Abstract
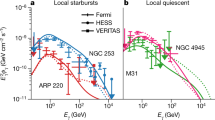
The Milky Way is known to be an abundant source of γ-ray photons1, now determined to be mainly diffuse in nature and resulting from interstellar processes2. In the soft γ-ray domain, point sources are expected to dominate, but the lack of sensitive high-resolution observations did not allow for a clear estimate of the contribution from such sources3,4. Even the best imaging experiment5 revealed only a few point sources, accounting for about 50% of the total Galactic flux6. Theoretical studies were unable to explain the remaining intense diffuse emission7,8. Investigating the origin of the soft γ-rays is therefore necessary to determine the dominant particle acceleration processes and to gain insights into the physical and chemical equilibrium of the interstellar medium7. Here we report observations in the soft γ-ray domain that reveal numerous compact sources. We show that these sources account for the entirety of the Milky Way's emission in soft γ-rays, leaving at most a minor role for diffuse processes.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Schönfelder, V. The Universe in Gamma Rays (A&A Library, Springer, 2001)
Strong, A. W., Moskalenko, I. V. & Reimer, O. Diffuse continuum gamma rays from the Galaxy. Astrophys. J. 537, 763–784 (2000)
Kinzer, R. L., Purcell, W. R. & Kurfess, J. D. Gamma-ray emission from the inner Galactic ridge. Astrophys. J. 515, 215–225 (1999)
Valinia, A., Kinzer, R. L. & Marshall, F. E. Measurement of the Galactic X-ray/gamma-ray background radiation: contribution of point sources. Astrophys. J. 534, 277–282 (2000)
Paul, J. et al. SIGMA: the hard X-ray and soft gamma-ray telescope on board the GRANAT space observatory. Adv. Space Res. 11, (8)289–(8)302 (1991)
Purcell, W. R. et al. Diffuse galactic gamma-ray continuum. Astron. Astrophys. Suppl. Ser. 120, 389–392 (1996)
Pohl, M. Limits for an inverse bremsstrahlung origin of the diffuse Galactic soft gamma-ray emission. Astron. Astrophys. 339, 587–590 (1998)
Dogiel, V. A., Inoue, H., Schönfelder, V. & Strong, A. W. The origin of diffuse X-ray emission from the Galactic ridge. I. Energy output of particle sources. Astrophys. J. 581, 1061–1070 (2002)
Webber, W. R. in Composition and Origin of Cosmic Rays (ed. Shapiro, M. M.) 83–100 (Boston, Dordrecht, 1983)
Skibo, J. G., Ramaty, R. & Purcell, W. R. Implications of the diffuse Galactic continuum. Astron. Astrophys. Suppl. Ser. 120, 403–406 (1996)
Lebrun, F. et al. Nature of the Galactic soft gamma-ray emission. Astrophys. Lett. Commun. 38, 457–460 (1999)
Winkler, C. et al. The INTEGRAL mission. Astron. Astrophys. 411, L1–L6 (2003)
Ubertini, P. et al. IBIS: the imager on-board INTEGRAL. Astron. Astrophys. 411, L131–L139 (2003)
Vedrenne, G. et al. The spectrometer aboard INTEGRAL. Astron. Astrophys. 411, L63–L70 (2003)
Lebrun, F. et al. ISGRI: the INTEGRAL Soft Gamma-Ray Imager. Astron. Astrophys. 411, L141–L148 (2003)
Goldwurm, A. et al. The INTEGRAL/IBIS scientific data analysis. Astron. Astrophys. 411, L223–L229 (2003)
Walter, R. et al. INTEGRAL discovery of a bright highly obscured galactic X-ray binary source IGR J16318–4848. Astron. Astrophys. 411, L427–L432 (2003)
Strong, A. W. et al. Diffuse continuum emission from the inner Galaxy: first results from INTEGRAL/SPI. Astron. Astrophys. 411, L447–L450 (2003)
Wang, Q. D., Gotthelf, E. V. & Lang, C. C. A faint discrete source origin for the highly ionized iron emission from the Galactic centre region. Nature 415, 148–150 (2002)
Gros, A. et al. The INTEGRAL IBIS/ISGRI point spread function and source location accuracy. Astron. Astrophys. 411, L179–L183 (2003)
Acknowledgements
This paper is based on observations with INTEGRAL, an ESA project with instruments and science data centre funded by ESA member states (especially the PI countries: Denmark, France, Germany, Italy, Switzerland and Spain), the Czech Republic and Poland, and with the participation of Russia and the USA. We thank CNES for its support during the ISGRI development and in the INTEGRAL data analysis.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing financial interests.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lebrun, F., Terrier, R., Bazzano, A. et al. Compact sources as the origin of the soft γ-ray emission of the Milky Way. Nature 428, 293–296 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1038/nature02407
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nature02407
- Springer Nature Limited
This article is cited by
-
Gamma-ray telescopes
Experimental Astronomy (2009)
-
Prospects in space-based gamma-ray astronomy
Experimental Astronomy (2006)