Abstract
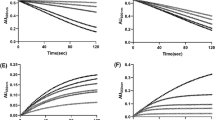
SUB-MITOCHONDRIAL particles prepared from horse or ox heart contain two species of cytochrome b in equal amounts, one (bi) affected by antimycin and the other (b) not affected1–3. In addition to its well known inhibitory effect on the respiratory chain, acting between cytochromes b and c1, antimycin brings about an increased reduction of the total cytochrome b present in sub-mitochondrial particles and causes a shift in absorption of 1–2 nm towards longer wavelengths of the b band. This “redshift” is best studied with the wavelength pair 566–560 nm, for the absorption maximum of ferrocytochrome b is at 563 nm, and A566–560 nm is not affected by the redox state of cytochrome b (ref. 1). Sigmoidal curves for the antimycin effect are found with sub-mitochondrial particles4 and with intact white potato (W. D. Bonner and E. C. S., unpublished) or rat heart (H. J. W., J. A. B. and E. C. S., unpublished) mitochondria in the presence of uncoupler, and linear (or hyperbolic) with energized mitochondria (state 4). To explain these antimycin effect curves, it is proposed that antimycin, a multi-site inhibitor in particles, reacts preferentially with and stabilizes a high-energy form of cytochrome bi (bi∼X) (refs. 4 and 5).
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chance, B., J. Biol Chem., 233, 1223 (1958).
Slater, E. C., and Colpa-Boonstra, J. P., in Haematin Enzymes (edit. by Falk, J. E., Lemberg, R., and Morton, R. K.), 2, 575 (Pergamon, London, 1961).
Berden, J. A., and Slater, E. C., Biochim. Biophys. Acta (in the press).
Bryla, J., Kaniuga, Z., and Slater, E. C., Biochim. Biophys. Acta, 189, 317 (1969).
Slater, E. C., Koninkl. Nederl. Akad. Wetenschappen, Natuurkunde, 78, 123 (1969).
Fessenden, J. M., and Racker, E., J. Biol. Chem., 241, 2483 (1966).
Lee, C. P., Azzone, G. F., and Ernster, L., Nature, 201, 152 (1964).
Löw, H., and Vallin, I., Biochim. Biophys. Acta, 69, 361 (1963).
Wilson, D. F., and Dutton, P. L., Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun., 39, 59 (1970).
Chance, B., and Williams, G. R., Adv. Enzymol., 17, 65 (1956).
Slater, E. C., Nature, 172, 975 (1953).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
SLATER, E., LEE, C., BERDEN, J. et al. High-energy Forms of Cytochrome b. Nature 226, 1248–1249 (1970). https://doi.org/10.1038/2261248a0
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/2261248a0
- Springer Nature Limited
This article is cited by
-
Detection of conformational changes in Complex III of the respiratory chain by a maleimido spin label
Journal of Bioenergetics and Biomembranes (1979)
-
Oxidative phosphorylation, a history of unsuccessful attempts: Is it only an experimental problem?
Journal of Bioenergetics (1972)