Abstract
The widespread evolution of glyphosate-resistant (GR) Bassia scoparia in the U.S. Great Plains poses a serious threat to the long-term sustainability of GR sugar beet. Glyphosate resistance in B. scoparia is due to an increase in the EPSPS (5-enolpyruvyl-shikimate-3-phosphate) gene copy number. The variation in EPSPS gene copies among individuals from within a single GR B. scoparia population indicated a differential response to glyphosate selection. With the continued use of glyphosate in GR sugar beet, the effect of increasing glyphosate rates (applied as single or sequential applications) on the fitness of GR B. scoparia individuals with variable EPSPS gene copies was tested under field conditions. The variation in EPSPS gene copy number and total glyphosate rate (single or sequential applications) did not influence any of the reproductive traits of GR B. scoparia, except seed production. Sequential applications of glyphosate with a total rate of 2214 g ae ha−1 or higher prevented seed production in B. scoparia plants with 2–4 (low levels of resistance) and 5–6 (moderate levels of resistance) EPSPS gene copies. Timely sequential applications of glyphosate (full recommended rates) can potentially slow down the evolution of GR B. scoparia with low to moderate levels of resistance (2–6 EPSPS gene copies), but any survivors (highly-resistant individuals with ≥ 8 EPSPS gene copies) need to be mechanically removed before flowering from GR sugar beet fields. This research warrants the need to adopt ecologically based, multi-tactic strategies to reduce exposure of B. scoparia to glyphosate in GR sugar beet.
Similar content being viewed by others
Introduction
Kochia [Bassia scoparia (L.) A. J. Scott] is one of the most troublesome summer annual broadleaf weed species in croplands and noncroplands across North American Great Plains1. B. scoparia possesses several unique biological attributes, including early and extended period of emergence, low seed persistence, aggressive growth, and tolerance to various biotic and abiotic stresses, prolific seed production, and tumble mechanism of seed dispersal1,2,3. B. scoparia is a monoecious plant species with a protogynous flowering that manifests a high outcrossing and pollen-mediated gene flow within and among field populations4,5. Consequently, B. scoparia is a genetically diverse weed species, with a high tendency to evolve herbicide resistance5,6.
Bassia scoparia is ranked among top six most problematic weeds of sugar beet (Beta vulgaris L.)7,8. Sugar beet is particularly sensitive to early-season competition from B. scoparia that may result in significant beet root yield reductions (up to 95%)9,10,11. In general, B. scoparia is more difficult to control in sugar beet than in corn (Zea mays L.), soybean [Glycine max (L.) Merr.], wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) or fallow12.Limited herbicide options and widespread occurrence of B. scoparia populations with resistance to triflusulfuron (ALS inhibitor) in conventional sugar beet has led to a rapid adoption of GR sugar beet in the U.S.13,14. Two to three applications of glyphosate have been a common practice for weed control in GR sugar beet14. Ironically, several GR B. scoparia populations have been reported in the Great Plains region since its first discovery in wheat-fallow systems in the western Kansas in 200715. Currently, GR B. scoparia from sugar beet fields have been reported from Montana, Wyoming, Nebraska, Colorado, Idaho and Oregon6,16. These reports on GR B. scoparia from sugar beet fields pose a serious threat to the long-term sustainability of GR sugar beet technology.
Glyphosate resistance in B. scoparia has evolved through amplification of the target gene that encodes the 5-enolpyruvyl-shikimate-3-phosphate synthase (EPSPS) enzyme (a key enzyme of the shikimate pathway)15,17,18. It has been proposed that amplified EPSPS copies are generally arranged in tandem in GR B. scoparia genome and a mobile genetic element with a FHY3/FAR1-like gene is responsible for the origin of the EPSPS gene duplication event and the evolution of glyphosate resistance19,20. Previous studies have also shown that increased EPSPS copies in GR B. scoparia correlate positively with higher EPSPS transcription, EPSPS protein, and glyphosate resistance levels16,17,18,19.
Predicting the pleiotropic effects of EPSPS gene amplification and overexpression on fitness attributes of any GR plant species can be challenging21. Fitness costs associated with EPSPS gene amplification in GR B. scoparia have previously been studied in the absence of glyphosate and shown mixed results. For instance, a greenhouse study using inbred lines of GR and glyphosate-susceptible (GS) B. scoparia exhibited no differences in growth and reproductive parameters under intraspecific competition22. However, the GR B. scoparia has shown reduced seed longevity, slower germination rate, and less total germination than the GS B. scoparia in other studies23,24. Additionally, a competitive greenhouse study using segregating F2 populations of GR B. scoparia indicated that plants with higher EPSPS copy numbers had reduced seed count and weight, reduced competitive ability, and reduced final height in mixed stands25. However, the observed growth and reproductive parameters were highly variable and fitness consequences varied with the genetic background25.
