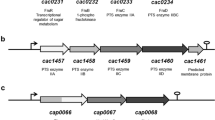
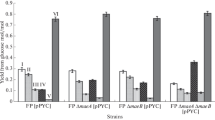
The utilization of maltose by Clostridium acetobutylicum ATCC 824 was investigated. Glucose was used preferentially to maltose, when both substrates were present in the medium. Maltose phosphoenolpyruvate (PEP)-dependent phosphotransferase system (PTS) activity was detected in extracts prepared from cultures grown on maltose, but not glucose or sucrose, as the sole carbon source. Extract fractionation and PTS reconstitution experiments revealed that the specificity for maltose is contained entirely within the membrane in this organism. A putative gene system for the maltose PTS was identified (from the C. acetobutylicum ATCC 824 genome sequence), encoding an enzyme IIMal and a maltose 6-phosphate hydrolase.
Journal of Industrial Microbiology & Biotechnology (2001) 27, 298–306.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received 12 September 2000/ Accepted in revised form 30 November 2000
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tangney, M., Winters, G. & Mitchell, W. Characterization of a maltose transport system in Clostridium acetobutylicum ATCC 824. J Ind Microbiol Biotech 27, 298–306 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.jim.7000125
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.jim.7000125