Abstract
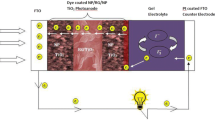
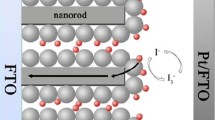
Herein, we report dye-sensitized solar cells (DSCs) based on conventional nanocrystalline TiO2 photoanodes decorated with one-dimensional (1D) CNT–TiO2 core–shell structures (CTH). The core–shell nanotubes are synthesized by a simple sol–gel template-assisted method via in situ deposition of TiO2 on the surface of non-covalently functionalized CNTs. The core–shell nanotubes are well characterized by various techniques. Field emission scanning electron microscopy (FESEM) and transmission electron microscopy (TEM) images show that formation of the TiO2 shell on the surface of the CNT core follows a layer or Frank–van der Merwe growth mode, resulting in a highly uniform interface with excellent charge transfer from the TiO2 conduction band into the CNTs. The thickness and crystal structure of the TiO2 shell can be tailored by controlling the processing parameters. X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) and Raman spectroscopy verify that CNTs have no surface defects and are well preserved using the employed method and the subsequent heat treatment in air, respectively. UV-vis spectroscopy and photoluminescence spectroscopy reveal an extension to visible regions with an increase in overall intensity and a significant reduction in charge recombination due to a shift of the Fermi level toward positive potentials. We find an increase by up to 37% in the DSC device’s power conversion efficiency by incorporating the CNT–TiO2 core–shell nanotubes into the nanoparticle TiO2 photoanode due to the charge recombination reduction and electron injection enhancement.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
B. ORegan and M. Grätzel, A low-cost, high-efficiency solar cell based on dye-sensitized colloidal TiO2 films, Nature, 1991, 353, 737–740.
H. Asgari Moghaddam, S. Jafari and M. R. Mohammadi, Enhanced efficiency of over 10% in dye-sensitized solar cells through C and N single- and co-doped TiO2 singlelayer electrode, New J. Chem., 2017, 41, 9453–9460.
Md. K. Nazeeruddin, E. Baranoff and M. Gratzel, Dye-sensitized solar cells: A brief overview, Sol. Energy, 2011, 85, 1172–1178.
A. M. Bakhshayesh and M. R. Mohammadi, Development of nanostructured porous TiO2 thick film with uniform spherical particles by a new polymeric gel process for dyesensitized solar cell applications, Electrochim. Acta, 2013, 89, 90–97.
L. M. Peter, Characterization and modeling of dye-sensitized solar cells, J. Phys. Chem. C, 2007, 111, 6601–6612.
M. Mojaddami, M. R. Mohammadi and H. R. Madaah Hosseini, Improved efficiency of dye-sensitized solar cells based on a single layer deposition of skein-like TiO2 nanotubes, J. Am. Ceram. Soc., 2014, 97, 2873–2879.
S. S. Mali, S. K. Desai, D. S. Dalavi, C. A. Betty, P. N. Bhosale and P. S. Patil, CdS-sensitized TiO2 nanocorals: hydrothermal synthesis, characterization, application, Photochem. Photobiol. Sci., 2011, 10, 1652–1658.
A. M. Bakhshayesh and M. R. Mohammadi, The improvement of electron transport rate of TiO2 dye-sensitized solar cells using mixed nanostructures: The influences of nanowire to nanoparticle weight ratio and phase composition, Ceram. Int., 2013, 39, 7343–7353.
M. Y. Yen, M. C. Hsiao, S. H. Liao, P. Liu, H. M. Tsai, C. M. Ma, N. W. Pu and M. D. Ger, Preparation of graphene/multi-walled carbon nanotube hybrid and its use as photoanodes of dye-sensitized solar cells, Carbon, 2011, 49, 3597–3606.
E. Nouri, Y. L. Wang, Q. Chen, J. J. Xu, G. Paterakis, V. Dracopoulos, Z. X. Xu, D. Tasis, M. R. Mohammadi and P. Lianos, Introduction of Graphene Oxide as Buffer Layer in Perovskite Solar Cells and the Promotion of Soluble n-Butyl-substituted Copper Phthalocyanine as Efficient Hole Transporting Material, Electrochim. Acta, 2017, 233, 36–43.
Q. Chang, Z. Ma, Y. Lin, Y. Xiao, L. Huang, S. Xu and W. Shia, In situ grown hybrid nanocarbon composite for dye sensitized solar cells, Electrochim. Acta, 2015, 166, 134–141.
N. T. Hieu, S. J. Baik, O. H. Chung and J. S. Park, Fabrication and characterization of electrospun carbon nanotubes/titanium dioxide nanofibers used in anodes of dye-sensitized solar cells, Synth. Met., 2014, 193, 125–131.