Considerable variation in EPSPS gene copy number (3 to 13 copies) among individuals from within a single GR B. scoparia population suggests a differential response among individuals to varying glyphosate rates22. Considering the continued use of GR sugar beet technology in conjunction with extensive use of glyphosate for broad-spectrum weed control, it is crucial to understand the impact of glyphosate applications on the population dynamics of GR B. scoparia population with variable EPSPS gene copy numbers. Hence, the main goal of this research was to determine the survival (% control) and reproductive characteristics of GR B. scoparia with low to high levels of resistance (based on EPSPS gene copy numbers) in response to varying glyphosate rates under field conditions.
Results
The year-by-treatment interaction was not significant for any of the observed response variables in the field study; therefore, all data were combined across the two years. A differential response of B. scoparia plants with varying EPSPS copy numbers was observed across glyphosate rates tested. The B. scoparia plants with ≥ 2 EPSPS gene copies survived the field-use rate (870 g ae ha−1) of glyphosate, but plants with 1 EPSPS gene copy number did not survive. Therefore, except for percent visible control, other response variables were not obtained for plants with one EPSPS gene copy number (GS) treated with ≥ 870 g ae ha−1 of glyphosate.
Effect of EPSPS gene copy number on reproductive traits of B. scoparia in the absence of glyphosate
In the absence of glyphosate, the EPSPS gene copy number had no effect on time to 50% flowering (P = 0.17), time to set seeds (P = 0.18), pollen viability (P = 0.23), seeds plant-1 (P = 0.94), and seed viability (P = 0.41), but had a significant effect on 1000-seed weight and seedling (progeny) radicle length (P < 0.01) (Table 1). The averaged 1000-seed weight of GR B. scoparia plants (2–4, 5–6 and ≥ 8 EPSPS gene copies) were lower (0.60 g) compared to the averaged 1000-seed weight of GS plants with 1 EPSPS gene copy (0.85 g) at Tukey–Kramer’s HSDα(0.05) = 0.09. Similarly, the averaged seedling radicle length from progeny seeds of GR B. scoparia plants were lower (0.45 cm) compared to the averaged seedling radicle length from progeny seeds of GS plants (0.74 cm) at Tukey–Kramer’s HSDα(0.05) = 0.17. These results suggest that GS B. scoparia plants (those with 1 EPSPS gene copy) may be more competitive than the GR plants in the absence of glyphosate. Nevertheless, the high outcrossing nature of B. scoparia and the flow of resistance genes facilitated through shedding of equally viable pollens from resistant plants may contribute to sufficient number of GR individuals in field populations, even if the use of glyphosate is discontinued.
Effect of EPSPS gene copy number and glyphosate on control and reproductive traits of GR. B. scoparia
Visible control
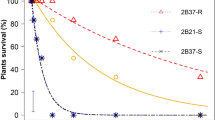
The EPSPS gene copy number, total glyphosate rate (applied as single or sequential applications), and their interactions influenced B. scoparia percent visible control (P < 0.01, Table 2). A single application of glyphosate (1265 g ae ha−1) provided poor (11%) control of GR B. scoparia plants with 2–4 EPSPS gene copies, and no control of B. scoparia plants with 5–6 or ≥ 8 EPSPS gene copies. Two sequential applications of glyphosate (a total of 1740 g ae ha−1) provided 72% control of GR plants with 2–4 EPSPS gene copies, 36% control for plants with 5–6 EPSPS gene copies, and < 5% control for GR plants with ≥ 8 EPSPS gene copies. Two sequential applications of glyphosate (a total of 2214 g ae ha−1) had 98% and 95% control of GR plants with 2–4 and 5–6 EPSPS gene copies, respectively; however, control was poor (< 10%) for plants with ≥ 8 EPSPS gene copies. Even with four sequential applications of glyphosate (a total of 3954 g ae ha−1, maximum labeled use rate of glyphosate in GR sugar beet in a growing season), control of GR B. scoparia with ≥ 8 EPSPS gene copies averaged 31% only. Glyphosate rate-response analysis indicated that the total glyphosate rate needed to achieve 90% control (ED90 values) was 1971 and 2123 g ae ha−1 for GR B. scoparia with 2–4 and 5–6 EPSPS gene copies, respectively (Table 3). For GR B. scoparia with ≥ 8 EPSPS gene copies, the total rate of glyphosate needed to achieve 90% control was estimated to be > 4000 g ae ha−1, indicating very high resistance and might not be controlled if present in GR sugar beet.
Seed production
The EPSPS gene copy number, total glyphosate rate (applied as single or sequential applications), and their interactions influenced GR B. scoparia seed production (P < 0.01, Table 2). Glyphosate rate-response analysis indicated that the total glyphosate rate needed for 99% seed reduction (SR99 values) was 1902 and 2130 g ae ha−1 for GR plants with 2–4 and 5–6 EPSPS gene copies, respectively (Table 3). The SR99 value for GR B. scoparia plants with ≥ 8 EPSPS gene copies were estimated to be > 4000 g ae ha−1 of glyphosate. This indicates that seed production in highly resistant plants will not be prevented even with four sequential applications of the maximum-labeled use rate of glyphosate (total of 3954 g ae ha−1 of glyphosate) in a GR sugar beet field. However, seed production of GR B. scoparia plants with 2–4 (low-level resistance) and 5–6 (moderate level resistance) EPSPS gene copies that emerge before the 2-leaf stage of sugar beet can be prevented with three sequential applications of glyphosate, with a total rate of 3084 g ae ha−1. However, any survivors may increase the risk of GR progenies with higher levels of evolved resistance in the population.
