Abstract
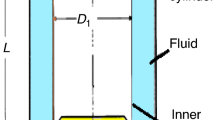
THE thermal conductivity of a mixture of two gases does not, in general, vary linearly with the composition of the mixture. For two gases of similar molecular weight the degree of non-linearity is small, while for systems of widely different molecular weight, linearity rarely extends beyond 0.05 mole fraction from either pure component. Mixtures containing appreciable amounts of both components are of interest experimentally, and in the theory of transport phenomena. The collection of such conductivity data is usually time-consuming.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Boheman, J., and Purnell, J. H., J. App. Chem., 8, 433 (1958).
Aris, R., Proc. Roy. Soc., A, 235, 67 (1956).
Pratt, G. L., and Purnell, J. H., Anal. Chem., 32, 1213 (1960).
Wachsmith, J., Phys. Z., 9, 235 (1908).
Molecular Theory of Gases and Liquids, by Hirschfelder, Curtiss and Bird (John Wiley and Sons Inc., 1954).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
EVANS, E., KENNEY, C. A Flow Method for Determining the Thermal Conductivity of Gas Mixtures. Nature 203, 184–185 (1964). https://doi.org/10.1038/203184b0
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/203184b0
- Springer Nature Limited