Abstract
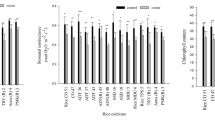
Malaysian rice (Oryza sativa L.) cultivars MR84 and MR185 were grown in greenhouse chambers and exposed to four different levels of ozone from 28th August, 2001 to 22nd January, 2002. Four ozone levels were selected in close relation to the Malaysian peri-urban ambient level (approximately 30 ppb, 8 hr mean), the Malaysian guideline level (approximately 60 ppb) and possible future higher ozone levels (approximately 90 ppb). Both morphological and physiological parameters showed distinctive impacts of ozone treatments. The plants treated with the highest ozone concentration showed different morphological development, probably induced by severe foliar injury and physiological adaptation of the plants to the ozone stress. The physiological measurements revealed a high sensitivity at the early and late vegetative stages. It was concluded that MR84, which was found to be physiologically sensitive, responded to ozone relatively quickly and altered its morphology to compensate for effects on growth and yield, while MR185, found to be physiologically insensitive, responded to ozone stress slowly which resulted in more severe impacts on growth and yield parameters. Slight growth stimulation was observed at the lowest (30 ppb) ozone level for MR185, whilst negative impacts on growth occurred at both of the higher ozone levels. The study provided useful insights into the earlier findings of an open-top chamber filtration study on the same cultivars in the field at a peri-urban site in Malaysia. The present study proved that yield could be reduced substantially when other parameters associated with grain yield were affected, which was accompanied by increasing yellowing of leaves and premature senescence.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adams, R. M., Glyer, J. D. and McCarl, B. A.: 1988, ‘The NCLAN economic assessment: approach, findings and implications’, in W. W. Heck, O. C. Taylor, and D. T. Tingey (eds), Assessment of Crop Loss from Air Pollutants, London: Elsevier Applied Science, pp. 473–504
Agrawal, M., Nandi, P. K. and Rao, D. N.: 1982, ‘Effect of ozone and sulphur dioxide pollutants separately and in mixture on chlorophyll and carotenoid pigments of Oryza sativa,’ Water, Air, Soil Pollut. 18, 449–454
Anbazhagan, M., Krishnamurthy, R. and Bhagwat, K. A.: 1989, ‘The performance of three cultivars of rice grown near to, and distant from, a fertiliser plant’, Environ. Pollut. 58, 125–137.
Asakawa, F., Tanaka, H. and Kusaki, S.: 1981, ‘Effects of air pollution on rice growth and yields’, Jpn. J. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 52, 201–206 (Written in Japanese).
Ashmore, M. R.: 1991, ‘Air pollution and agriculture’, Outlook on Agriculture 20, 139–144
Bell, J. N. B., McNeill, S., Houlden, G., Brown, V. C. and Mansfield, P. J.: 1993, ‘Atmospheric change; effect on plant pests and diseases’, Parasitology 106, 11–14
Barber, J., Malkin, S. and Telfer, A.: 1989, ‘The origin of chlorophyll fluorescence in vivo and its quenching by the Photosystem II reaction centre’, Phil. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B323, 227–239
Barnes, J. D., Reiling, K., Davison, A. W. and Renner, C. J.: 1988, ‘Interaction between ozone and winter stress’, Environ. Pollut. 53, 235–254.
Barnes, J. D., Velissariou, D., Davison, A. W. and Holevas, C. D.: 1990, ‘Comparative ozone sensitivity of old and modern Greek cultivars of spring wheat’, New Phytol.. 116, 707–714.
Bolhar-Nordenkampf, H. R. and Oquist, G.: 1993, ‘Chlorophyll fluorescence as a tool in photosynthesis research’, in D. O. Hall, J. M. O. Schrlock, H. R. Bolhar-Nordenkampf, R. C. Leegood and S. P. Long (eds), Photosynthesis and Production in a Changing Environment: A Field and Laboratory Manual, London: Chapman and Hall, pp. 193–206.
