Abstract
The oleaginous yeast Yarrowia lipolytica is a potent cell factory as it is able to use a wide variety of carbon sources to convert waste materials into value-added products. Nonetheless, there are still gaps in our understanding of its central carbon metabolism. Here we present an in-depth study of Y. lipolytica hexokinase (YlHxk1), a structurally unique protein. The greatest peculiarity of YlHxk1 is a 37-amino acid loop region, a structure not found in any other known hexokinases. By combining bioinformatic and experimental methods we showed that the loop in YlHxk1 is essential for activity of this protein and through that on growth of Y. lipolytica on glucose and fructose. We further proved that the loop in YlHxk1 hinders binding with trehalose 6-phosphate (T6P), a glycolysis inhibitor, as hexokinase with partial deletion of this region is 4.7-fold less sensitive to this molecule. We also found that YlHxk1 devoid of the loop causes strong repressive effect on lipase-encoding genes LIP2 and LIP8 and that the hexokinase overexpression in Y. lipolytica changes glycerol over glucose preference when cultivated in media containing both substrates.
Similar content being viewed by others
Introduction
Yarrowia lipolytica is an oleaginous yeast that has become a biotechnological workhorse due to its industrially-relevant abilities. This yeast synthesize high concentration of intracellular lipids and secrete high amount of proteins as well as organic acids and polyols1,2,3,4,5,6. Y. lipolytica is able to use both hydrophobic (e.g. n-alkanes, lipids) and hydrophilic (e.g. monosaccharides, glycerol, organic acids) carbon sources7,8,9,10,11,12. However, wild strains of Y. lipolytica utilize only a handful of sugar substrates, namely glucose, fructose and mannose. These hexoses are transported inside the cell via hexose transporters and incorporated to the central carbon metabolism after their phosphorylation by hexose kinases. This yeast has two enzymes with hexokinase activity—glucokinase (YlGlk1) and hexokinase (YlHxk1). YlGlk1 exclusively catalyses the phosphorylation of glucose, while YlHxk1 acts on glucose and fructose13. This is in contrast with the model yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae, which possesses two hexokinases—ScHxk1 and ScHxk2, which derive from the whole genome duplication (WGD14). ScHxk2 plays the main role in glucose phosphorylation and participates in glucose catabolic repression in S. cerevisiae15,16.
YlHxk1 is a 534 amino acid protein encoded by a 2041 bp YlHXK1 gene (YALI0B22308g) containing an intron13. The deletion of YlHXK1 extends the doubling time of the corresponding mutant by approximately 15% compared to the wild strain and makes the yeast unable to grow on fructose13. Y. lipolytica hexokinase has a Km of 0.38 mM and 3.56 mM for glucose and fructose, respectively13. YlHxk1 is extremely sensitive to trehalose-6-phoshpate (T6P), a yeast glycolytic inhibitor, exhibiting a Ki of 0.0036 mM13,17. To date, no other studied hexokinase showed this level of inhibition. Overexpression of YlHXK1 substantially increases carbon flux through glycolysis18, enhances sugar utilization, reduces filamentation, and improves lipid accumulation from fructose in a high-lipid accumulating strain up to 55%19. Additionally, YlHxk1 successfully substitutes hexokinase II from S. cerevisiae (ScHxk2) in glucose catabolite repression of invertase (encoded by SUC2 gene), what indicates the bifunctionality of this protein13. Furthermore, Fickers and colleagues20 reported that the expression of LIP2 gene, encoding an extracellular lipase in Y. lipolytica, is repressed by glucose and that YlHxk1 is involved in this process. It was also reported that YlHxk1 affects expression of several genes involved in erythritol biosynthesis and tricarboxylic acid cycle9. This observation, together with four potential nuclear localization sequences (NLS) in the primary structure of YlHxk113 indicates a bifunctional role of Y. lipolytica hexokinase similar to that of ScHxk2. Moreover, these yeasts show a peculiar carbon source utilization pattern, i.e. it utilizes glycerol first followed by glucose consumption21. Recent findings suggest that YlHxk1 might be involved in the regulation of this process9.
As in many known hexokinases, including ScHxk1, ScHxk2 and Kluyveromyces lactis hexokinase (KlHxk1), the YlHxk1 protein has conserved sugar and ATP binding sequences13,22,23. In ScHxk2, there are amino acid residues crucial for its catalytic activity. For example, D343 (D386 in YlHxk1) is a residue in the heart of the large lobe, away from the sugar binding cleft while E457 (E500 in YlHxk1) is a part of the highly conserved motif in hexokinase family proteins 457EDGSGAGAAV466 (500EDGSGVGAAL509 in YlHxk1) at the C-terminal end24. Mutations of these residues severely affect catalytic activity and substrate recognition and were reported to change the derepression of SUC2 by glucose as in S. cerevisiae hxk2 null mutant24. On the other hand, the S15 is a phosphorylation/dephosphorylation site required for shuttling back and forth of the protein between the nucleus and the cytoplasm25 while the amino acids 7–15 function as NLS in ScHxk226. Although these residues are conserved in YlHxk1, no reports on their functions were provided so far.
The most interesting feature of YlHxk1 is a sequence of 37 amino acids forming a loop structure not present in other known and characterized hexokinases13. The loop region is located after the 146th amino acid residue and flanked by the ATP and glucose binding domains. Until now, the function of this element remains elusive.
Here, we report the structure–function analysis of the hexokinase YlHxk1 of Y. lipolytica. The main emphasis is put on the characterization of the 37-amino acid loop and determination of its potential functions. Both bioinformatic and experimental data are provided to deepen our knowledge on the influence of hexokinase on the central carbon metabolism in Y. lipolytica. Additionally, the kinetic parameters of hexokinase from Yarrowia yakushimensis, the only protein among the Yarrowia clade missing the mysterious loop region, are provided.
Results
The loop region is present in most of the Yarrowia clade yeast species hexokinases
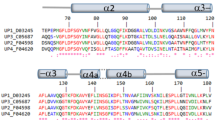
The BLAST analysis of YlHxk1, ScHxk1, ScHxk2 and KlHxk1 showed that the additional amino acid region in YlHxk1 missing in other hexokinases includes 37 residues (148A–184I; Fig. 1A). Here, we were interested whether this unusual element constitutes a general rule in hexokinases of the yeast belonging to the Yarrowia clade27. Sequences alignment (Fig. 1B) of YlHxk1p with 12 other hexokinases showed that the loop is present in all analysed sequences but YayaHxk1p, a Y. yahushimensis hexokinase, in which the loop region is composed of 9 instead of 37 amino acids. The phylogenetic tree (Fig. 1C) and the distance matrix (Supplementary Table S1) showed that YayaHxk1p along with YaphHxk1p and CahiHxk1p are the most distant proteins to YlHxk1. Using SWISS-MODEL (https://swissmodel.expasy.org/) a three-dimensional YlHxk1p model has been built on a K. lactis KlHxk1p hexokinase template (Fig. 2A). The predicted structure shows that the loop is conformationally located outside the catalytic domains and seemingly takes no part in catalytic functions of the enzyme.
