Abstract
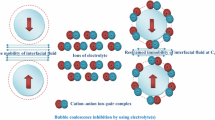
THE foaminess of ocean waves, relative to fresh water, has long been attributed to the effect of salts in reducing bubble coalescence9. This phenomenon is exploited in extraction processes using froth flotation1, in which the extraction efficiency increases as the bubble size gets smaller. But whereas the bubble-stabilizing effect of surfactants is well understood, the effect of salts is not; the fact that salts decrease the surface tension of water and that they are desorbed from the air–water interface would, if anything, be expected to destabilize bubbles. Here we report the results of experiments conducted to study the stabilization of bubbles by salts. We find that bubble coalescence is inhibited by some salts whereas others have no effect and that this inhibition occurs only upon the 'matching' of a two-valued empirical property assigned to each anion and cation. We believe these observations can be explained only by the local influence of the ions on water structure, possibly in a way related to the hydrophobic interaction2–8.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Klasson, V. I. & Mokrousov, V. A. An Introduction to the Theory of Flotation (Butterworths, London, 1963).
Israelachvilli, J. N. & Pashley, R. M. Nature 300, 341–342 (1982).
Pashley, R. M., McGuiggan, P. M., Ninham, B. W. & Fennell Evans, D. Science 299, 1088–1089 (1985).
Claesson, P. M., Blom, C. E., Herder, P. C. & Ninham, B. W. J. Coll. Int. Sci. 114, 234–242 (1986).
Rabinovich, Y. I. & Derjaguin, B. V. Coll. Surf. 30, 243–251 (1988).
Christenson, H. K., Claesson, P. M. & Pashley, R. M. Proc. Ind. Acad. Sci. (Chem. Sci.) 98, 379–389 (1987).
Christenson, H. K. & Claesson, P. M. Science 239, 390–392 (1988).
Christenson, H. K., Fang, J., Ninham, B. W. & Parker, J. L. J. phys. Chem. 94, 8004–8006 (1990).
Lessard, R. R. & Zieminski, S. A. Ind. Eng. Chem. Fundam. 10, 260–269 (1971).
Collins, G. L. & Jameson, G. J. Chem. Eng. Sci. 31, 985–991 (1976).
Chan, D. Y. C. & Horn, R. G. J. chem. Phys. 83, 5311–5324 (1985).
Blake, T. D. & Kitchener, J. A. J. chem. Soc. Farad. Trans. I. 68, 1435–1442 (1972).
Cain, F. W. & Lee, J. C. J. Coll. Int. Sci. 106, 70–85 (1985).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Craig, V., Ninham, B. & Pashley, R. Effect of electrolytes on bubble coalescence. Nature 364, 317–319 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1038/364317a0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/364317a0
- Springer Nature Limited
This article is cited by
-
Effect of Sodium and Potassium Ions on the Flotation of Low-Rank Coal in the Presence of Different Collectors: A Theoretical and Experimental Study
Mining, Metallurgy & Exploration (2024)
-
Effect of chemical species and temperature on the stability of air nanobubbles
Scientific Reports (2023)
-
Key Factors and Changing Rules of Foam Stability in Gas Well Field
Chemistry and Technology of Fuels and Oils (2023)
-
In situ measurements of void fractions and bubble size distributions in bubble curtains
Experiments in Fluids (2023)
-
Virus and bacteria inactivation by CO2 bubbles in solution
npj Clean Water (2019)