Abstract
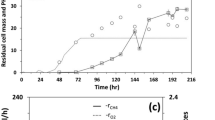
The cell growth and CoQ10 (coenzyme Q10) formation of Rhizobium radiobacter WSH2601 were investigated in a 7-1 bioreactor under different dissolved oxygen (DO) concentrations. A maximal CoQ10 content (C/B) of 1.91 mg/g dry cell weight (DCW) and CoQ10 concentration of 32.1 mg/l were obtained at the appropriate DO concentration of 40% (of air saturation). High DO concentration was favourable to the cell growth of Rhizobium radiobacter WSH2601. In order to achieve the maximal yield of CoQ10 production, a new DO-stat feeding strategy was proposed, which significantly improved cell growth and CoQ10 formation. With this strategy, the maximal CoQ10 concentration and DCW reached 51.1 mg/l and 23.9 g/l, respectively, which were 67 and 44.8% higher than those obtained in the batch culture with DO concentration controlled.
Similar content being viewed by others

References
Konstantin, K., Kishimoto, M., Seki, T. & Yoshida, T. 1990 A balanced DO-stat and its application to the control of acetic acid excretion by recombinant Escherichia coli. Biotechnology and Bioengineering 36, 750–758.
Kuratsu, Y., Sakurai, M., Hagino, H. & Inuzuka, K. 1984 Aerationagitation effect on coenzyme Q10 production by Agrobacterium species. Journal Fermentation Technology 62, 305–308.
Meganathan, R. 2001 Ubiquinone biosynthesis in microorganisms. FEMS Microbiology Letters 203, 131–139.
Pfefferle, C., Theobald, U., Gurtler, H. & Fiedler, H.P. 2000 Improved secondary metabolite production in the genus Streptosporangium by optimization of the fermentation conditions. Journal of Biotechnology 80, 135–142.
Podgornik, H., Podgornik, A., Milavec, P. & Perdih, A. 2001 The effect of agitation and nitrogen concentration on lignin peroxidase (LiP) isoform composition during fermentation of Phanerochaete chrysosporium. Journal of Biotechnology 88, 173–176.
Sakato, K., Tanaka, H., Shibata, S. & Kuratsu, Y. 1992 Agitationaeration studies on coenzyme Q10 production using Rhodopseudomonas spheroides. Biotechnology and Applied Biochemistry 16, 19–28.
Shu, C.H. & Liao, C.C. 2002 Optimization of L-phenylalanine production of Corynebacterium glutamicum under product feedback inhibition by elevated oxygen transfer rate. Biotechnology and Bioengineering 77, 131–141.
Winrow, M.J. & Rudney, H. 1971 The biosynthesis of ubiquinone. Methods in Enzymology, vol. 18, pp. 214–232.
Wu, Z.F., Du, G.C. & Chen, J. 2002 Studies on the Purification and Quantitative Analysis of Coenzyme Q10 in culture. Journal of Wuxi University of Light Industry 4, 420–423.
Wu, Z.F., Weng, P.F. Du, G.C. & Chen, J. 2001 Advances of Coenzyme Q10 function studies. Journal of Ningbo University 2, 85–88.
Yamada, Y., Haneda, K, Murayama, S. & Shiomi, S. 1991 Application of fuzzy control system fermentation. Journal of Chemical Engineering 24, 94–99.
Zupke, C., Sinskey, A.J. & Stephanopoulos, G. 1995 Intracellular flux analysis applied to the effect of dissolved oxygen on hybridomas. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology 44, 27–36.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wu, Z., Du, G. & Chen, J. Effects of dissolved oxygen concentration and DO-stat feeding strategy on CoQ10 production with Rhizobium radiobacter . World Journal of Microbiology and Biotechnology 19, 925–928 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1023/B:WIBI.0000007322.19802.57
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/B:WIBI.0000007322.19802.57