and ventricular dimensions. J Clin Invest 1965;44:2051–62.
Wiener L, Dwyer EM Jr, Cox JW. Left ventricular hemodynamics in exercise-induced angina pectoris. Circulation 1968;38:240–9.
Parker JO, Ledwich JR, West RO, Case RB. Reversible cardiac failure during angina pectrois: hemodynamic effects of atrial pacing in coronary artery disease. Circulation 1969;39:745–57.
Slutsky R, Karliner J, Ricci D, Schuler G, Pfisterer M, Peterson K, Ashburn W. Response of left ventricular volume to exercise in man assessed by radionuclide equilibrium angiography. Circulation 1997;60:565–71.
Stolzenberg J. Dilatation of left ventricular cavity on stress thallium scan as an indicator of ischemic disease. Clin Nucl Med 1980;5:289–91.
Iskandrian AS, Heo J, Nguyen T, Lyons E, Paugh E. Left ventricular dilatation and pulmonary thallium uptake after single-photon emission computer tomography using thallium-201 during adenosine-induced coronary hyperemia. Am J Cardiol 1990;66:807–11.
Takeishi Y, Tono-oka I, Ikeda K, Komatani A, Tsuiki K, Yasui S. Dilatation of the left ventricular cavity on dipyridamole thallium-201 imaging: a new marker of triple-vessel disease. Am Heart J 1991;121:466–75.
Marcassa C, Galli M, Baroffio C, Campini R, Giannuzzi P. Transient left ventricular dilation at quantitative stress-rest sestamibi tomography: clinical, electrocardiographic, and angiographic correlates. J Nucl Cardiol 1999;6:397–405.
Van Tosh A, Hecht S, Berger M, Roberti R, Luna E, Horowitz SF. Exercise echocardiographic correlates of transient dilatation of the left ventricular cavity on exercise thallium-201 SPECT imaging. Chest 1994;106:1725–9.
Bestetti A, Di Leo C, Alessi A, Triulzi A, Tagliabue L, Tarolo GL. Post-stress end-systolic left ventricular dilation: a marker of endocardial post-ischemic stunning. Nucl Med Commun 2001; 22:685–93.
Weiss AT, Berman DS, Lew AS, Nielsen J, Potkin B, Swan HJ, et al. Transient ischemic dilation of the left ventricle on stress thallium-201 scintigraphy: a marker of severe and extensive coronary artery disease. J Am Coll Cardiol 1987;9:752–9.
Chouraqui P, Rodrigues EA, Berman DS, Maddahi J. Significance of dipyridamole-induced transient dilation of the left ventricle during thallium-201 scintigraphy in suspected coronary artery disease. Am J Cardiol 1990;66:689–94.
Kurata C, Wakabayashi Y, Shouda S, Mikami T, Tawarahara K. Quantification of left ventricular size on exercise thallium-201 single-photon emission tomography. Eur J Nucl Med 1996;23: 762–7.
Hansen CL, Sangrigoli R, Nkadi E, Kramer M. Comparison of pulmonary uptake with transient cavity dilation after exercise thallium-201 perfusion imaging. J Am Coll Cardiol 1999;33: 1323–7.
Aksut SV, Mallavarapu C, Russell J, Heo J, Iskandrian AS. Implications of increased lung thallium uptake during exercise single photon emission computed tomography imaging. Am Heart J 1995;130:367–73.
Bingham JB, McKusick KA, Strauss HW, Boucher CA, Pohost GM. Influence of coronary artery disease on pulmonary uptake of thallium-201. Am J Cardiol 1980;46:821–6.
Gill JB, Ruddy TD, Newell JB, Finkelstein DM, Strauss HW, Boucher CA. Prognostic importance of thallium uptake by the lungs during exercise in coronary artery disease. N Engl J Med 1987;317:1486–9.
Jain D, Thompson B, Wackers FJ, Zaret BL. Relevance of increased lung thallium uptake on stress imaging in patients with unstable angina and non-Q wave myocardial infarction: results of the Thrombolysis in Myocardial Infarction (TIMI)-IIIB Study. J Am Coll Cardiol 1997;30:421–9.
Villanueva FS, Kaul S, Smith WH, Watson DD, Varma SK, Beller GA. Prevalence and correlates of increased lung/heart ratio of thallium-201 during dipyridamole stress imaging for suspected coronary artery disease. Am J Cardiol 1990;66: 1324–8.
Takeishi Y, Chiba J, Abe S, Komatani A, Takahashi K, Tomoike H. Noninvasive identification of left main and three-vessel coronary artery disease by thallium-201 single photon emission computed tomography during adenosine infusion. Ann Nucl Med 1994;8:1–7.
Mazzanti M, Germano G, Kiat H, Kavanagh PB, Alexanderson E, Friedman JD, et al. Identification of severe and extensive coronary artery disease by automatic measurement of transient ischemic dilation of the left ventricle in dual-isotope myocardial perfusion SPECT. J Am Coll Cardiol 1996;27:1612–20.
McClellan JR, Travin MI, Herman SD, Baron JI, Golub RJ, Gallagher JJ, et al. Prognostic importance of scintigraphic left ventricular cavity dilation during intravenous dipyridamole technetium-99m sestamibi myocardial tomographic imaging in predicting coronary events. Am J Cardiol 1997;79:600–5.
Krawczynska EG, Weintraub WS, Garcia EV, Folks RD, Jones ME, Alazraki NP. Left ventricular dilatation and multivessel coronary artery disease on thallium-201 SPECT are important prognostic indicators in patients with large defects in the left anterior descending distribution. Am J Cardiol 1994;74:1233–9.
Sugihara H, Shiga K, Umamoto I, Harada Y, Katahira T, Nakagawa T, et al. Assessment of transient dilation of the left ventricular cavity in patients with hypertrophic cardiomyopathy by exercise thallium-201 scintigraphy [in Japanese]. Kaku Igaku 1990;27:1281–9.
Robinson VJ, Corley JH, Marks DS, Eberhardt LW, Eubig C, Burke GJ, et al. Causes of transient dilatation of the left ventricle during myocardial perfusion imaging. AJR Am J Roentgenol 2000;174:1349–52.
Fitzgerald J, Danias PG. Effect of motion on cardiac SPECT imaging: recognition and motion correction. J Nucl Cardiol 2001;8:701–6.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
McLaughlin, M.G., Danias, P.G. Transient ischemic dilation: A powerful diagnostic and prognostic finding of stress myocardial perfusion imaging. J Nucl Cardiol 9, 663–667 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1067/mnc.2002.124979
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1067/mnc.2002.124979