(A) Sequence alignment of YlHxk1, ScHxk1, ScHxk2 and KlHxk1; (B) sequence alignment of the loop region of hexokinases in the Yarrowia clade; (C) phylogenetic tree of the hexokinases based on Maximum likelihood. Bootstrap values are shown next to the branches. The tree is drawn to scale, with branch lengths representing the number of substitutions per site.
The loop in YlHxk1 is indispensable for growth on glucose and fructose
To characterize YlHxk1 and to infer biological functions of its elements, a set of Y. lipolytica transformants expressing native and modified YlHxk1 as well as heterologous hexokinases from S. cerevisiae (ScHxk2) and Y. yakushimensis (YayaHxk1) under the control of constitutive TEF promoter (to avoid promoter impact on gene expression) were constructed in a Y. lipolytica Po1d hxk1 glk1 genetic background (Table 1). Constructed strains can be divided into three groups: (1) expressing native hexokinases (YlHxk1, ScHxk2, YayaHxk1); (2) expressing YlHxk1 with deletion of large amino acid sequences (YlHxk1Δ7-15, YlHxk1Δloop, YlHxk1Δ155-182); and (3) expressing YlHxk1 with point mutations (YlHxk1 S15A, YlHxk1 D386E, YlHxk1 E500G, YlHxk1 D386E E500G). Due to the randomness of overexpression cassette incorporation into the genome, three strains of each gene variant were created, resulting in a total of 30 Y. lipolytica strains. Apart from YlHxk1Δloop and YlHxk1Δ155-182, which were created to infer the loop’s role(s), the mutations were introduced in order to compare functions of particular amino acids and sequences to the well-known ScHxk2.
Growth profiles of the obtained transformants in a medium containing glucose, fructose and mixture of both were determined using microplate reader. The experiments revealed that the transformants of each genotype show very similar growth profiles. For that reason, only one strain of each genotype was used for further investigations, reducing the number of strains to 10, which growth profiles are presented in Supplementary Fig. S2.
The microculture experiment showed that Y. lipolytica strain expressing YlHxk1Δloop was unable to grow on neither glucose nor fructose. With that exception, overexpression of all other hexokinases restored the growth on both hexoses of the hxk1 glk1 mutant (Supplementary Fig. S2). All the strains grew faster on glucose than on fructose.
Consistent with the growth profiles, the strain expressing YlHxk1Δloop was unable to use any of the given carbon source in monosubstrate cultures (Fig. 3). The differences in terms of growth and substrate utilization among the other transformants were only subtle.
During cultivation in a medium containing a mixture of glucose and fructose, all strains (except YlHxk1Δloop, which did not grow at all) used glucose prior to fructose (Fig. 4). Some transformants were able to smoothly switch from glucose to fructose utilization (YlHxk1, YlHxk1Δ7-15, YlHxk1 D386E and YlHxk1 D386E E500G), while others showed a longer adaptation period. Interestingly, strains expressing YlHxk1Δ155-182 and YlHxk1 S15A had steep slopes of glucose utilization in the initial 3 h of cultivation. Moreover, the growth profile of the strain YlHxk1 E500G resembled diauxic growth, what could also be observed for YlHxk1 D386E E500G, YlHxk1 S15A and YlHxk1Δ155-182 strains (Fig. 4).
Deletion of the loop in YlHxk1 results in a complete loss of hexokinase activity and hinders binding with an inhibitor
The hexokinase activity measurements in the whole-cell extracts showed that deletion of the 37-amino acid loop in YlHxk1 caused complete loss of activity as for the Y. lipolytica hxk1 glk1 strain (Fig. 5A). All other hexokinases had higher activity towards glucose than fructose. The highest activity for both substrates was shown for enzyme from Y. yakushimensis (YayaHxk1). Interestingly, YlHxk1 enzyme with a short loop (YlHxk1Δ155-182, mimicking YayaHxk1) was much less efficient than the native YlHxk1 with 3.4- and 2.8-fold lower activities for glucose and fructose, respectively (Fig. 5A). In general, all modifications in YlHxk1 decreased its activity, except for the double point mutation (D386E E500G), which increased the activity 1.6- and 1.7-fold for glucose and fructose, respectively, compared to the native YlHxk1.
Deletion of the amino acids 7–15 in YlHxk1 increased its affinity for glucose, with Km value over 5.5-fold lower than for native YlHxk1, a behaviour similar to the S15A substitution, however much more severe. In contrast, the same modifications decreased the affinity of the corresponding enzymes for fructose (Table 2). An opposite situation was observed for YlHxk1 E500G, with an increased affinity for fructose (2.5-fold) and a decreased affinity for glucose (about a half). Analysis of the YlHxk1 with a short loop (YlHxk1Δ155-182) showed increased Km for both substrates, what contrasted to YayaHxk1, the enzyme with naturally short loop, which was characterized by very similar Km values to YlHxk1. The highest Km fold-change for fructose was observed for ScHxk2. Due to the lack of activity, YlHxk1Δloop was not analysed for substrate affinity.
Analysis of the inhibitory constant (Ki) towards the glycolysis inhibitor (T6P) showed over 4.7-fold higher value for YlHxk1 with short loop (YlHxk1Δ155-182) compared to native YlHxk1 (Fig. 5B). On the other hand, D386E and double D386E E500G mutations made YlHxk1 more sensitive to T6P.