Other reproductive traits
For GR B. scoparia plants, the variation in EPSPS gene copy number (those with 2–4, 5–6, ≥ 8 EPSPS gene copies), total glyphosate rate (applied as single or sequential applications), and their interactions did not influence time to 50% flowering, time to seed set, pollen viability, 1000-seed weight, seed viability, and seedling radicle length (Table 2). These results indicate that seedling vigor of progenies from GR B. scoparia plants (2 to ≥ 8 EPSPS gene copies) will be comparable regardless of the glyphosate rate, and if let to set seed can potentially build up resistance very rapidly due to pollen-mediated gene flow. The range for time to 50% flowering was 39–41 days after transplanting, time to set seeds was 57–60 days after transplanting, pollen viability was 82–86%, 1000-seed weight was 0.59–0.61 g, seed viability was 94–99%, and radicle length was 0.53–0.54 cm across EPSPS gene copy numbers and total glyphosate rates.
Relative fitness
Variation in EPSPS gene copy number (2–4, 5–6, and ≥ 8 EPSPS gene copies), total glyphosate rate (applied as single or sequential applications), and their interactions had a significant effect on the relative fitness of GR B. scoparia (Table 4). In the presence of glyphosate applied at total rates ≥ 2214 g ae ha−1, GR B. scoparia plants with 2–4 and 5–6 EPSPS gene copies were not fit (both had w = 0; failed to produce offspring) (Table 4). Although four sequential applications of glyphosate (total rate of 3954 g ae ha−1) provided little control (31%) of B. scoparia plants with ≥ 8 EPSPS gene copies, there was a significant reduction in their relative fitness (w = 0.46) compared to their fitness at a single application of 870 or 1265 g ae ha−1 (w = 0.74 and w = 0.73, respectively) (Table 4). The results imply that in the presence of glyphosate, GR plants will produce less number of offspring than the most successful genotype (susceptible B. scoparia plants with 1 EPSPS gene copy and a w of 1.0 in the absence of glyphosate). Selection coefficient (s = 1 − w) is the measure of the relative strength of the selection agent acting against a genotype26. The selection coefficient was 1.0 when glyphosate was applied sequentially with a total of at least 2214 g ae ha−1 on GR plants with 2–4 or 5–6 EPSPS gene copies, implying that the magnitude of fitness reduction of GR plants with low to moderate levels of resistance was 100% at those glyphosate rates in the field.
Discussion
This field study evaluated the reproductive fitness of B. scoparia with variable EPSPS gene copy numbers to increasing glyphosate rates applied as single or sequential applications, simulating glyphosate applications in GR sugar beet. The GS and GR B. scoparia sub-populations were derived from within a single field population; hence, expected to have similar genetic backgrounds21,22,25. Fitness consequences of glyphosate resistance alleles in weed species may vary across genetic backgrounds25. This is more complicated for B. scoparia with a high genetic diversity due to pollen and seed mediated gene flow accompanied by tumble mechanism of seed dispersal within and among fields4,5,6. Furthermore, the GR and GS subpopulatons were subjected to three generations of recurrent group selection which allowed us to use relatively homozygous plants for this fitness study. Seedlings from the selected GR B. scoparia subpopulation showed a variable level of glyphosate resistance evident from two to ≥ 8 EPSPS gene copies, conferring low to high levels of resistance.
Results indicated that a discontinuity of glyphosate use would favor GS (one EPSPS gene copy number) over GR B. scoparia because of a greater progeny seedling vigor (higher 1000-seed weight and radicle length) of the former in the absence of glyphosate. The GS individuals would be at a competitive advantage over GR individuals through an earlier establishment and a more vigorous growth in the absence of glyphosate in the field. These findings are consistent with Martin et al.25, who reported that progeny seed weights of GR B. scoparia plants (10 EPSPS gene copies) from Canada were less compared to GS plants (one EPSPS gene copy) in a greenhouse study. However in this field study, there were no differences in other reproductive traits (time to flowering, time to set seeds, pollen viability, seeds plant−1, or seed viability) between GR and GS B. scoparia. Fitness consequences may vary depending on life history stages24. Also in previous studies (field and greenhouse), no fitness differences were observed between GR and GS B. scoparia in their vegetative growth or seed production but GR individuals had a lower total germination and a slower germination rate than GS individuals22,24. Delayed germination and less seedling vigor and subsequent early-season competitiveness may possibly suggest a fitness cost endowed by glyphosate resistance alleles in this weed species23,24,25. This fitness study was conducted in the absence of crop (fallow); however, results might not be very different in the presence of sugar beet which is among the least competitive crops against B. scoparia9,10,11. It is also acknowledged that fitness outcomes may vary depending on the presence and extent of crop competition (e.g. B. scoparia would be less competitive in the presence of cereals or corn compared to fallow or sugar beet)25,27.
