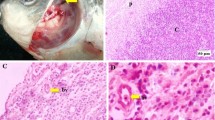
Abstract
ONE of the present-day beliefs is that the thymus is the original source of precursors of the small lymphocyte1. If this were true, antibody developed against thymus cell antigen might react with cells of the lymphoid series. The purpose of this investigation was to determine whether such antibodies could be developed. The ultimate aim was to explore the usefulness of these antibodies for the depression of the immune response to permit homograft survival either by their use as carriers of large doses of radioactive isotope or by their inherent cytotoxic effect.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lanni, F., and Campbell, D., Stanford Medical Bulletin, 6, 97 (1948).
Nairn, R. C., Ghose, T., Fothergill, J. E., and McEntegart, M. G., Nature, 196, 385 (1962).
Nairn, R. C., Richmond, H. G., McEntegart, M. G., and Fothergill, J. E., Brit. Med. J., ii, 1335 (1960).
Sober et al., J. Amer. Chem. Soc., 78, 756 (1956).
Helmkamp et al., Univ. of Rochester U.S.A.C.C. Project report No. UR-568.
Arnason et al., Blood J. Hematol., 20 (5), 617 (1962).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
HINTZ, B., WEBBER, M. Antithymic Antibody Localization in the Mouse. Nature 208, 797–798 (1965). https://doi.org/10.1038/208797a0
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/208797a0
- Springer Nature Limited