Overexpression of hexokinase changes substrate utilization pattern in Y. lipolytica
To further investigate the physiological role of hexokinase in Y. lipolytica and the function of the additional loop, we analysed the utilization of glucose and glycerol in a mixed culture by Y. lipolytica strains overexpressing native YlHxk1 and heterologous YayaHxk1 from Y. yakushimensis. The last one was used due to the lack of the additional loop. In the mixed cultures both strains preferred glucose over glycerol. Only when glucose was almost completely exhausted from the medium, glycerol utilization began (Fig. 6A,B). We also analysed the consumption of both substrates by the wild strains Y. lipolytica W29 and Y. yakushimensis CBS 10253 (Fig. 6C,D). The profile of substrate utilization showed different behaviour of these microorganisms. In contrast to the Y. lipolytica transformants, strains W29 and CBS 10253 consumed glucose and glycerol concomitantly from the beginning of the process, followed by rapid glycerol utilization and inhibition of glucose utilization after the logarithmic growth. Only when glycerol was almost completely exhausted, glucose utilization started again. This resulted in a second growth phase of Y. yakushimensis strain (39th hour; Fig. 6D). Interestingly, Y. yakushimensis required 12- and 24 h more than Y. lipolytica W29 to completely utilize glycerol and glucose, respectively.
The loop in YlHxk1 is important in gene expression regulation
Expression patterns of genes encoding lipases varied depending on the overexpressed hexokinase and in each of the analyzed strains the two most expressed genes were LIP2 and LIP8 (Fig. 7A). The expression patterns can be roughly divided into three sets: (1) set of LIP2 and LIP8; (2) set of LIP9 and (3) set of LIP13 and LIP17. In the first one the overexpression of hexokinase caused severe repression of LIP2 and LIP8. This effect was even more pronounced in a strain expressing YlHxk1 devoid of loop in which LIP2 and LIP8 transcript levels were 0.4- and 3.1-fold lower compared to the YlHxk1 strain, respectively and 5.9- and 70-fold lower when compared to the wild-type, respectively. In the second set consisting of LIP9 alone the hexokinase overexpression regardless of its modification or origin also inhibited lipase expression, however the lowest ΔCq values were observed for YlHxk1Δ155-182 and YayaHxk1 strains. In contrast to the set of LIP2 and LIP8, a mutant with YlHxk1Δloop did not exhibit here such strong repressive effect. Interestingly, in the case of LIP13 and LIP17, which showed very weak signals, the pattern was completely different (Fig. 7A). The overexpression of native hexokinase induced expression of these genes while YlHxk1 without the loop ceased their expression almost entirely. YayaHxk1 and YlHxk1Δ155-182 had similar effect on the transcript levels of LIP13 and LIP17.
Impact of hexokinase on gene expression levels in Y. lipolytica. (A) Transcript levels of lipase-encoding genes; (B) expression of hexose transporters and N-acetylglucosamine transporter (YALI0D09801g); (C) expression of the genes involved in utilization of glycerol (GUT1), acetate (ACS2) and n-alkanes (ALK1).
The impact of hexokinase variants on the expression of the genes involved in utilization of various carbon sources was also analyzed. For hexose transporters, the three genes had three different expression patterns (Fig. 7B). The overexpression of hexokinase did not change the expression of YHT1 except when the loop was deleted. No expression and no changes were observed for YHT3. In the case of YHT4 the deletion of the loop had a strong inducing effect on its expression whereas other mutants exhibited strong repression. Additionally, the overexpression of hexokinase irrespective of its variant decreased transcript levels of the N-acetylglucosamine transporter (YALI0D09801g). Overexpression of YlHxk1 had no real effect on expression of GUT1 (glycerol kinase) with an exception of YlHxk1Δloop which increased the expression 1.5-fold (Fig. 7C). The transcript levels of ACS2 (acetyl-CoA synthetase) and ALK1 (n-alkane inducible cytochrome P450) decreased in a result of hexokinase overexpression but in the case of ACS2 the repression effect was less drastic in the strain overexpressing YlHxk1Δloop.
Discussion
The present study aimed to characterize the hexokinase YlHxk1 of the yeast Y. lipolytica using bioinformatic as well as experimental methods. The protein was previously studied by Petit and Gancedo13. However, we have intended to add an in-depth understanding of its functioning by focusing on different elements of this protein. In particular, we focused on elucidating the role of the 37-amino acid loop in YlHxk1, which to the best of our knowledge is not present in any previously studied hexokinases.
The amino acid sequences alignment of YlHxk1 and other known-hexokinases, including ScHxk2 confirmed the essential difference between these enzymes—the presence of a 37-amino acid loop in YlHxk1. The additional region was also present in almost all hexokinases from the yeast belonging to the Yarrowia clade except for Hxk1 from Y. yakushimensis28. A phylogenetic tree constructed based on amino acid sequences of hexokinases showed that YayaHxk1, YaphHxk1 and the most protruding CahiHxk1 are the most distant proteins in relation to YlHxk1. This phylogeny does not corroborate the species tree previously published from a concatenation of 97 proteins29. This finding suggests that this protein in Y. yakushimensis has undergone a particular evolution, different from that of its counterpart in the other Yarrowia species.
The loop, which function is unknown, has no sequence similarities outside the Yarrowia clade. It prompted us to predict its structure and infer its potential functions. From the three-dimensional YlHxk1 model built using SWISS-MODEL30 on a Kluyveromyces lactis KlHxk1p hexokinase template it was found that the loop is conformationally located outside the canonical domains and seemingly takes no part in its catalytic functions. Yet again, the structure of this loop could not be assigned to any known protein structures by the SWISS-MODEL software. In turn, the YayaHxk1, compared to the other proteins from the Yarrowia clade, has much shorter fragment consisting of only 9 instead of 37 amino acids. The predicted model of YayaHxk1 revealed that this short sequence forms an α-helix, which is not present in YlHxk1 (Fig. 2B). This might stem directly from the chemical nature of the amino acids forming the short loop in YayaHxk1. Similar structure could be obtained by deleting the 155–182 region in YlHxk1 and substituting the sequence 148AHE150 to 148ESS150 as in YayaHxk1 (Supplementary Fig. S3).
The bioinformatic analyses delivered insights into the potential impact of the 37-amino acid loop on the functioning of YlHxk1, which deserved to be verified experimentally. Therefore, we prepared a Y. lipolytica strain deprived of hexose kinases (hxk1 glk1) which was the basis for constructing strains expressing various variants of YlHxk1 and heterologous hexokinases. Except for a strain expressing hexokinase missing the loop (YlHxk1Δloop), all other modifications restored the growth of the corresponding strain on both glucose and fructose. The former modification produced a protein with no hexokinase activity. These results were confirmed by hexokinase activity measurement using whole cell extracts. The protein with loop deletion showed no kinase activity neither for glucose nor for fructose. As this structure is conformationally located outside the active site, we hypothesize that the loop removal causes changes in the enzyme conformation, rendering the protein unable to bind glucose/fructose, ATP or both, what in turn leads to loss of its catalytic function.