Calatayud, A. and Barreno, E.: 2001, ‘Chlorophyll a fluorescence, antioxidant enzymes and lipid peroxidation in tomato in response to ozone and benomyl’, Environ. Pollut. 115, 283–289.
Collinson, S. T., Ellis, R. H., Summerfield, R. J. and Roberts, E. H.: 1995, ‘Relative importance of air and floodwater temperatures on the development of rice (Oryza sativa)’, Expl. Agric. 31, 151–160.
Department of Agriculture Malaysia: 1999, Pakej Teknologi Padi (Reference Package of Technology on Paddy). Jabatan Pertanian Semenanjung Malaysia, Selangor (written in Malay).
Feng, Z-W., Jin, M-H., Zhang, F-Z. and Huang, Y-Z.: 2003, ‘Effects of ground-level ozone (O3) pollution on the yields of rice and winter wheat in the Yangtze River Delta’, J. Environ. Sci. 15, 360–362
Fuhrer, J.: 1994, ‘Effects of ozone on managed pasture: I. Effects of open-top chambers on microclimate, ozone flux, and plant growth’, Environ. Pollut. 86, 297–305
Grünhage, L., Jäger, H.-J, Haenel, H.-D., Löpmeier, F.-J. and Hanewald, K.: 1999, ‘The European critical levels for ozone: Improving their usage’, Envron. Pollut. 105, 163–173.
Heagle, A. S.: 1989, ‘Ozone and crop yield’, Annu. Rev. Phytopathol. 27, 397–423.
Heck, W. W., Dunning, J. A., Reinert, R. A., Prior, S. A., Rangaooa, M. and Benepal, P. S.: 1988, ‘Differential responses of four bean cultivars to chronic doses of ozone’, J. Amer. Soc. Hort. Sci. 113, 46–51.
Heck, W. W.: 1989, ‘Assessment of crop losses from air pollutants in the United States’, in J. J. MacKenzie and M. El-Ashry (eds), Air Pollutions Toll on Forests and Crops, New Haven: Yale University Press, pp. 235–315.
Jin, M., Feng, Z. and Zhang, F.: 2001, ‘Impacts of ozone on the biomass and yield of rice in open-top chambers’, J. Environ. Sci. 13, 233–236.
Jo, W. K., Yoon, I. H. and Nam, C. W.: 2000, ‘Analysis of air pollution in two major Korean cities: trends, seasonal variations, daily 1 hr maximum versus other hour-based concentrations, and standard exceedances’, Environ. Pollut. 110, 11–18.
Katase, M., Ushijima, T. and Tazaki, T.: 1983, ‘The Relationship between absorption of sulphur dioxide (SO2) and inhibition of photosynthesis in several plants’, The Botanical Magazine Tokyo 96, 1–13.
Kobayashi, K., Okada, M. and Nouchi, I.: 1995, ‘Effects of ozone on dry matter partitioning and yield of Japanese cultivars of rice (Oryza sativa L.)’, Agric. Ecos. Environ. 53, 109–122.
Krause, G. H. and Weis, E.: 1984, ‘Chlorophyll fluorescence as a tool in plant physiology. II. Interpretation of fluorescence signals’, Photosynt. Res. 5, 139–157.
Lee, Y. C., Calori, G., Hills, P. and Carmichael, G. R.: 2002, ‘Ozone episodes in urban Hong Kong 1994–1999’, Atmos. Environ. 36, 1957–1968.
Maggs, R. and Ashmore, M. R.: 1998, ‘Growth and yield responses of Pakistan rice (Oryza sativa L.) cultivars to O3 and NO2’, Environ. Pollut. 103, 159–170.
Marshall, F. M., Ashmore, M. R. and Hinchcliffe F.: 1997, A Hidden Threat to Food Production; Air Pollution and Agriculture in the Developing World. Gatekeeper Series No. 73. London; International Institute for Environment and Development.
