Abstract
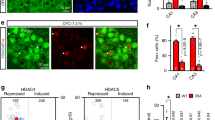
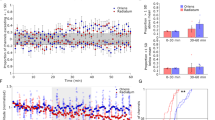
The hippocampus is required for many forms of long-term memory in both humans and animals1, and formation of long-lasting memories requires the synthesis of new proteins2. Furthermore, the long-term potentiation (LTP) of hippocampal synapses, a widely studied model of memory, also depends on both de novo gene transcription and protein synthesis3 and results in the activation of transcription from promotors containing the cAMP response element (CRE)4. Expression of several genes is induced during the establishment of LTP; these include the immediate-early genes (IEGs) BDNF (brain-derived neurotrophic factor), zif268 and C/EBPβ (CCAAT-enhancer binding protein β), all of which contain CRE sites within their promotor regions3,5. However, these genes induced by LTP are not known to be rapidly induced following learning in a natural setting. Here we demonstrate rapid and selective induction of BDNF expression during hippocampus-dependent contextual learning.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Milner, B., Squire, L. R. & Kandel, E. R Neuron 20, 445–468 (1998).
Davis, H. P. & Squire, L. R. Psychol. Bull. 96, 518–559 (1984).
Thomas, K. L. & Hunt, S. P. in Cortical Plasticity: LTP and LTD. (eds. Fazeli, M. S. & Collingridge, G. L.) 103–136 (BIOS Scientific, Oxford, 1996).
Impey, S. et al. Neuron 16, 973–982 (1996).
Tao, X., Finkbeiner, S., Arnold, D. B., Shaywitz, A. J. & Greenberg, M. E. Neuron 20, 709–726 (1998).
Impey, S. et al. Nat. Neurosci. 1, 595–601 (1998).
Kiernan, M. J. & Westbrook, R. F. Q. J. Exp. Psychol. B 46, 271–288 (1993).
Fanselow, M. Anim. Learn. Behav. 18, 264–270 (1990).
Wisden, W. & Morris, B. J. in In Situ Hybridisation Protocols for the Brain (eds. Wisden, W. & Morris, B. J.) 9–34 (Academic, London, 1994).
Fanselow, M. S. & LeDoux, J. E. Neuron 23, 229–232 (1999).
Patterson, S. L., Grover, L. M., Schwartzkroin, P. A. & Bothwell, M. Neuron 9, 1081–1088 (1992).
Korte, M. et al. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 92, 8856–8860 (1995).
Minichiello, L. et al. Neuron 24, 401–414 (1999).
Bannerman, D. M., Good, M. A., Butcher, S. P., Ramsay, M. & Morris, R. G. M. Nature 378, 182–186 (1995).
Linnarsson, S., Bjorklund, A. & Ernfors, P. Eur. J. Neurosci. 9, 2581–2587 (1997).
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by an MRC Programme Grant G9537855 and an MRC Co-operative in Brain, Behaviour and Neuropsychiatry. J.H. was supported by Trinity College, Cambridge under an MD/Ph.D. program. We thank Caroline Morrison for technical assistance.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hall, J., Thomas, K. & Everitt, B. Rapid and selective induction of BDNF expression in the hippocampus during contextual learning. Nat Neurosci 3, 533–535 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1038/75698
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/75698
- Springer Nature America, Inc.
This article is cited by
-
Glucose may Contribute to Retrieval and Reconsolidation of Contextual Fear Memory Through Hippocampal Nr4a3 and Bdnf mRNA Expression and May Act Synergically with Adrenaline
Molecular Neurobiology (2024)
-
Novelty-induced memory consolidation is accompanied by increased Agap3 transcription: a cross-species study
Molecular Brain (2023)
-
TrkC Intracellular Signalling in the Brain Fear Network During the Formation of a Contextual Fear Memory
Molecular Neurobiology (2023)
-
The effects of interval training on peripheral brain derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) in young adults: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Scientific Reports (2021)
-
Rottlerin, BDNF, and the impairment of inhibitory avoidance memory
Psychopharmacology (2021)