The highest hexokinase activity was observed for the Y. lipolytica strain expressing hexokinase from Y. yakushimensis. At the same time, the affinities of YayaHxk1 for both glucose and fructose did not differ from the obtained for strain with YlHxk1. Significantly increased activity compared to YlHxk1 (over 4.5- and 7-fold, for glucose and fructose, respectively) might stem from the environmental adaptation of Y. yakushimensis. This yeast species has only been isolated from a gut of a termite31. Because termites consume dead plants at any level of decomposition32, its microbiome must be adapted to breakdown cellulose33, what in turn generates substantial amount of monosaccharides. It could be hypothesized that high activity of YayaHxk1 is advantageous for growth of Y. yakushimensis in high-sugar concentration environment. As the shorter loop in YayaHxk1 provided a clear improvement in hexokinase activity compared to YlHxk1, it could be expected that YlHxk1 mimicking YayaHxk1 (YlHxk1Δ155-182) would behave in the similar manner. However, that was not the case; alteration in the loop region of YlHxk1 caused severe decrease in activity and affinity for both glucose and fructose. Despite that, it has to be noted that the loop in YayaHxk1 differs from YlHxk1 not only in length, but also in the amino acid residues. It is possible that conformation induced by these residues might positively affect the catalytic activity of YayaHxk1, however, as mentioned above, this idea needs to be verified experimentally.
The strain expressing YlHxk1 with E500G mutation grew similarly on both glucose and fructose. As evidenced by the fold-change in Km compared to the native enzyme, better growth and fructose utilization was a direct effect of increased affinity towards this hexose. On the other hand, this modification caused over twofold decrease in activity for both glucose and fructose compared to the unmodified protein. It was previously reported this mutation in ScHxk2 severely affects catalytic activity and substrate recognition24.
After determining kinetic parameters of hexokinases we set to analyse the impact of introduced modifications on the interactions with inhibitor. T6P is an intermediate in the biosynthesis of trehalose from glucose 6-phosphate and UDP-glucose and functions as a regulator of glycolysis in yeast, filamentous fungi and plants17,34,35,36. Petit and Gancedo13 reported that YlHxk1 is extremely sensitive to inhibition by T6P. In this study we wanted to point out the element of YlHxk1 that evokes this sensitivity. As YlHxk1Δloop lacked activity on glucose and fructose, it was impossible to assess its interaction with T6P. Instead, we used the strain expressing YlHxk1 with a short loop (YlHxk1Δ155-182) that could partially substitute for YlHxk1Δloop in this experiment. YlHxk1Δ155-182 showed significantly higher Ki towards T6P indicating that the loop plays an important role in the enzyme-inhibitor interaction. The S15A substitution also increased Ki, however, much less dramatically than in the case of YlHxk1Δ155-182. The S15A mutation in ScHxk2 causes impairments in phosphorylation and dimerization25. On the other hand, the D386E point mutation increased the sensitivity towards T6P. In S. cerevisiae Hxk2, the consensus amino acids D386 and E500 were associated with derepression of SUC2 gene by glucose as seen in ScHXK2 null mutant, as well as with impairments in catalytic activity and substrate recognition24. However, these mutations have not been associated with T6P.
Following the inhibitory effect of T6P on glycolysis, we hypothesized, that Y. lipolytica may require very strict control of the metabolism at this point and that the very high sensitivity of YlHxk1 to T6P may be the way to slow down the incorporation of glucose when alternative carbon source is present in the medium. In line with this hypothesis, the qRT-PCR analysis showed that TPS1 gene, encoding T6P synthase37, was less expressed during glucose utilization in the wild-type strain (Supplementary Fig. S4). Wild strains of Y. lipolytica prefer glycerol over glucose9,21. However, overexpression of either YlHxk1 or YayaHxk1 reversed the order of substrate consumption. This may be the result of the amount of hexokinase in the cell, which cannot be inhibited by T6P anymore. We also checked the behaviour of the wild Y. yakushimensis strain in the medium with mixture of glucose and glycerol. At first, this species used both substrates simultaneously, followed by inhibition of glucose utilization. Only after glycerol was exhausted from the medium, glucose could be used again. We speculate that this phenomenon may be also partially connected to the differences in the hexokinase structure. However, this hypothesis has to be further investigated. Nonetheless, our research showed a relationship between the loop in YlHxk1 and the inhibition of this protein by T6P.
Apart from the catalytic function, hexokinases also contribute to the regulation of gene expression as a crucial component of the main glucose repression pathway in S. cerevisiae as reviewed in38. The YlHxk1 was previously reported to act in a similar manner to ScHxk2 by repressing LIP2 gene encoding extracellular lipase20, as well as influencing expression of genes involved in tricarboxylic acid cycle and erythritol biosynthesis9. Additionally, YlHxk1 successfully substituted ScHxk2 in repression of the invertase-encoding gene (SUC2) in S. cerevisiae13. The moonlighting proteins such as hexokinase, acting in different cellular compartments, contain certain signal sequence(s) that allow for their transport e.g. from the cytoplasm to the nucleus where the repressor/activator complexes are assembled26,39. The literature data indicates that approximately 10% of ScHxk2 is located in the nucleus and that this localization is important for glucose catabolite repression40. A sequence of two positively charged amino acids flanking three residues, one of which is proline may act as NLS. Petit and Gancedo13 identified four such sequences in YlHxk1: 8KPPSR12, 281KDIPK285, 314KVLPR318 and 527KPGVK513. The bioinformatic tools, such as SeqNLS41 allows to predict NLS using primary protein sequence. According to SeqNLS, YlHxk1p presents only one NLS sequence, 3HLGPRKPPSRK13 (Supplementary Fig. S1) which shows 66.67% identity to the decapeptide 7KKPQARKGSM16, important for nuclear localization of ScHxk240. In the current study, we verified if the 3HLGPRKPPSRK13 fragment of YlHxk1 sequence acts as a NLS. Therefore, we checked the impact of the introduced mutations on the expression of genes encoding lipases and genes responsible for utilization of various carbon sources. Consistent with the study of Fickers et al.20, overexpression of YlHXK1 caused almost twofold reduction of LIP2 expression confirming hexokinase influence on gene expression in Y. lipolytica. The lowest LIP2 expression were observed in strain expressing YlHxk1Δloop while the transcript level in a strain expressing YlHxk1 without suspected NLS was not that much decreased. Similar behaviour was observed for the LIP8 gene expression. Expression of the other analyzed lipases was very low in all strains, however, interesting pattern could be seen for LIP13 and LIP17 as YlHXK1 overexpression induced expression of these genes. For the 7–15 region the obtained result is counter-intuitive. Hexokinase without the NLS should be unable to get into the nucleus. Therefore, expression of the genes including LIP2 and LIP8 could be expected at least at the level of wild-type strain or even elevated. That is the opposite to what we observed in our experiment and due to that we cannot state that 3HLGPRKPPSRK13 is the NLS in YlHxk1.