Results from this research may aid in predicting the evolutionary trajectory of GR B. scoparia under field conditions with the continued use of glyphosate. This is more important to understand when there is a lack of other effective sites-of-action herbicides to control this weed in sugar beet. This is the first study to report the fitness traits of GR B. scoparia with low to high levels of resistance (2 to ≥ 8 EPSPS gene copies) in the presence of varying glyphosate rates in the field. Irrespective of the total glyphosate rate, the variation in EPSPS gene copy number had no effect on the fitness traits except seed production in GR B. scoparia. Sequential applications of glyphosate with a total rate of 2214 g ae ha−1 or higher prevented seed production of GR B. scoparia with low and moderate glyphosate resistance (2–4 and 5–6 EPSPS gene copies, respectively), implying the importance of timely, sequential applications of glyphosate at full recommended rates in GR sugar beet. However, the highly resistant B. scoparia with ≥ 8 EPSPS gene copies surviving four sequential applications of glyphosate (total rate of 3,954 g ae ha−1) should be manually removed before they flower (to prevent gene flow through pollen or seeds) in GR sugar beet fields. More importantly, the results indicate that offspring from glyphosate survivors may increase the probability of genotypes with increased EPSPS gene copy numbers in a field population of B. scoparia.
A zero-tolerance approach against seed production from GR B. scoparia plants should be adopted in GR sugar beet fields. Sugar beet growers should adopt an integrated weed management (IWM) program to manage GR B. scoparia. This includes the use of mechanical and ecological approaches such as tillage, cover crops, and diverse crop rotations that employ different cultural management practices (planting dates, harvest dates, and crop canopy) and effective alternative herbicides other than glyphosate (in rotational crops) to reduce the frequency of GR B. scoparia on their sugar beet fields27. Selecting the most competitive crops such as cereals or corn in rotation with sugar beet will be important in reducing seed inputs of B. scoparia27,28. This will also provide an opportunity to reduce kochia seed banks being exposed to glyphosate, thereby slowing down the evolution and spread of glyphosate resistance. Selection of a late-planted crop grown in the U.S. Great Plains such as dry beans, in a diverse crop rotation plan could also reduce herbicide exposures through non-chemical control tactics such as stale seedbed27. These IWM tactics would be more important for a weed like B. scoparia with a short-lived seed2,3.
Future studies on understanding the fitness attributes of glyphosate resistance alleles in B. scoparia under varied biotic and abiotic stresses (herbivory, disease, and crop competition) will further help to validate these results and aid in developing long-term IWM strategies in sugar beet-based crop rotations of the U.S. Great Plains. In addition, future research should assess the frequency of GR resistance alleles of B. scoparia over multiple years under diverse management practices in crop production fields.
Methods
Seed source
Seeds of a segregating GR B. scoparia population identified from a wheat field (45°54′54.76″N; 108°14′44.15″W) in 2013 in Hill County, Montana, USA (designated as MT009) were used. The field was under a continuous no-till wheat-fallow rotation for > 8 years and had a history of repeated glyphosate use (at least 3 applications per year) for weed control during the summer fallow phase prior to winter wheat planting. The permission of land owner was obtained prior to B. scoparia seed collection. All experimental research and field studies on plants, including the collection of plant material complied with the Montana State University guidelines and state/US legislation. Seeds of the field-collected population were used to generate GS and GR B. scoparia subpopulations through recurrent group selection procedure as described below.
Development of GS and GR subpopulations
Field collected seeds of MT009 population were sown on the surface of plastic trays (53 by 35 by 10 cm) filled with commercial potting soil (VERMISOIL, Vermicrop Organics, 4265 Duluth Avenue, Rocklin, CA, USA) in a greenhouse in the fall of 2013 at the Montana State University Southern Agricultural Research Center (MSU-SARC) near Huntley, MT, USA. Growth conditions in greenhouse were maintained at 25/22 ± 2 °C day/night temperatures and 16/8 h day/night photoperiods supplemented with metal halide lamps (450 μmol m-2 s-1). After emergence, approximately 200 uniform seedlings were individually transplanted in plastic pots (10-cm diam) containing the same potting mixture and grown for 6 weeks. A set of three clones (3 shoot cuttings) from each plant were then prepared and transplanted in plastic pots (10-cm diam) as described by Kumar and Jha22. At the 8- to 10-cm height, all cloned seedlings were separately treated with 435 (0.5×), 870 (1×), and 1740 (2×) g ae ha−1 of glyphosate (Roundup Powermax, Bayer Crop Science, Saint Louis, MO, USA) where 1× = field-use rate of glyphosate. All three glyphosate treatments included ammonium sulfate (2% w/v). Glyphosate applications were made using a cabinet spray chamber (Research Track Sprayer, De Vries Manufacturing, RR 1 Box 184, Hollandale, MN, USA) equipped with an even flat-fan nozzle tip (Teejet 8001EXR, Spraying System Co., Wheaton, IL, USA), calibrated to deliver 140 L ha−1 of spray solution at 276 kPa. Treated seedlings were returned to the greenhouse, watered as needed, and fertilized [Miracle-Gro water soluble fertilizer (24-8-16), Scotts Miracle-Gro Products Inc., 14111 Scottslawn Road, Marysville, OH, USA] bi-weekly to maintain good plant growth. At 21 days after treatment, clones surviving the 2× rate of glyphosate were considered as ‘glyphosate-resistant (GR)’ and the clones that did not survive 1× rate of glyphosate were considered as ‘glyphosate-susceptible (GS)’. The parent B. scoparia plants corresponding to survived (resistant) or not-survived (susceptible) clones were transplanted separately in 20-L plastic pots (group of 3 to 4 plants pot−1) containing same potting soil for seed production. All 3- to 4 plants in each pot were collectively covered with a single pollination bag (DelStar Technologies, Inc., 601 Industrial drive, Middletown, DE, USA) prior to flower initiation to restrict cross-pollination between GR and GS plants. At maturity, seeds from the respective GR and GS parent plants were collected and cleaned separately using an air column blower. The collected seeds from GR plants were subjected to three generations of recurrent group selection with the 2× rate of glyphosate in each generation. Seeds of GS plants were also subjected to recurrent group selection for three generations without glyphosate. Progenies of the GS plants were grown and sprayed with 1× rate of glyphosate to confirm the susceptibility to glyphosate in each generation23. This procedure allowed the development of relatively genetically homogenous GR and GS subpopulations from within a single B. scoparia population.
