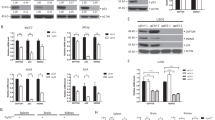
Abstract
Although Kruppel-like factor 5 (KLF5) is a transcription factor that has been implicated in pathways critical to carcinogenesis, controversy persists as to whether it functions as a tumor suppressor or as an oncogene. Here, we describe a novel role for KLF5 in a p53-independent apoptotic pathway. Using RNA-interference technology, we show that cells deficient in KLF5 have increased sensitivity to DNA damage, regardless of p53 status. Both p53 and p53-dependent factors are unaffected by KLF5 depletion. Instead, the apoptotic phenotype consequent to damage is associated with reduced bad phosphorylation, and downregulation of Pim1. Consistently, transfection of wild-type Pim1 is sufficient to rescue this phenotype. Previous data have shown a number of putative Sp1-binding consensus sequences on the Pim1 promoter. Remarkably, chromatin immunoprecipitation studies show that KLF5 binds to the Pim1 promoter, and that binding increases soon after damage. These results identify a novel, p53-independent apoptotic pathway through which KLF5 functions in response to DNA damage. Therapeutic deregulation of this pathway could be used to modulate chemosensitivity.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aho TL, Sandholm J, Peltola KJ, Mankonen HP, Lilly M, Koskinen PJ . (2004). Pim-1 kinase promotes inactivation of the pro-apoptotic Bad protein by phosphorylating it on the Ser112 gatekeeper site. FEBS Lett 571: 43–49.
Amaravadi R, Thompson CB . (2005). The survival kinases Akt and Pim as potential pharmacological targets. J Clin Invest 115: 2618–2624.
Bateman NW, Tan D, Pestell RG, Black JD, Black AR . (2004). Intestinal tumor progression is associated with altered function of KLF5. J Biol Chem 279: 12093–12101.
Bergmann A . (2002). Survival signaling goes BAD. Dev Cell 3: 607–608.
Black AR, Black JD, Azizkhan-Clifford J . (2001). Sp1 and Kruppel-like factor family of transcription factors in cell growth regulation and cancer. J Cell Physiol 188: 143–160.
Chao DT, Korsmeyer SJ . (1998). BCL-2 family: regulators of cell death. Annu Rev Immunol 16: 395–419.
Chen C, Benjamin MS, Sun X, Otto KB, Guo P, Dong XY et al. (2006). KLF5 promotes cell proliferation and tumorigenesis through gene regulation in the TSU-Pr1 human bladder cancer cell line. Int J Cancer 118: 1346–1355.
Chen C, Bhalala HV, Qiao H, Dong JT . (2002). A possible tumor suppressor role of the KLF5 transcription factor in human breast cancer. Oncogene 21: 6567–6572.
Chen C, Bhalala HV, Vessella RL, Dong JT . (2003). KLF5 is frequently deleted and down-regulated but rarely mutated in prostate cancer. Prostate 55: 81–88.
Chen C, Sun X, Ran Q, Wilkinson KD, Murphy TJ, Simons JW et al. (2005a). Ubiquitin-proteasome degradation of KLF5 transcription factor in cancer and untransformed epithelial cells. Oncogene 24: 3319–3327.
Chen CN, Lin JJ, Chen JJ, Lee PH, Yang CY, Kuo ML et al. (2005b). Gene expression profile predicts patient survival of gastric cancer after surgical resection. J Clin Oncol 23: 7286–7295.
Dong JT . (2001). Chromosomal deletions and tumor suppressor genes in prostate cancer. Cancer Metastasis Rev 20: 173–193.
Felsher DW . (2003). Cancer revoked: oncogenes as therapeutic targets. Nat Rev Cancer 3: 375–380.
Ghaleb AM, Nandan MO, Chanchevalap S, Dalton WB, Hisamuddin IM, Yang VW . (2005). Kruppel-like factors 4 and 5: the yin and yang regulators of cellular proliferation. Cell Res 15: 92–96.
Hammerman PS, Fox CJ, Birnbaum MJ, Thompson CB . (2005). Pim and Akt oncogenes are independent regulators of hematopoietic cell growth and survival. Blood 105: 4477–4483.
Iyer NG, Chin SF, Ozdag H, Daigo Y, Hu DE, Cariati M et al. (2004). p300 regulates p53-dependent apoptosis after DNA damage in colorectal cancer cells by modulation of PUMA/p21 levels. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 101: 7386–7391.
Kaczynski J, Cook T, Urrutia R . (2003). Sp1- and Kruppel-like transcription factors. Genome Biol 4: 206.
Kho PS, Wang Z, Zhuang L, Li Y, Chew JL, Ng HH et al. (2004). p53-regulated transcriptional program associated with genotoxic stress-induced apoptosis. J Biol Chem 279: 21183–21192.