YlHxk1 without the loop had a strong repressive effect on the YHT1 gene encoding major hexose transporter. Surprisingly, opposite behaviour was observed for YHT4-encoding gene. This observation suggests different regulatory networks playing role in expression of these genes and hexokinase being their important component. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first time the influence of hexokinase on expression of hexose transporter genes was analyzed in Y. lipolytica. In the model yeast S. cerevisiae the transcriptional regulation of hexose transporters occurs via Rgt1-mediated pathway which does not include hexokinase42. Furthermore, from our data it transpires that YlHxk1 plays a role in regulation of expression of other genes including ACS2, ALK1 and GUT1.
Based on the presented results we hypothesize that hexokinase devoid of the loop is easier to transport through the nuclear pore or bind more easily with other proteins forming the repressor complex (e.g. Mig1). It might also be possible that the loop takes part in the recruitment of the transcription machinery. In S. cerevisiae, the main hexokinase (ScHxk2) directly interacts with Mig1 in a cluster with DNA fragments containing the MIG1 binding site e.g. of SUC2 promoter39. Similar interaction may occur in Y. lipolytica, however, further experiments, such as localization study using GFP-fused proteins or yeast two hybrid system, are required. Interestingly, YayaHxk1 successfully substituted for YlHxk1 in repression of most of the genes.
Conclusion
The presented work gives valuable insights into the understanding of hexokinase functioning and more broadly, on sugar assimilation in Y. lipolytica. A substantial progress was achieved by showing that the 37-amino acid extra-loop in the central region of YlHxk1 is essential for activity of this protein and through that on growth on glucose and fructose. Furthermore, hexokinase from Y. yakushimensis (YayaHxk1) containing shorter loop also allows for normal growth, with a much higher enzymatic activity of the corresponding Y. lipolytica transformant on glucose and fructose. Alterations of the loop region and in other amino acids induce a panel of changes in hexokinase activity, affinity towards glucose and fructose as well as sensitivity to T6P. The overexpression of YlHxk1 changes the peculiar pattern of substrate utilization in Y. lipolytica allowing glucose being used more preferably than glycerol. Additionally, our study reveals that overexpression of YlHxk1 and its different variants interferes with the expression of genes encoding lipases, hexose transporters and genes encoding proteins involved in utilization of alternative to glucose or fructose carbon sources. Moreover, the loop region appears to be an important element of YlHxk1 implicated in its regulatory function.
Methods
Media and culture conditions
The strains of Y. lipolytica and Y. yakushimensis were routinely maintained in YPD medium consisting of 10 g/L yeast extract, 10 g/L peptone, 20 g/L glucose or glycerol with 10 g/L agar (for plates) at 28 oC. Minimal (YNB) medium for selection of the Y. lipolytica transformants was prepared using 1.7 g/L yeast nitrogen base (without amino acid and ammonium sulfate, Sigma-Aldrich, Saint Louis, MI), 10 g/L glycerol, 5 g/L NH4Cl, 50 mM phosphate buffer pH 6.8 with 10 g/L agar. The Escherichia coli strains harboring plasmids were cultured overnight in LB medium (5 g/L yeast extract, 10 g/L triptone, 10 g/L NaCl with 10 g/L agar in plates and 0.05 mg/L kanamycin) at 37 °C. For long-term storage the strains were kept at − 80 °C in 500 g/L glycerol.
Plasmid preparation
In this study, two types of plasmids were used. Gene disruption-carrying cassettes were constructed using pCR-Blunt II TOPO vector (Invitrogen, Carlsbad, CA), whereas plasmids used for gene overexpression were based on a JMP62 plasmid19. All genomic sequences were retrieved from GRYC database (http://gryc.inra.fr/).
The disruption cassettes were prepared as described in27. Briefly, 1 kb fragments representing promoter (P) and terminator (T) sequences of YlHXK1 (YALI0B22308g) and YlGLK1 (YALI0E15488g) were amplified by PCR from Y. lipolytica W29 genomic DNA and subsequently fused using PCR-fusion technique. The obtained PT fragments were cloned into pCR-Blunt II TOPO vector. Resulting plasmids were then digested with I-SceI restriction enzyme and the I-SceI digested URA3ex (U) or LEU2ex (L) marker was inserted to obtain the disruption cassettes.
The overexpression cassettes were constructed by PCR amplification of hexokinase from the genomic DNA of Y. lipolytica W29 and genomic DNA of Y. yakushimensis CBS 10253. The mutated versions of Y. lipolytica hexokinase were also prepared and include: YlHxk1Δ7-15, YlHxk1Δloop, YlHxk1Δ155-182, YlHxk1 S15A, YlHxk1 D386E, YlHxk1 E500G, YlHxk1 D386E E500G. Annotated DNA sequence of YlHXK1 is presented on Supplementary Fig. S1. Obtained PCR fragments with the appropriate restriction enzyme sites were then digested and ligated into BamHI/BglII and XmaJI (AvrII) digested JMP62 vector carrying a strong constitutive TEF promoter. All constructs were verified using PCR and DNA-sequencing (Genomed S.A, Warsaw, Poland).
Strain construction
Prior to transformation, the strains were grown overnight on YPD plates. The whole inoculation loop of biomass was suspended in 100 µL of transformation solution consisting of 125 µL of 500 g/L PEG, 6.25 µL of 2 M DTT and 6.25 µL of 2 M LiAc containing 10 µL of NotI digested disruption or overexpression cassettes (500 ng of DNA) and 5 µL carrier DNA (10 mg/mL; Invitrogen, Carlsbad, CA). Prepared cell suspensions were mixed using vortex and incubated at 28 °C for 30 min. Subsequently, the samples were mixed again, incubated at 42 °C for 10 min, plated onto selection media (YNB with glycerol) and incubated at 28 °C for 48 h. The obtained transformants were verified by PCR on their genomic DNA extracted as in43 with appropriate primers (JMP62-pTEF-START and reverse primers for gene amplification). The primers used in this study are listed in Supplementary Table S2 and the strains are presented in Table 1.
