Abstract
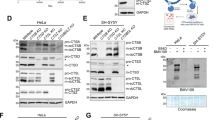
γ-Secretase is a membrane protein complex with an unusual aspartyl protease activity that catalyses the regulated intramembranous cleavage of the β-amyloid precursor protein (APP) to release the Alzheimer's disease (AD)-associated amyloid β-peptide (Aβ) and the APP intracellular domain (AICD)1. Here we show the reconstitution of γ-secretase activity in the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae, which lacks endogenous γ-secretase activity. Reconstituted γ-secretase activity depends on the presence of four complex components including presenilin (PS)1, nicastrin (Nct)2, APH-1 (refs 3–6) and PEN-2 (refs 4, 7), is associated with endoproteolysis of PS8, and produces Aβ and AICD in vitro. Thus, the biological activity of γ-secretase is reconstituted by the co-expression of human PS, Nct, APH-1 and PEN-2 in yeast.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Haass, C. & Steiner, H. Trends Cell Biol. 12, 556–562 (2002).
Yu, G. et al. Nature 407, 48–54 (2000).
Goutte, C., Tsunozaki, M., Hale, V.A. & Priess, J.R. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 99, 775–779 (2002).
Francis, R. et al. Dev. Cell 3, 85–97 (2002).
Lee, S.F. et al. J. Biol. Chem. 277, 45013–45019 (2002).
Gu, Y. et al. J. Biol. Chem. 278, 7374–7380 (2002).
Steiner, H. et al. J. Biol. Chem. 277, 39062–39065 (2002).
Thinakaran, G. et al. Neuron 17, 181–190 (1996).
Esler, W.P. et al. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 99, 2720–2725. (2002).
Edbauer, D., Winkler, E., Haass, C. & Steiner, H. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 99, 8666–8671 (2002).
Steiner, H., Pesold, B. & Haass, C. FEBS Lett. 463, 245–249 (1999).
Wolfe, M.S. et al. Nature 398, 513–517 (1999).
Li, Y.M. et al. Nature 405, 689–694 (2000).
Yu, C. et al. J. Biol. Chem. 276, 43756–43760 (2001).
Sastre, M. et al. EMBO Rep. 2, 835–841 (2001).
Acknowledgements
We thank R. Nixon, A. Diehlmann and C. Miller for reagents, G. Basset for technical assistance and S. Eimer, H. Feldmann and B. Meier for helpful discussion. This work was supported by the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft, the DIADEM project funded by the European Community, and the National Genome Research Network (NGFN).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Edbauer, D., Winkler, E., Regula, J. et al. Reconstitution of γ-secretase activity. Nat Cell Biol 5, 486–488 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1038/ncb960
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/ncb960
- Springer Nature Limited
This article is cited by
-
Enzyme-substrate hybrid β-sheet controls geometry and water access to the γ-secretase active site
Communications Biology (2023)
-
Cooperation of N- and C-terminal substrate transmembrane domain segments in intramembrane proteolysis by γ-secretase
Communications Biology (2023)
-
Alzheimer’s disease – the journey of a healthy brain into organ failure
Molecular Neurodegeneration (2022)
-
γ-Secretase in Alzheimer’s disease
Experimental & Molecular Medicine (2022)
-
Contributive Role of Hyperglycemia and Hypoglycemia Towards the Development of Alzheimer’s Disease
Molecular Neurobiology (2022)