Thermomonospora curvata
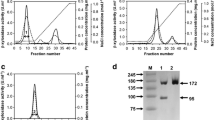
produced a thermostable β-xylosidase during growth on birch xylan. The enzyme, extracted by sonication of early stationary phase mycelia, was purified by isoelectric focusing and size exclusion HPLC. The isoelectric point was pH 4.8. The molecular weight was estimated to be 102 000 by size exclusion HPLC and 112 000 by SDS-PAGE. Maximal activity occurred at pH 6–7 and 60–68°C. K m values for xylobiose and p-nitrophenyl-β -D-xylopyranoside were 4.0 M and 0.6 M respectively. The enzyme was sensitive to low levels of Hg2+ (50% inhibition at 0.2 μM), but was stimulated by Co2+ and Pb2+. Addition of the xylosidase to a xylanase reaction mixture increased the liberation of xylose equivalents from xylan and decreased the proportion of xylobiose in the hydrolysate.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received 14 April 1997/ Accepted in revised form 21 October 1997
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Stutzenberger, F., Bodine, A. Thermostable β-xylosidase from Thermomonospora curvata . J Ind Microbiol Biotech 20, 55–60 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.jim.2900479
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.jim.2900479