Microcultures
The growth profiles of Y. lipolytica strains growing on glucose, fructose and a mixture of both sugars were obtained using a Synergy H1 microplate reader (BioTek Instruments, Winooski, VT). Prior to the experiment, the cells were grown overnight in 5 mL YPD, washed thrice with sterile distilled water to remove any YPD residuals and standardized to OD600 = 10. The cultures were carried out in 96-well microtiter plates (NEST, Wuxi, China) with a working volume of 200 µL, 600 rpm linear shaking and initial OD600 of 0.5. The media consisted of 1.7 g/L YNB, 5 g/L NH4Cl, 50 mM phosphate buffer pH 6.8 and 10 g/L of glucose, or fructose. The temperature was maintained at 28 °C throughout the process. The growth was monitored by measuring optical density in 30 min intervals. Experiments were conducted in three biological replicates.
Substrate utilization kinetics
The kinetics of hexose utilization was performed in 250 mL Erlenmeyer flasks with 50 mL of medium composed of 1.7 g/L YNB, 5 g/L NH4Cl, 50 mM phosphate buffer pH 6.8 and 10 g/L of glucose, fructose or mixture of both. The inoculum was prepared as in the Microcultures subsection. The initial OD600 was set up at 0.5 and cultures were incubated at 28 °C on a rotary shaker with 180 rpm shaking speed. Experiments were conducted in three biological replicates. The samples were taken every 3 h. The growth was monitored by measuring optical density at 600 nm using SmartSpec Plus spectrophotometer (Biorad, Hercules, CA). Monosaccharides concentration was determined using Dionex UltiMate 3000 HPLC instrument (Dionex-Thermo Fisher, UK) equipped with a Carbohydrate H + column (Thermo Scientific, Waltham, MA) coupled to an UV (λ = 210 nm) and RI (Shodex, Ogimachi, Japan) detectors. The column was eluted with 25 mM trifluoroacetic acid (TFA) at 65 °C and a flow rate of 0.6 mL/min.
Kinetics of glucose and glycerol utilization by Y. yakushimensis and Y. lipolytica transformants overexpressing native YlHXK1 and a heterologous YayaHXK1 in a mixed culture were investigated as described above, with 10 g/L of glucose and 10 g/L of glycerol. Experiments were performed in three biological replicates.
Preparation of yeast whole-cell extracts
A volume of 50 mL of YNB medium with glycerol in 250 mL Erlenmeyer flasks were inoculated to OD600 = 0.5 with biomass prepared as in the Microcultures section. The cultures were carried out at 28 °C and 180 rpm for 24 h. The cells were then centrifuged (4500 rpm/5 min/4 °C) and resuspended in an ice-cold PBS buffer pH 7.4. Next, the suspensions were standardized to OD600 = 1 using PBS, transferred to 2 mL Eppendorf tubes with 1/3 volume glass beads (425–600 µm diameter) and homogenized using BeadBug Microtube Homogenizer (Benchmark Scientific, Edison, NJ) at 4000 rpm for 1 min. The procedure was repeated thrice with 2 min incubations on ice between homogenizations. Whole-cell extracts prepared like so were then analysed for protein concentration using Bradford assay44 and standardized to a concentration of 30 µg/mL with PBS for further analyses.
Hexokinase activity assay and Michaelis constant determination
Hexokinase activity in the standardized whole-cell extracts (30 µg/mL protein) was measured with 20 mM glucose or fructose using Hexokinase Colorimetric Assay Kit (Merck, Darmstadt, Germany) according to the supplied protocol and Synergy H1 microplate reader (BioTek). The Michaelis constants (Km) for glucose and fructose were determined by measuring hexokinase activity as described above using 5, 10, 15 and 20 mM of the appropriate hexose. The experiments were performed in three biological replicates.
Trehalose-6 phosphate inhibition assay
The inhibition constants were determined by measuring hexokinase activity in the standardized whole-cell extracts (30 µg/mL protein) with 20 mM glucose as described above with the addition of 0.5, 1, 2.5 and 5 mM trehalose 6-phosphate (Cayman Chemical, Ann Arbor, MI). The inhibition assays were performed in three biological replicates.
Gene expression analysis
Yarrowia lipolytica mutants were cultivated in 250 mL Erlenmeyer flasks with 50 mL of medium composed of 1.7 g/L YNB, 5.1 g/L NH4Cl, 50 mM phosphate buffer pH 6.8 and 2 g/L of glycerol to a mid-exponential growth phase (12 h). From the collected samples, RNA was immediately extracted using Total RNA Mini kit (A&A Biotechnology, Gdynia, Poland) according to the supplied protocol and its concentration and quality was verified using Biochrom WPA Biowave DNA spectrophotometer (Biochrom Ltd., Cambridge, UK) Extracted RNA samples were treated with DNase (A&A Biotechnology, Gdynia, Poland) and reverse transcribed to cDNA using Maxima First Strand cDNA Synthesis Kit for RT-qPCR (Thermo Scientific). The obtained cDNA samples were then used for qPCR reaction using Maxima SYBR Green qPCR Master Mix (Thermo Scientific) and primers listed in Table S2 in the PCRmax Eco 48 thermal cycler (Illumina, San Diego, CA). The expression of analyzed genes was standardized to the expression of actin (YlACT1, YALI0D08272g) gene. The gene expression levels were examined in three biological replicates.
Bioinformatic methods
The amino acid sequences of YlHxk1, ScHxk1, ScHxk2 and K. lactis hexokinase (KlHxk1) were retrieved from the GRYC (http://gryc.inra.fr/) and NCBI databases45. The sequences of the hexokinases from the yeast species of the Yarrowia clade are available in Supplementary File S1; they have been predicted from the genome sequence published by Červenak et al.29. All the amino acid sequences are numbered starting from the initiator methionine. The sequences were compared using Blastp46, aligned with ClustalOmega47 and the resulting alignments were visualized using JalView 2.11.1.048. The three-dimensional models of hexokinases were generated using SWISS-MODEL30 and visualized with PyMOL (The PyMOL Molecular Graphics System, Version 2.4.0, Schrödinger, LLC). A phylogenetic tree for hexokinases was constructed by using the Maximum Likelihood method with the JTT matrix-based model. A discrete Gamma distribution was used to model evolutionary rate differences among sites (4 categories (+G, parameter = 0.9178)). The rate variation model allowed for some sites to be evolutionarily invariable ([+I], 14.63% sites). All positions containing gaps were removed. There were a total of 484 positions in the final dataset. Bootstrap values were calculated from 100 replicates. Evolutionary analyses were conducted in MEGA749. The potential NLS in YlHxk1 were predicted using SeqNLS41.
