Abstract
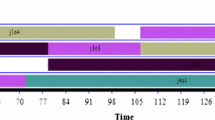
In this paper, a cost-based job shop problem (JIT-JSP) is proposed to model the multi-order processing procedure in a just-in-time (JIT) environment. The objective of JIT-JSP is to minimize three costs: work-in-process holding cost of half-finished orders, inventory holding cost of finished orders and backorder cost of unfulfilled orders. A modified tabu search (MTS) method is developed to improve the schedule quality by searching the neighbourhood of a feasible schedule iteratively. The MTS method is comprised of three components that help to ensure a more effective searching procedure: neighbourhood structure, memory structure and filter structure. Computational results show that the MTS method significantly improves the initial schedule generated by an arbitrarily selected dispatching rule.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adams J, Balas E and Zawack D (1988). The shifting bottleneck procedure for job shop scheduling . Mngt Sci 34: 391–401.
Balas E (1969). Machine scheduling via disjunctive graphs: An implicit enumeration algorithm . Opns Res 17: 941–957.
Beasley J (1990). OR-library: Distributing test problems by electronic mail. J Opl Res Soc 41: 1069–1072. http://people.brunel.ac.uk/~mastjjb/jeb/info.html.
Blackstone JHJ, Phillips DT and Hogg GL (1982). A state-of-the-art survey of dispatching rules for manufacturing job shop operations . Int J Prod Res 20: 27–45.
De Bontridder K (2005). Minimizing total weighted tardiness in a generalized job shop . J Scheduling 8: 479–496.
Eilon S and Chowdhury IG (1976). Due dates in job shop scheduling . Int J Prod Res 14: 223–237.
Gen M, Tsujimura Y and Kubota E (1994). Solving job shop scheduling problem by genetic algorithm . In: Gielen SCAM and Kappen HJ (eds). Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Systems, Man and Cybernetics Vol. 2. IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, pp. 1577–1582.
Glover F (1989). Tabu search-part i . ORSA J Comput 1: 193–200.
Kan AHKR (1976). Machine Scheduling Problems: Classification, Complexity and Computations . Martinus Nijhoff: Dordrecht.
Logendran R and Sonthinen A (1997). A tabu search-based approach for scheduling job-shop type flexible manufacturing systems . J Opl Res Soc 48: 264–277.
Muth J and Thompson G (1963). Industrial Scheduling . Prentice-Hall: Englewood Cliffs, NJ.
Natarajan K, Mohanasundaram K, Babu BS, Suresh S, Raj KAAD and Rajendran C (2007). Performance evaluation of priority dispatching rules in multi-level assembly job shops with jobs having weights for flowtime and tardiness . Int J Adv Manuf Technol 31: 751–761.
Nowicki E and Smutnicki C (1996). A fast taboo search algorithm for the job shop problem . Mngt Sci 42: 797–813.
Nowicki E and Smutnicki C (2005). An advanced tabu search algorithm for the job shop problem . J Scheduling 8: 145–159.
Pinedo M (1995). Scheduling Theory, Algorithms and Systems . Prentice-Hall: Englewood Cliffs, NJ.
Pinedo M and Singer M (1999). A shifting bottleneck heuristic for minimizing the total weighted tardiness in a job shop . Nav Res Logist 46: 1–17.
Scrich C, Armentano V and Laguna M (2004). Tardiness minimization in a flexible job shop: A tabu search approach . J Intell Manuf 15: 103–115.
Taillard ED (1994). Parallel taboo search techniques for the job shop scheduling problem . ORSA J Comput 6: 108–117.
Thiagarajan S and Rajendran C (2003). Scheduling in dynamic assembly job shops with jobs having different holding and tardiness costs . Int J Prod Res 41: 4453–4483.
Thiagarajan S and Rajendran C (2005). Scheduling in dynamic assembly job-shops to minimize the sum of weighted earliness, weighted tardiness and weighted flowtime of jobs . Comput Ind Eng 49: 463–503.
Van Laarhoven PJM, Aarts EHL and Lenstra JK (1992). Job shop scheduling by simulated annealing . Opns Res 40: 113–125.
Vepsalainen APJ and Morton TE (1987). Priority rules for job shops with weighted tardiness costs . Mngt Sci 33: 1035–1047.
Watson JP, Beck JC, Howe AE and Whitley LD (2003). Problem difficulty for tabu search in job shop scheduling . Artif Intell 143: 189–217.
Watson JP, Howe AE and Whitley LD (2006). Deconstructing Nowicki and Smutnicki's i-TSAB tabu search algorithm for the job-shop scheduling problem . Comput Opns Res 33: 2623–2644.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhu, Z., Ng, K. & Ong, H. A modified tabu search algorithm for cost-based job shop problem. J Oper Res Soc 61, 611–619 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1057/jors.2009.9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1057/jors.2009.9