Macdonald A, Campbell DG, Toth R, McLauchlan H, Hastie CJ, Arthur JS . (2006). Pim kinases phosphorylate multiple sites on Bad and promote 14-3-3 binding and dissociation from Bcl-XL. BMC Cell Biol 7: 1.
Meeker TC, Loeb J, Ayres M, Sellers W . (1990). The human Pim-1 gene is selectively transcribed in different hemato-lymphoid cell lines in spite of a G + C-rich housekeeping promoter. Mol Cell Biol 10: 1680–1688.
Mitsiades CS, Mitsiades N, Koutsilieris M . (2004). The Akt pathway: molecular targets for anti-cancer drug development. Curr Cancer Drug Targets 4: 235–256.
Nagai R, Shindo T, Manabe I, Suzuki T, Kurabayashi M . (2003). KLF5/BTEB2, a Kruppel-like zinc-finger type transcription factor, mediates both smooth muscle cell activation and cardiac hypertrophy. Adv Exp Med Biol 538: 57–65. Discussion 66.
Nandan MO, Yoon HS, Zhao W, Ouko LA, Chanchevalap S, Yang VW . (2004). Kruppel-like factor 5 mediates the transforming activity of oncogenic H-Ras. Oncogene 23: 3404–3413.
Polyak K, Waldman T, He TC, Kinzler KW, Vogelstein B . (1996). Genetic determinants of p53-induced apoptosis and growth arrest. Genes Dev 10: 1945–1952.
Rainio EM, Ahlfors H, Carter KL, Ruuska M, Matikainen S, Kieff E et al. (2005). Pim kinases are upregulated during Epstein-Barr virus infection and enhance EBNA2 activity. Virology 333: 201–206.
Ruvolo PP, Deng X, May WS . (2001). Phosphorylation of Bcl2 and regulation of apoptosis. Leukemia 15: 515–522.
Safe S, Abdelrahim M . (2005). Sp transcription factor family and its role in cancer. Eur J Cancer 41: 2438–2448.
Seoane J, Le HV, Massague J . (2002). Myc suppression of the p21(Cip1) Cdk inhibitor influences the outcome of the p53 response to DNA damage. Nature 419: 729–734.
Shi H, Zhang Z, Wang X, Liu S, Teng CT . (1999). Isolation and characterization of a gene encoding human Kruppel-like factor 5 (IKLF): binding to the CAAT/GT box of the mouse lactoferrin gene promoter. Nucleic Acids Res 27: 4807–4815.
Sun R, Chen X, Yang VW . (2001). Intestinal-enriched Kruppel-like factor (Kruppel-like factor 5) is a positive regulator of cellular proliferation. J Biol Chem 276: 6897–6900.
Suzuki T, Aizawa K, Matsumura T, Nagai R . (2005). Vascular implications of the Kruppel-like family of transcription factors. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 25: 1135–1141.
Vousden KH, Lu X . (2002). Live or let die: the cell's response to p53. Nat Rev Cancer 2: 594–604.
Yang Y, Goldstein BG, Chao HH, Katz JP . (2005). KLF4 and KLF5 regulate proliferation, apoptosis and invasion in esophageal cancer cells. Cancer Biol Ther 4: 1216–1221.
Zhao Y, Tan J, Zhuang L, Jiang X, Liu ET, Yu Q . (2005). Inhibitors of histone deacetylases target the Rb-E2F1 pathway for apoptosis induction through activation of proapoptotic protein Bim. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102: 16090–16095.
Acknowledgements
We thank Dr B Vogelstein and P Koskinen for kindly providing reagents, and Drs M van der Heijden and A Thiagarajan for critically evaluating the manuscript. This project was funded by the Cancer Research and Education Fund from the National Cancer Centre, Singapore and through a Singhealth Foundation grant.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on the Oncogene web site (http://www.nature.com/onc).
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhao, Y., Hamza, M., Leong, H. et al. Kruppel-like factor 5 modulates p53-independent apoptosis through Pim1 survival kinase in cancer cells. Oncogene 27, 1–8 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1210625
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1210625
- Springer Nature Limited
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
KLF5 and p53 comprise an incoherent feed-forward loop directing cell-fate decisions following stress
Cell Death & Disease (2023)
-
KLF5 functions in proliferation, differentiation, and apoptosis of chicken satellite cells
3 Biotech (2019)
-
GNA13 expression promotes drug resistance and tumor-initiating phenotypes in squamous cell cancers
Oncogene (2018)
-
PIM-1 mRNA expression is a potential prognostic biomarker in acute myeloid leukemia
Journal of Translational Medicine (2017)
-
Long noncoding RNA EGFR-AS1 mediates epidermal growth factor receptor addiction and modulates treatment response in squamous cell carcinoma
Nature Medicine (2017)