Abstract
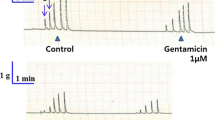
CURARE-LIKE effects due to streptomycin and neomycin have been reported1–3. These two antibiotics have been shown to be capable of exerting a curariform block of the neuromuscular transmission2–4. One of us (G.B.) observed that some patients under heavy antibiotic treatment were more sensitive to the muscular relaxant action of d-tubocurarine. We have therefore begun to study the influence exerted by the most widely used antibiotics on the sensitivity of rabbits to the paralysing activity of curarizing drugs.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Loder, R. E., and Walker, G. F., Lancet, i, 812 (1959).
Pittinger, G. B., and Long, J. P., Antibiotics and Chemotherapy, 8, 198 (1958).
Foldes, F. F., Anæsthesia, 13, 191 (1958).
Brazil, O. V., and Corrado, A. P., J. Pharmacol., 120, 452 (1957).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
BEZZI, G., GESSA, G. Neuromuscular Blocking Action of some Antibiotics. Nature 184, 905–906 (1959). https://doi.org/10.1038/184905a0
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/184905a0
- Springer Nature Limited
This article is cited by
-
Die Gefahren der neuromuskul�rblockierenden Wirkung von Antibiotica
Klinische Wochenschrift (1971)