Determination of EPSPS gene copy number
Previously established protocols were adopted to estimate the relative EPSPS gene copy number in seedlings of GR and GS subpopulations through quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction (qPCR)16,17,18. The ALS gene was used as reference since the relative ALS gene copy number and transcript abundance did not vary across B. scoparia samples17,18,29. Relative EPSPS:ALS gene copy number is a ratio of EPSPS to ALS PCR product fluorescence. Due to small differences in amplicon size, qPCR run conditions, and fluorescence detection, the values presented were estimates of relative gene copy number29.
A total of 600 seedlings from the GR (450 seedlings) and GS (150 seedlings) B. scoparia subpopulations (developed by recurrent group selection) were grown in a greenhouse at MSU-SARC near Huntley, MT, USA in 2015 and 2016 to select enough plants for the field study each year. At 4-to 6-cm height, young leaf tissues (100 mg) from each seedling were sampled, frozen with liquid nitrogen and ground into powder using mortar and pestle. Genomic DNA were extracted from the tissue samples using the protocol from Qiagen Dneasy plant mini kit (Qiagen Inc., Valencia, CA, USA). Genomic DNA quantity and quality were determined using a Smartspec Plus spectrophotometer (Bio-Rad Company, CA, USA) and gel electrophoresis with 1% agarose, respectively. High quality genomic DNA (260/280 ratio of ≥ 1.8) were used to determine the relative EPSPS gene copy number. Two sets of primers to amplify the EPSPS and ALS genes, the final reaction volume and reagents used for each qPCR reaction, and the qPCR conditions used in this study were the same as previously described by Kumar and Jha22. Each qPCR reaction was performed on a Bio-Rad 96-well PCR plate in triplicates and fluorescence was detected using CFX Connect Real-Time PCR detection system. A negative control consisting of 250 nM of each forward and reverse primer, 1× Perfecta SYBR Green supermix, and deionized water with no DNA template was included. The EPSPS genomic copy number relative to ALS gene was estimated by ΔCT method (ΔCT = CT, ALS-CT, EPSPS)18,29. The relative increase in the EPSPS gene copy number was calculated as 2ΔCT.
Survival and fecundity traits of GR and GS B. scoparia subpopulations
Seedlings (4- to 6-cm tall) of GR and GS B. scoparia subpopulations with known EPSPS gene copy numbers were transplanted into a fallow field in the summer of 2015 and 2016 at the MSU-SARC near Huntley, MT, USA. All transplanted B. scoparia seedlings were equally spaced at 1.5 m apart from each other and all plants were fertilized biweekly [2 to 3 g of MIRACLE-GRO water soluble fertilizer (24-8-16)] and irrigated as and when needed to avoid moisture stress. Experiments were conducted with a factorial arrangement of treatments (Factor A and Factor B) in a randomized complete block design, with 6 replications. Each transplanted B. scoparia seedling was an experimental unit. The factor A (4 levels) was comprised of B. scoparia plants with 1, 2–4, 5–6, and ≥ 8 EPSPS gene copy numbers, which were categorized as susceptible, low, moderate, and highly resistant plants, respectively based on their percent visible injury response to glyphosate. The factor B (ten levels) was comprised of increasing rates of glyphosate applied as single or sequential applications. Current labels of glyphosate allow a total of 3954 g ae ha−1 in split POST applications in GR sugar beet. As per the label, the maximum glyphosate rate of 2214 g ae ha−1 is allowed from crop emergence to 8-leaf stage of sugar beet and 1740 g ae ha−1 of glyphosate from 8-leaf stage to canopy closure or 30 days prior to sugar beet harvest. Hence, the tested total glyphosate rates were 0, 108, 217, 435, 870, 1265, 1740 [870 followed by ( +) 870], 2214 [1265 + 949], 3084 [1265 + 949 + 870], and 3954 [1265 + 949 + 870 + 870] g ae ha−1 along with ammonium sulfate (2% w/v). Sequential applications were made at 7- to 14-day intervals, with first application at 8- to 10-cm tall B. scoparia seedlings using a CO2-operated backpack sprayer fitted with a single AIXR 8001 flat-fan nozzle calibrated to deliver 94 L ha−1. Glyphosate rates and applications timings were selected to simulate the 2-leaf, 6-leaf, 8–10 leaf, and the canopy closure stage of GR sugar beet.
