Abstract
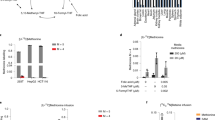
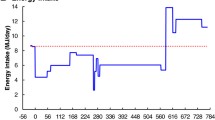
The metabolism of (2-14C) + (3',5',7,9-3H) folic acid was studied in normal rats, tumour-bearing rats and rats treated with methotrexate (MTX). The experiments were designed to investigate changes in the catabolism and folate. The breakdown of folate to scission products was again demonstrated to be a normal phenomenon. Catabolites excreted included p-acetamidobenzoate, p-acetamidobenzoyl-L-glutamate, 3H2O, urea and a number of pterins. The catabolic process was decreased in the presence of a tumour and increased by the administration of MTX. MTX also led to the excretion of 4 additional radioactive pterins not found in normal urine. The possible mechanisms of folate breakdown are discussed with reference to the point of action of MTX.
Similar content being viewed by others
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Saleh, A., Pheasant, A. & Blair, J. Folate catabolism in tumour-bearing rats and rats treated with methotrexate. Br J Cancer 44, 700–708 (1981). https://doi.org/10.1038/bjc.1981.256
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/bjc.1981.256
- Springer Nature Limited