References
Gao, R. et al. Enhanced lipid production by Yarrowia lipolytica cultured with synthetic and waste-derived high-content volatile fatty acids under alkaline conditions. Biotechnol. Biofuels 13(1), 1–16 (2020).
Gorczyca, M., Kaźmierczak, J., Steels, S., Fickers, P. & Celińska, E. Impact of oxygen availability on heterologous geneexpression and polypeptide secretion dynamics in Yarrowia lipolytica-based protein production platforms. Yeast 37(9–10), 559–568 (2020).
Rakicka, M., Biegalska, A., Rymowicz, W., Dobrowolski, A. & Mirończuk, A. M. Polyol production from waste materials by genetically modified Yarrowia lipolytica. Biores. Technol. 243, 393–399 (2017).
Rymowicz, W., Rywińska, A., Żarowska, B. & Juszczyk, P. Citric acid production from raw glycerol by acetate mutants of Yarrowia lipolytica. Chem. Pap. 60(5), 391–394 (2006).
Rywińska, A., Tomaszewska-Hetman, L., Rakicka-Pustułka, M., Juszczyk, P. & Rymowicz, W. Alpha-ketoglutaric acid production from a mixture of glycerol and rapeseed oil by Yarrowia lipolytica using different substrate feeding strategies. Sustainability 12(15), 6109 (2020).
Wróbel-Kwiatkowska, M., Turski, W., Kocki, T., Rakicka-Pustułka, M. & Rymowicz, W. An efficient method for production of kynurenic acid by Yarrowia lipolytica. Yeast 37(9–10), 541–547 (2020).
Fickers, P., Nicaud, J. M., Gaillardin, C., Destain, J. & Thonart, P. Carbon and nitrogen sources modulate lipase production in the yeast Yarrowia lipolytica. J. Appl. Microbiol. 96(4), 742–749 (2004).
Fukuda, R. & Ohta, A. (2013). Utilization of hydrophobic substrate by Yarrowia lipolytica. In Yarrowia Lipolytica (ed. Barth, G.) 111–119 (Springer, 2013).
Hapeta, P., Kerkhoven, E. J. & Lazar, Z. Nitrogen as the major factor influencing gene expression in Yarrowia lipolytica. Biotechnol. Rep. 27, e00521 (2020).
Lubuta, P., Workman, M., Kerkhoven, E. J. & Workman, C. T. Investigating the influence of glycerol on the utilization of glucose in Yarrowia lipolytica using RNA-Seq-based transcriptomics. G3 Genes Genomes Genet. 9(12), 4059–4071 (2019).
Rywińska, A. et al. Glycerol as a promising substrate for Yarrowia lipolytica biotechnological applications. Biomass Bioenerg. 48, 148–166 (2013).
Workman, M., Holt, P. & Thykaer, J. Comparing cellular performance of Yarrowia lipolytica during growth on glucose and glycerol in submerged cultivations. Amb Express 3(1), 58 (2013).
Petit, T. & Gancedo, C. Molecular cloning and characterization of the gene HXK1 encoding the hexokinase from Yarrowia lipolytica. Yeast 15(15), 1573–1584 (1999).
Conant, G. C. & Wolfe, K. H. Increased glycolytic flux as an outcome of whole-genome duplication in yeast. Mol. Syst. Biol. 3(1), 129 (2007).
Gancedo, J. M., Clifton, D. & Fraenkel, D. G. Yeast hexokinase mutants. J. Biol. Chem. 252, 4443–4444 (1977).
Rose, M., Albig, W. & Entian, K. D. Glucose repression in Saccharomyces cerevisiae is directly associated with hexose phosphorylation by hexokinases PI and PII. Eur. J. Biochem. 199(3), 511–518 (1991).
Blázquez, M. A., Gancedo, J. M. & Gancedo, C. Use of Yarrowia lipolytica hexokinase for the quantitative determination of trehalose 6-phosphate. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 121(2), 223–227 (1994).
Qiang, S. et al. Promoting the synthesis of precursor substances by overexpressing Hexokinase (Hxk) and Hydroxymethylglutaryl-CoA Synthase (Erg13) to elevate β-carotene production in engineered Yarrowia lipolytica. Front. Microbiol. 11, 1346 (2020).
Lazar, Z., Dulermo, T., Neuvéglise, C., Crutz-Le Coq, A. M. & Nicaud, J. M. Hexokinase—a limiting factor in lipid production from fructose in Yarrowia lipolytica. Metab. Eng. 26, 89–99 (2014).
Fickers, P., Nicaud, J. M., Destain, J. & Thonart, P. Involvement of hexokinase Hxk1 in glucose catabolite repression of LIP2 encoding extracellular lipase in the yeast Yarrowia lipolytica. Curr. Microbiol. 50(3), 133–137 (2005).
Rywińska, A., Rymowicz, W., Żarowska, B. & Skrzypiński, A. Comparison of citric acid production from glycerol and glucose by different strains of Yarrowia lipolytica. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 26(7), 1217–1224 (2014).
Kuettner, E. B. et al. Crystal structure of hexokinase KlHxk1 of Kluyveromyces lactis a molecular basis for understanding the control of yeast hexokinase functions via covalent modification and oligomerization. J. Biol. Chem. 285(52), 41019–41033 (2010).
Kuser, P. R., Krauchenco, S., Antunes, O. A. & Polikarpov, I. The high resolution crystal structure of yeast hexokinase PII with the correct primary sequence provides new insights into its mechanism of action. J. Biol. Chem. 275(27), 20814–20821 (2000).
Hohmann, S. et al. Novel alleles of yeast hexokinase PII with distinct effects on catalytic activity and catabolite repression of SUC2. Microbiology 145(3), 703–714 (1999).
Fernández-García, P., Peláez, R., Herrero, P. & Moreno, F. Phosphorylation of yeast hexokinase 2 regulates its nucleocytoplasmic shuttling. J. Biol. Chem. 287(50), 42151–42164 (2012).
Peláez, R., Herrero, P. & Moreno, F. Functional domains of yeast hexokinase 2. Biochem. J. 432(1), 181–190 (2010).