Data collection
Percent visible control (relative to the non-treated) on a scale of 0 to 100 (0 means no control and 100 means complete plant death30) for each individual plant (240 plants total each year) were assessed at 7, 14, and 21 days after glyphosate treatment. Data on number of days from transplanting to 50% flowering (half of the inflorescences from each plant were covered with visible flowers) and seed set (seeds on half of the inflorescences from each plant were turned brown) were recorded for an individual plant. Each plant was covered with a pollination bag (DelStar Technologies, Inc., 601 Industrial drive, Middletown, DE, USA) prior to flowering to prevent any cross-pollination. At the time of flowering, pollens from each survived plant were collected in early morning hours (between 8 to 10 am). At maturity, each individual plant was harvested and threshed to determine 1000-seed weight and seeds plant−1.
Pollen and progeny seed viability
Pollens and seeds collected from individual B. scoparia plants (240 plants total each year) were tested for viability using a tetrazolium test. Pollens were collected in petri dishes by shaking the whole plant at the time of flowering. Four sub-samples of pollens from each petri dish were transferred into glass slides. The pollens in the glass slides were soaked with a tetrazolium chloride solution (10 g L−1), sealed with a cover slip using a nail polish and were incubated at room temperature for an hour. Viable (red) and non-viable pollens (yellow/white) were counted using a simple microscope. The physical structure of viable and non-viable pollens was also checked for any deformity using a compound microscope. Pollen viability for individual plants (240 plants total each year) was calculated as percent viable pollens of the total number of pollens counted.
For seed viability test, twenty-five intact seeds collected from each individual plant (240 plants total each year) from the field were evenly placed in between two layers of filter papers (WHATMAN Grade 2, SigmaAldrich, St Louis, MO, USA) inside a 10-cm-diameter petri dish. Seeds were soaked with a 5-ml of distilled water and the filter papers were kept moist for the entire duration of the germination test. Light is not required for B. scoparia seed germination31, so the petri dishes were wrapped with a thin aluminum foil and placed inside an incubator (VMR International, Sheldon Manufacturing, Cornelius, OR, USA) with alternating day/night temperatures set to 20/25 °C23. Seeds with a visible uncoiled radicle tip longer than the seed diameter was considered germinated32,33. Radicle length was measured from three randomly selected germinated seeds 24 h after incubation to test the seedling vigor. The number of germinated seeds in each petri dish were counted daily until no further germination was observed for 10 consecutive days. Non-germinated seeds were tested for viability by soaking the seeds with tetrazolium chloride solution (10 g L−1) for 24 h23,34. Seeds with a red-stained embryo examined under a dissecting microscope (tenfold magnification) were considered viable35. Seed viability was expressed as the percentage of total viable seeds.
Relative fitness (w)
Fitness is the evolutionary potential for success of a genotype based on survival, competitive ability, and reproduction. Individuals with the greatest number of offspring and with the most genes contributing to the gene pool of a population are considered most fit genotypes36. Fitness of a genotype is determined by comparison of its vigor, productivity or competitiveness relative to the other genotype by quantifying specific traits such as seed dormancy, flowering date, seedling vigor, seed production, and other factors that can possibly influence the survival and reproductive success of a genotype36,37. In this study, relative fitness (w) of GR B. scoparia was calculated as the reproductive rate (seed production plant−1) of a resistant genotype (B. scoparia plants with 2–4, 5–6, and ≥ 8 EPSPS gene copies) relative to the maximum reproductive rate of the susceptible genotype (B. scoparia plants with 1 EPSPS gene copy) in the population. The relative fitness (w) of susceptible plants was assumed to be one.