K. Woan, G. Pyrgiotakis and W. Sigmund, Photocatalytic Carbon-Nanotube–TiO2 Composites, Adv. Mater., 2009, 21, 2233–2239.
M. R. Hoffmann, S. T. Martin, W. Y. Choi and D. W. Bahnemann, Environmental Applications of Semiconductor Photocatalysis, Chem. Preview, 1995, 95, 69–96.
W. D. Wang, P. Serp, P. Kalck and J. L. Faria, Visible light photodegradation of phenol on MWNT-TiO2 composite catalysts prepared by a modified sol–gel method, J. Mol. Catal. A: Chem., 2005, 235, 194–199.
J. Yu, J. Fan and B. Cheng, Dye-sensitized solar cells based on anatase TiO2 hollow spheres/carbon nanotube composite films, J. Power Sources, 2011, 196, 7891–7898.
J. Chen, B. Li, J. Zheng, J. Zhao and Z. Zhu, Role of Carbon Nanotubes in Dye-Sensitized TiO2-Based Solar Cells, J. Phys. Chem. C, 2012, 1162, 814848–814856.
M. Barberio, D. R. Grosso, A. Imbrogno and F. Xu, Preparation and photovoltaic properties of layered TiO2/carbon nanotube/TiO2 photoanodes for dye-sensitized solar cells, Superlattices Microstruct., 2016, 91, 158–164.
S. Sun, L. Gao and Y. Liu, Optimization of the cutting process of multi-wall carbon nanotubes for enhanced dyesensitized solar cells, Thin Solid Films, 2011, 519, 2273–2279.
K.-M. Lee, C.-W. Hu, H.-W. Chen and K.-C. Ho, Incorporating carbon nanotube in a low-temperature fabrication process for dye-sensitized TiO2 solar cells, Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells, 2008, 92, 1628–1633.
R. Verdejo, S. Lamoriniere, B. Cottam, A. Bismarck and M. Shaffer, Removal of oxidation debris from multi-walled carbon nanotubes, Chem. Commun., 2007, 5, 513–515.
Z. Luo, A. Oki, L. Carson, L. Adams, G. Neelgund, N. Soboyejo, G. Regisford, M. Stewart, K. Hibbert, G. Beharie, C. K. Brown and P. Traisawatwong, Thermal stability of functionalized carbon nanotubes studied by, in situ transmission electron microscopy, Chem. Phys. Lett., 2011, 513, 88–93.
G. De Filpo, F. P. Nicoletta, L. Ciliberti, P. Formoso and G. Chidichimo, Non-covalent functionalisation of single wall carbon nanotubes for efficient dye-sensitised solar cells, J. Power Sources, 2015, 274, 274–279.
M. Barberio, V. Pingitore, P. Barone, M. Davoli, F. Stranges, F. Xua and A. Bonanno, Synthesis of carbon nanotube/TiO2 composites by titanium evaporation in ultra high vacuum ambient, Microelectron. Eng., 2013, 108, 213–217.
K. M. Lee, C. W. Hu, H. W. Chen and K. C. Ho, Incorporating carbon nanotube in a low-temperature fabrication process for dye-sensitized TiO2 solar cells, Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells, 2008, 92, 1628–1633.
N. Massihi, M. R. Mohammadi, A. M. Bakhshayesh and M. Abdi-Jalebi, Controlling electron injection and electron transport of dye-sensitized solar cells aided by incorporating CNTs into a Cr-doped TiO2 photoanode, Electrochim. Acta, 2013, 111, 921–929.
A. M. Bakhshayesh, M. R. Mohammadi, N. Massihi and M. H. Akhlaghi, Improved electron transportation of dyesensitized solar cells using uniform mixed CNTs–TiO2 photoanode prepared by a new polymeric gel process, J. Nanopart. Res., 2013, 15, 1961–1970.
M. Krissanasaeranee, S. Wongkasemjit, A. K. Cheetham and D. Eder, Complex carbon nanotube-inorganic hybrid materials as next-generation photocatalysts, Chem. Phys. Lett., 2010, 496, 133–138.
D. Eder and A. H. Windle, Morphology control of CNT-TiO2 hybrid materials and rutile nanotubes, J. Mater. Chem., 2008, 18, 2036–2043.
M. R. Mohammadi, D. J. Fray and A. Mohammadi, Sol-Gel Nanostructured Titanium Dioxide: Controlling the Crystal Structure, Crystallite Size, Phase Transformation, Packing and Ordering, Microporous Mesoporous Mater., 2008, 112, 392–402.
