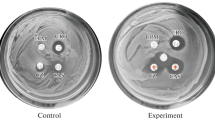
Abstract
IN the bacteriological examination of blood or exudates of patients under treatment with penicillin, it is necessary to inactivate any penicillin present if viable penicillin-sensitive organisms are to grow. The routine testing of penicillin products for sterility also requires a means of neutralizing the antibacterial effect of penicillin. The coli-penicillinase method1 has the disadvantages that the preparation is turbid and the activity of the final product varies.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Harper, G. J., Lancet, ii, 569 (1943).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
UNGAR, J. Penicillinase from B. subtilis. Nature 154, 236–237 (1944). https://doi.org/10.1038/154236b0
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/154236b0
- Springer Nature Limited
This article is cited by
-
Purification de la pénicillinase deBacillus cereus
Experientia (1954)
-
Some mycological aspects of penicillin production
The Botanical Review (1950)
-
Antibiotic products of fungi
The Botanical Review (1947)
-
A Thermostabile, Fungistatic Factor from Escherichia coli
Nature (1945)