Statistical analyses
A natural logarithm transformation was performed on data for time to 50% flowering, time to seed set, seeds plant−1. An arcsine square root transformation was performed on data for pollen viability, visible control, seed viability, and relative fitness (w) before subjecting to analysis of variance, however all data were presented in their back-transformed values. No transformation was needed for 1000-seed weight and radicle length data. Experimental year, B. scoparia plants with different EPSPS copy number groups, glyphosate rate, and their interactions were considered fixed effects and replication nested within a year was considered as a random effect in the model. Data on percent visible control, time to 50% flowering, pollen viability, time to seed set, 1000-seed weight, and seeds plant−1, seed viability and radicle length were subjected to ANOVA using Proc Mixed in SAS (SAS version 9.4, SAS Institute, Cary, NC, USA) to test the significance of experimental run, treatment factors, and interactions. The ANOVA assumptions for normality of residuals and homogeneity of variance were tested using Proc Univariate and PROC GLM in SAS. Means were separated using Tukey–Kramer’s HSD with α = 0.05. Furthermore, data on percent visible control and seeds plant-1 for each group of B. scoparia plants with different EPSPS gene copy number were regressed against total glyphosate rates using a four-parameter log-logistic model Eq. (1)38,39:
where Y is the percent visible control or seed production plant−1 (% of nontreated); d is the upper asymptote (the highest estimated % control or % seed reduction); c is the lower asymptote (the lowest estimated % control or % seed reduction); ED50 is the effective rate of glyphosate needed to achieve 50% control or 50% reduction in seed production; and b denotes the slope around the inflection point “ED50.” Slope parameter (b) indicates the response rate of each group of B. scoparia plants with different EPSPS gene copy number to glyphosate rates (i.e., a slope with a large negative value suggests a rapid response of selected B. scoparia group). The Akaike Information Criterion (AIC) was used to select the nonlinear four-parameter model. A lack-of-fit test (P > 0.10) was used to confirm that the nonlinear regression model Eq. (1) described the response data for each B. scoparia group38. Parameter estimates, ED90, and SR99 values (i.e. effective rate required for 90% control or effective rate required for 99% reduction in seed production) for each group of B. scoparia plants with different EPSPS gene copy number were determined using the ‘drc’ package in R software37,39. Parameter estimates of B. scoparia groups were compared using the approximate t-test with the ‘compParm’ and ‘EDcomp’ functions in the ‘drc’ package of the R software39,40.
Data availability
The datasets generated and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Kumar, V., Jha, P., Dille, J. A. & Stahlman, P. W. Emergence dynamics of kochia (Kochia scoparia) populations from the U.S. Great Plains: A multisite-year study. Weed Sci. 66, 25–35 (2018).
Dille, J. A. et al. Kochia emergence profiles across the central Great Plains. Weed Sci. 65, 614–625 (2017).
Friesen, L. F., Beckie, H. J., Warwick, S. I. & Van Acker, R. C. The biology of Canadian weeds. 138. Kochia scoparia (L.) Schrad. Can. J. Plant. Sci. 89, 141–167 (2009).
Beckie, H., Blackshaw, R., Hall, L. & Johnson, E. Pollen- and seed-mediated gene flow in kochia (Kochia scoparia). Weed Sci. 64, 624–633 (2016).
Mengistu, L. W. & Messersmith, C. G. Genetic diversity of kochia. Weed Sci. 50, 498–503 (2002).
Heap, I. International Survey of Herbicide Resistant Weeds. http://www.weedscience.org. Accessed 11 Mar 2020 (2020).
Van Wychen, L. 2016 Survey of the most common and troublesome weeds in broadleaf crops, fruits & vegetables in the United States and Canada. in Weed Science Society of America National Weed Survey Dataset. http://wssa.net/wp-content/uploads/2016-Weed-Survey_Broadleaf-crops.xlsx. Accessed 20 Dec 2020 (2016).
Van Wychen, L. 2017 Survey of the most common and troublesome weeds in grass crops, pasture and turf in the United States and Canada. in Weed Science Society of America National Weed Survey Dataset. http://wssa.net/wp-content/uploads/2017-Weed-Survey_Grass-crops.xlsx. Accessed 20 Dec 2019 (2017).
Mesbah, A., Miller, S. D., Fornstrom, K. J. & Legg, D.E. Sugar beet–weed interactions. in University of Wyoming. Agricultural Experiment Station B-998 (1994).
Weatherspoon, D. M. & Schweizer, E. E. Competition between sugar beet and five densities of kochia. Weed Sci. 19, 125–128 (1971).
Schweizer, E. E. & Dexter, A. G. Weed control in sugar beet (Beta vulgaris) in North America. Rev. Weed Sci. 3, 1133 (1987).
Sbatella, G. M. et al. Herbicide options for glyphosate-resistant kochia (Bassia scoparia) management in the Great Plains. Weed Technol. 33, 658–663. https://doi.org/10.1017/wet.2019.48 (2019).
Fernandez-Cornejo, J., Wechsler, S. J. & Milkove, D. L. The adoption of genetically engineered alfalfa, canola and sugar beets in the United States. Econ. Res. Serv. Econ. Inf. Bull. 163, 22 (2016).
Kniss, A. R. Comparison of conventional and glyphosate-resistant sugar beet the year of commercial introduction in Wyoming. J. Sugar Beet Res. 47, 127–134 (2010).
Godar, A. S., Stahlman, P. W., Jugulam, M. & Dille, J. A. Glyphosate-resistant kochia (Kochia scoparia) in Kansas: EPSPS gene copy number in relation to resistance levels. Weed Sci. 63, 587–595 (2015).
Gaines, T. A. et al. EPSPS gene copy number and whole-plant glyphosate resistance level in Kochia scoparia. PLoS ONE 11, e0168295 (2016).
Kumar, V., Jha, P., Giacomini, D., Westra, E. P. & Westra, P. Molecular basis of evolved resistance to glyphosate and acetolactate synthase-inhibitor herbicides in kochia (Kochia scoparia) accessions from Montana. Weed Sci. 63, 758–769 (2015).