Fickers, P., Le Dall, M. T., Gaillardin, C., Thonart, P. & Nicaud, J. M. New disruption cassettes for rapid gene disruption and marker rescue in the yeast Yarrowia lipolytica. J. Microbiol. Methods 55(3), 727–737 (2003).
Michely, S., Gaillardin, C., Nicaud, J. M. & Neuvéglise, C. Comparative physiology of oleaginous species from the Yarrowia clade. PLoS One 8(5), e63356 (2013).
Červenák, F. et al. Identification of telomerase RNAs in species of the Yarrowia clade provides insights into the co-evolution of telomerase, telomeric repeats and telomere-binding proteins. Sci. Rep. 9(1), 1–15 (2019).
Waterhouse, A. et al. SWISS-MODEL: Homology modelling of protein structures and complexes. Nucleic Acids Res. 46(W1), W296–W303 (2018).
Groenewald, M. & Smith, M. T. The teleomorph state of Candida deformans Langeron & Guerra and description of Yarrowia yakushimensis comb. Nov.. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 103(5), 1023–1028 (2013).
Eggleton, P. An introduction to termites: Biology, taxonomy and functional morphology. In Biology of Termites: A Modern Synthesis 1st edn (eds Bignell, D. E. et al.) 1–26 (Springer, 2010).
Bashir, Z. et al. Diversity and functional significance of cellulolytic microbes living in termite, pill-bug and stem-borer guts. Sci. Rep. 3, 2558 (2013).
Arisan-Atac, I., Wolschek, M. F. & Kubicek, C. P. Trehalose-6-phosphate synthase A affects citrate accumulation by Aspergillus niger under conditions of high glycolytic flux. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 140(1), 77–83 (1996).
Deroover, S., Ghillebert, R., Broeckx, T., Winderickx, J. & Rolland, F. Trehalose-6-phosphate synthesis controls yeast gluconeogenesis downstream and independent of SNF1. FEMS Yeast Res. 16, 4 (2016).
Ponnu, J., Wahl, V. & Schmid, M. Trehalose-6-phosphate: Connecting plant metabolism and development. Front. Plant Sci. 2, 70 (2011).
Flores, C. L., Gancedo, C. & Petit, T. Disruption of Yarrowia lipolytica TPS1 gene encoding trehalose-6-P synthase does not affect growth in glucose but impairs growth at high temperature. PLoS One 6, 9 (2011).
Simpson-Lavy, K. & Kupiec, M. Carbon catabolite repression in yeast is not limited to glucose. Sci. Rep. 9(1), 1–10 (2019).
Ahuatzi, D., Herrero, P., De La Cera, T. & Moreno, F. The glucose-regulated nuclear localization of hexokinase 2 in Saccharomyces cerevisiae is Mig1-dependent. J. Biol. Chem. 279(14), 14440–14446 (2004).
Herrero, P., Martı́nez-Campa, C. & Moreno, F. The hexokinase 2 protein participates in regulatory DNA-protein complexes necessary for glucose repression of the SUC2 gene in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. FEBS Lett. 434(1–2), 71–76 (1998).
Lin, J. R. & Hu, J. SeqNLS: Nuclear localization signal prediction based on frequent pattern mining and linear motif scoring. PLoS One 8(10), 76864 (2013).
Kim, J. H. & Johnston, M. Two glucose-sensing pathways converge on Rgt1 to regulate expression of glucose transporter genes in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J. Biol. Chem. 281(36), 26144–26149 (2006).
Querol, A., Barrio, E., Huerta, T. & Ramón, D. Molecular monitoring of wine fermentations conducted by active dry yeast strains. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 58(9), 2948–2953 (1992).
Bradford, M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal. Biochem. 72(1–2), 248–254 (1976).
Sayers, E. W. et al. Database resources of the national center for biotechnology information. Nucleic Acids Res. 48(D1), D9 (2020).
Altschul, S. F., Gish, W., Miller, W., Myers, E. W. & Lipman, D. J. Basic local alignment search tool. J. Mol. Biol. 215(3), 403–410 (1990).
Sievers, F. et al. Fast, scalable generation of high-quality protein multiple sequence alignments using Clustal Omega. Mol. Syst. Biol. 7(1), 539 (2011).
Waterhouse, A. M., Procter, J. B., Martin, D. M., Clamp, M. & Barton, G. J. Jalview Version 2—a multiple sequence alignment editor and analysis workbench. Bioinformatics 25(9), 1189–1191 (2009).
Kumar, S., Stecher, G. & Tamura, K. MEGA7: Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 7.0 for bigger datasets. Mol. Biol. Evol. 33(7), 1870–1874 (2016).
Juretzek, T. et al. Vectors for gene expression and amplification in the yeast Yarrowia lipolytica. Yeast 18(2), 97–113 (2001).
Acknowledgements
Authors would like to thank Prof. Carlos Gancedo for valuable discussions. PH acknowledges funding from Wroclaw University of Environmental and Life Sciences (“Innowacyjny Doktorat”, Grant no. D220/0006/17); PS received the financial support in the form of "BioTechNan—Interdisciplinary Environmental Doctoral Program KNOW in the field of Biotechnology and Nanotechnology". The project is co-financed by the European Union—European Social Fund—3.2 Doctoral studies of the Operational Program Knowledge, Education and Development 2014-2020. The publication is financed under the Leading Research Groups support project from the subsidy increased for the period 2020–2025 in the amount of 2% of the subsidy referred to Art. 387 (3) of the Law of 20 July 2018 on Higher Education and Science, obtained in 2019.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
P.H.—designed the experiments, performed bioinformatic analysis, strain construction, microcultivations, glucose and fructose utilization kinetics, enzymatic assays, qRT-PCR analyses, interpreted the data, wrote the manuscript; P.S.—performed glucose and glycerol utilization kinetics, qRT-PCR analyses, interpreted the data; C.N.—performed bioinformatic analysis, phylogenetic analysis, interpreted the data; Z.L.—conceptualized the research, designed the experiments, performed enzymatic assays, interpreted the data. All authors reviewed the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
About this article
Cite this article
Hapeta, P., Szczepańska, P., Neuvéglise, C. et al. A 37-amino acid loop in the Yarrowia lipolytica hexokinase impacts its activity and affinity and modulates gene expression. Sci Rep 11, 6412 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-021-85837-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-021-85837-8
- Springer Nature Limited
This article is cited by
-
High value-added products derived from crude glycerol via microbial fermentation using Yarrowia clade yeast
Microbial Cell Factories (2021)