M. R. Mohammadi, Method for preparing titania pastes for use in dye-sensitized solar cells, US Patent 8906711, 2014.
E. T. Thostensona, Z. Renb and T. W. Choua, Advances in the science and technology of carbon nanotubes and their composites: a review, Compos. Sci. Technol., 2001, 61, 1899–1912.
V. Augugliaro, V. Loddo, M. José López-Muñoz, C. Márquez-Álvarez, G. Palmisano, L. Palmisano and S. Yurdakal, Home-prepared anatase, rutile, and brookite TiO2 for selective photocatalytic oxidation of 4-methoxybenzyl alcohol in water: reactivity and ATR-FTIR study, Photochem. Photobiol. Sci., 2009, 8, 663–669.
T. S. Natarajan, J. Y. Lee, H. C. Bajaj, W.-K. Jo and R. J. Tayade, Synthesis of multiwall carbon nanotubes/TiO2 nanotube composites with enhanced photocatalytic decomposition efficiency, Catal. Today, 2017, 282, 13–23.
M. R. Mohammadi and D. J. Fray, Mesoporous and nanocrystalline sol-gel derived NiTiO3 at the low temperature: Controlling the structure, size and surface area by Ni:Ti molar ratio, Solid State Sci., 2010, 12, 1629–1640.
R. Saito, G. Dresselhaus and M. S. Dresselhaus, Physical properties of carbon nanotubes, Imperial College Press, London, 1998.
C. Y. Xu, P. X. Zhang and L. Yan, Blue shift of Raman peak from coated TiO2 nanoparticles, J. Raman Spectrosc., 2001, 32, 862–865.
S. Cui, R. Canet, A. Derre, M. Couzi and P. Delhaes, Characterization of multiwall carbon nanotubes and influence of surfactant in the nanocomposite processing, Carbon, 2003, 41, 797–809.
M. Barberio, P. Barone, A. Imbrogno, A. S. Ruffolo, M. La Russa, N. Arcuri and F. Xu, Study of band gap of carbon nanotube-titanium dioxide heterostructures, J. Chem. Chem. Eng., 2014, 8, 36–41.
Y. Koo, R. Malik, N. Alvarez, V. N. Shanov, M. Schulz, J. Sankar and Y. Yun, Free-standing carbon nanotube–titania photoactive sheets, J. Colloid Interface Sci., 2015, 448, 148–155.
Y. Yu, J. C. Yu, C. Y. Chan, Y. K. Che, J. C. Zhao, L. Ding, W. K. Ge and P. K. Wong, Enhancement of adsorption and photocatalytic activity of TiO2 by using carbon nanotubes for the treatment of azo dye, Appl. Catal., B, 2005, 61, 1–11.
E. Nouri, J. V. S. Krishna, C. V. Kumarc, V. Dracopoulos, L. Giribabu, M. R. Mohammadi and P. Lianos, Soluble tetratriphenylamine Zn phthalocyanine as Hole Transporting Material for Perovskite Solar Cells, Electrochim. Acta, 2016, 222, 875–880.
E. Nouri, M. R. Mohammadi and P. Lianos, Impact of preparation method of TiO2-RGO nanocomposite photo-anodes on the performance of dye-sensitized solar cells, Electrochim. Acta, 2016, 219, 38–48.
H. Zhou, C. Zhang, X. Wang, H. Li and Z. Du, Fabrication of TiO2-coated magnetic nanoparticles on functionalized multi-walled carbon nanotubes and their photocatalytic activity, Synth. Met., 2011, 161, 2199–2205.
P. Du, L. Song, J. Xiong, N. Li, L. Wang, Z. Xi, N. Wang, L. Gao and H. Zhu, Dye-sensitized solar cells based on anatase TiO2/multi-walled carbon nanotubes composite nanofibers photoanode, Electrochim. Acta, 2013, 87, 651–656.
V. B. Koli, A. G. Dhodamani, S. D. Delekara and S. H. Pawara, In situ sol-gel synthesis of anatase TiO2-MWCNTs nanocomposites and their photocatalytic applications, J. Photochem. Photobiol., A, 2017, 333, 40–48.
Y. Yu, J. C. Yu, J. G. Yu, Y. C. Kwok, Y. K. Che, J. C. Zhao, L. Ding, W. K. Ge and P. K. Wong, Enhancement of photocatalytic activity of mesoporous TiO2 by using carbon nanotubes, Appl. Catal., A, 2005, 289, 186–196.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ghartavol, H.M., Mohammadi, M.R., Afshar, A. et al. On the assessment of incorporation of CNT–TiO2 core–shell structures into nanoparticle TiO2 photoanodes in dye-sensitized solar cells. Photochem Photobiol Sci 18, 1840–1850 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1039/c9pp00100j
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1039/c9pp00100j