Wiersma, A. T. et al. Gene amplification of 5-enol-pyruvylshikimate-3-phosphate synthase in glyphosate-resistant Kochia scoparia. Planta 241, 463–474 (2015).
Jugulam, M. et al. Tandem amplification of a chromosomal segment harboring 5-enolpyruvylshikimate-3-phosphate synthase locus confers glyphosate resistance in Kochia scoparia. Plant Physiol. 166, 1200–1207 (2014).
Patterson, E. L., Pettinga, D. J., Ravet, K., Neve, P. & Gaines, T. A. Glyphosate resistance and EPSPS gene duplication: Convergent evolution in multiple plant species. J. Hered. 109, 117–125 (2017).
Vila-Aiub, M. M., Yu, Q. & Powles, S. B. Do plants pay a fitness cost to be resistant to glyphosate?. New Phytol. 223, 532–547 (2019).
Kumar, V. & Jha, P. Growth and reproduction of glyphosate-resistant and susceptible populations of Kochia scoparia. PLoS ONE 10, e0142675 (2016).
Kumar, V. & Jha, P. Effect of temperature on germination characteristics of glyphosate-resistant and glyphosate-susceptible kochia (Kochia scoparia). Weed Sci. 65, 361–370 (2017).
Osipitan, O. A. & Dille, J. A. Fitness outcomes related to glyphosate resistance in kochia (Kochia scoparia): What life history stage to examine?. Front. Plant Sci. 8, 1090 (2017).
Martin, S. L. et al. Glyphosate resistance reduces kochia fitness: Comparison of segregating resistant and susceptible F2 populations. Plant Sci. 261, 69–79 (2017).
Adam, A. et al. Selection coefficient. in Encyclopedia of Genetics, Genomics, Proteomics and Informatics (ed. Rédei, G. P.) 1775 (Springer, 2008).
Kumar, V., Jha, P., Jugulam, M., Yadav, R. & Stahlman, P. W. Herbicide-resistant kochia (Bassia scoparia) in North America: A review. Weed Sci. 67, 4–15 (2019).
Mosqueda, E. G. et al. Effect of crop canopy and herbicide application on kochia (Bassia scoparia) density and seed production. Weed Sci. 68, 278–284 (2020).
Gaines, T. A. et al. Gene amplification confers glyphosate resistance in Amaranthus palmeri. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 107, 1029–1034 (2010).
Frans, R., Talbert, R., Marx, D. & Crowley, H. Experimental design and techniques for measuring and analyzing plant responses to weed control practices. In Research Methods in Weed Science 3rd edn (ed. Camper, N. D.) 29–46 (Southern Weed Science Society, 1986).
Everitt, J. H., Alaniz, M. A. & Lee, J. B. Seed germination characteristics of Kochia scoparia. J. Range Manag. 36, 646–648 (1983).
Dyer, W. E., Chee, P. W. & Fay, P. K. Rapid germination of sulfonylurea-resistant Kochia scoparia L. accessions is associated with elevated seed levels of branched chain amino acids. Weed Sci. 41, 18–22 (1993).
Young, J. A., Evans, R. A., Stevens, R. & Everett, R. L. Germination of Kochia prostrata seed. Agron. J. 73, 957–961 (1981).
Sbatella, G. M. & Wilson, R. G. Isoxaflutole shifts kochia (Kochia scoparia L.) populations in continuous corn. Weed Technol. 24, 392–396 (2010).
Thompson, C. R., Thill, D. C. & Shafii, B. Germination characteristics of sulfonylurea-resistant and -susceptible kochia (Kochia scoparia). Weed Sci. 42, 50–56 (1994).
Radosevich, S. R., Holt, J. & Ghersa, G. Weed demography and population dynamics. in Weed Ecology: Implication for Management. 103–159 (Wiley, 1997).
Warwick, S. I. & Black, L. D. Relative fitness of herbicide-resistant and susceptible biotypes of weeds. Phytoprotection 75, 37–49 (1994).
Ritz, C. & Streibig, J. C. Bioassay analysis using R. J. Stat. Softw. 12, 1–22 (2005).
Ritz, C., Baty, F., Streibig, J. C. & Gerhard, D. Dose-response analysis using R. PLoS ONE 10, e0146021 (2015).
Knezevic, S. Z., Streibig, J. C. & Ritz, C. Utilizing R software package for dose–response studies: The concept and data analysis. Weed Technol. 21, 840–848 (2007).
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank the Western Sugar Cooperative Research Committee for the funding provided for this research. No conflicts of interest have been declared. We thank Mr. Ramawatar Yadav, Ms. Anjani, and Mr. Shane Leland for their technical assistance in conducting this research.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
P.J. and V.K. conceived and designed the experiments. C.L. performed the experiments. C.L., P.J., and A.D. analyzed the data. P.J. contributed the reagents/materials/analysis tools. C.L., P.J., V.K., and A.D. wrote and reviewed the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
About this article
Cite this article
Lim, C.A., Jha, P., Kumar, V. et al. Effect of EPSPS gene copy number and glyphosate selection on fitness of glyphosate-resistant Bassia scoparia in the field. Sci Rep 11, 16083 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-021-95517-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-021-95517-2
- Springer Nature Limited