Abstract
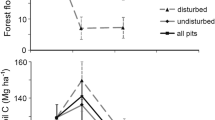
Present understanding of the global carbon cycle is limited by uncertainty over soil-carbon dynamics1,2,3,4,5,6. The clearing of the world's forests, mainly for agricultural uses, releases large amounts of carbon to the atmosphere (up to 2× 1015 g yr−1), much of which arises from the cultivation driving an accelerated decomposition of soil organic matter1,2,3,4. Although the effects of cultivation on soil carbon are well studied, studies of soil-carbon recovery after cultivation are limited4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11. Here we present a four-decade-long field study of carbon accumulation by pine ecosystems established on previously cultivated soils in South Carolina, USA7. Newly accumulated carbon is tracked by its distinctive 14C signature, acquired around the onset of forest growth from thermonuclear bomb testing that nearly doubled atmospheric 14CO2 in the 1960s. Field data combined with model simulations indicate that the young aggrading forest rapidly incorporated bomb radiocarbon into the forest floor and the upper 60 cm of underlying mineral soil. By the 1990s, however, carbon accumulated only in forest biomass, forest floor, and the upper 7.5 cm of the mineral soil. Although the forest was a strong carbon sink, trees accounted for about 80%, the forest floor 20%, and mineral soil <1%, of the carbon accretion. Despite high carbon inputs to the mineral soil, carbon sequestration was limited by rapid decomposition, facilitated by the coarse soil texture and low-activity clay mineralogy.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Schimel, D. S. Terrestrial ecosystems and the carbon cycle. Glob. Change Biol. 1, 77–91 (1995).
Oades, J. M. The retention of organic matter in soils. Biogeochemistry 5, 35–70 (1994).
Smith, T. M. et al . The global terrestrial carbon cycle. Wat. Air Soil Pollut. 70, 19–37 (1993).
Schlesinger, W. H. Biogeochemistry (Academic, Orlando, (1997).
Johnson, D. W. & Todd, D. E. in Management of Carbon Sequestration in Soil (eds Lal, R., Kimble, J. M., Follett, R. F. & Stewart, B. A.) 351–363 (CRC Press, Boca Raton, Florida, (1998).
Schlesinger, W. H. Evidence from chronosequence studies for a low carbon-storage potential of soils. Nature 348, 232–234 (1990).
Richter, D. D. & Markewitz, D. in Evaluation of Soil Organic Matter Models (eds Powlson, D., Smith, P. & Smith, J.) 397–407 (NATO ASI Ser. Vol. I 38, Springer, Berlin, (1996).
Jenkinson, D. S. The Rothamsted classical experiments: Are they still of use? Agron. J. 83, 2–10 (1991).
Leigh, R. A. & Johnston, A. E. Long-term Experiments in Agricultural and Ecological Sciences (CAB International, Wallingford, UK, (1994).
Harrison, K. G., Post, W. M. & Richter, D. D. Soil carbon turnover in a recovering temperate forest. Glob. Biogeochem. Cycles 9, 449–454 (1995).
Smith, P., Powlson, D. S., Smith, J. U. & Elliott, E. T. (eds) Evaluation and comparison of soil organic matter models. Geoderma 81, 1–225 (1997).
Likens, G. E. (ed.) Long-term Studies in Ecology: Approaches and Alternatives (Springer, New York, (1989).
Risser, P. (ed.) Long-term Ecological Research: An International Perspective (SCOPE, Wiley, New York, (1991).
Powers, R. & Van Cleve, K. Long-term ecological research in temperate and boreal forest ecosystems. Agron. J. 83, 11–24 (1991).
Tilman, D. et al . in Long-term Experiments in Agricultural and Ecological Sciences (eds Leigh, R. A. & Johnston, A. E.) 305–319 (CAB International, Wallingford, UK, (1994).
Richter, D. D. & Markewitz, D. The Biogeochemistry of a Forested Soil (Cambridge Univ. Press, in the press).
Wells, C. G. & Jorgensen, J. R. in Forest Soils and Forest Land Management (eds Bernier, B. & Winget, C. H.) 137–158 (Laval Univ. Press, Quebec, (1975).
Richter, D. D. et al . Soil chemical change during three decades in an old-field loblolly pine (Pinus taeda L.) ecosystem. Ecology 75, 1463–1473 (1994).
Markewitz, D. et al . Three decades of observed soil acidification in the Calhoun Experimental Forest: Has acid rain made a difference? Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 62, 1428–1439 (1998).
Richter, D. D. & Babbar, L. I. Soil diversity in the tropics. Adv. Ecol. Res. 21, 315–389 (1991).
Buol, S. A., Hole, F. D., McCracken, R. J. & Southard, R. J. Soil Genesis and Classification (Iowa State Univ. Press, Ames, (1997).
Jorgensen, J., Wells, C. G. & Metz, L. J. Nutrient changes in decomposing loblolly pine forest floor. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 44, 1307–1314 (1980).
Vogt, K. et al . Organic matter and nutrient dynamics in forest floors in young and mature Abies amabilis stands in western Washington, as affected by fine-root input. Ecol. Monogr. 53, 139–157 (1993).
Ruark, G. A. Modeling soil temperature effects on in situ decomposition rates for fine roots of loblolly pine. Forest Sci. 39, 118–129 (1993).
Van Lear, D. H., Kapeluck, P. R. & Parker, M. M. in Carbon Forms and Functions in Forest Soils (eds McFee, W. W. & Kelly, J. M.) 489–501 (Soil Science Soc. of America, Madison, Wisconsin, (1995).
Torn, M. S., Trumbore, S. E., Chadwick, O. A., Vitousek, P. M. & Hendricks, D. M. Mineral control of soil organic carbon storage and turnover. Nature 389, 170–173 (1997).
Trumbore, S. A. in Mass Spectrometry of Soils (eds Boutton, T. & Yamasaki, S.) 311–340 (Dekker, New York, (1996).
Urrego, M. J. B. Nutrient Accumulation in Biomass and Forest Floor of a 34-year-old Loblolly Pine Plantation. Thesis, North Carolina State Univ.(1993).
Acknowledgements
We thank P. Heine, N. Bethala, S. Buol, R. Christman, M. Hofmockel, V. Jin, J.Raikes, B. Megonigal, K. O'Neill, W. H. Schlesinger, J. Swanson and S. Zheng for contributions to this work. The Calhoun Experimental Forest was supported by the USDA Forest Service, Duke University, the Ecosystems Program of the NSF, and the National Research Initiative Ecosystems and Soils Programs of the USDA.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Richter, D., Markewitz, D., Trumbore, S. et al. Rapid accumulation and turnover of soil carbon in a re-establishing forest. Nature 400, 56–58 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1038/21867
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/21867
- Springer Nature Limited
This article is cited by
-
Structural stability and organic carbon stock of soils under three land use systems from semi-arid area of northern Ethiopia
International Journal of Environmental Science and Technology (2024)
-
Microbial properties determine dynamics of topsoil organic carbon stocks and fractions along an age-sequence of Mongolian pine plantations
Plant and Soil (2023)
-
Partitioning of root respiration into growth, maintenance, and ion uptake components in a young larch-dominated forest
Plant and Soil (2023)
-
Multiple soil map comparison highlights challenges for predicting topsoil organic carbon concentration at national scale
Scientific Reports (2022)
-
Isotope analysis reveals differential impacts of artificial and natural afforestation on soil organic carbon dynamics in abandoned farmland
Plant and Soil (2022)