Mathy, P.: 1988, ‘The European open-top chambers programme: objectives and implementation’, in W. W. Heck, O. C. Taylor and D. T. Tingey (eds), Assessment of Crop Loss from Air Pollutants, London: Elsevier Applied Science, pp. 505–513.
Musselman, R. C., Younglove, T. and McCool, P. M.: 1994, ‘Response of Phaseolus vulgaris L. to differing ozone regimes having identical total exposure’ Atmos. Environ. 28, 2727–2731.
Nakamura, H. and Saka, H.: 1978, ‘Photochemical oxidants injury in rice plants, III. Effect of ozone on physiological activities in rice plants’, Jap. Jour. Crop Sci. 47, 707–714 (written in Japanese).
Nishi, H., Ae, N. and Wakimoto, K.: 1985, ‘Growth inhibition in rice plants exposed to ozone at low concentration during their growth period’, Bull. Chugoku Natl. Agric. Exp. Stn. Series E, 22, 55–69 (written in Japanese with English summary).
Nishiyama, I: 1983 ‘Temperature injury of rice plant: especially on infertilization’, Jap. Jour. Crop Sci. 52, 108–117.
Nouchi, I., Ito, O., Harazono, Y. and Kobayashi, K.: 1991, ‘Effects of chronic ozone exposure on growth, root respiration and nutrient uptake of rice plants’, Environ. Pollut. 74, 149–164.
Nouchi, I., Ito, O., Harazono, Y. and Kouchi, H.: 1995, ‘Acceleration of 13C-labelled photosynthate partitioning from leaves to panicles in rice plants exposed to chronic ozone at the reproductive stage’, Environ. Pollut. 88, 253–260.
Reiling, K. and Davison, A. W.: 1992, ‘The response of native, herbaceous species to ozone: growth and fluorescence screening’, New Phytol. 120, 29–37.
Reiling, K. and Davison, A. W.: 1994, ‘Effects of exposure to ozone at different stages in the development of Plantago major L. on chlorophyll fluorescence and gas exchange’, New Phytol. 128, 509–514.
Shiau, J. F., Hsieh, S. P. Y., Kao, S. T., Leu, M. C. and Yang, J. S.: 1993, ‘Varietal sensitivities of rice, soybean and corn to sulphur dioxide’, Plant Pathol. Bull. 2, 43–51.
Takeoka, Y., Shimizu, M. and Wada, T.: 1993, ‘Chapter 1 Panicles’, in T. Matsuo and K. Hoshikawa (eds), Science of the Rice Plant: Volume 1 Morphology, Tokyo: Food and Agriculture Policy Research Centre (Nousan Gyoson Bunka Kyoukai), pp. 295–337.
UNECE ICP Vegetation: 2001, Air Pollution and Vegetation: Annual Report 2001, Natural Environment Research Council (NERC), Centre for Ecology and Hydrology, Bangor.
Wahid, A., Maggs, R., Shamsi, S. R. A., Bell, J. N. B. and Ashmore, M. R.: 1995, ‘Effects of air pollution on rice yield in the Pakistan Pubjab’, Environ. Pollut. 90, 323–329.
Wakamatsu, S., Uno, I., Ohara, T. and Schere, K. L.: 1999, ‘A study of the relationship between photochemical ozone and its precursor emissions of nitrogen oxides and hydrocarbons in Tokyo and surrounding areas’, Atmos. Environ. 33, 3097–3108.
Welfare, K., Flowers, T. J., Taylor, G. and Yeo, A. R.: 1996, ‘Additive and antagonistic effects of ozone and salinity on the growth, ion contents and gas exchange of five varieties of rice (Oryza sativa L.)’, Environ. Pollut. 92, 257–266.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ishii, S., Marshall, F.M. & Bell, J.N.B. Physiological and Morphological Responses of Locally Grown Malaysian Rice Cultivars (Oryza Sativa L.) to Different Ozone Concentrations. Water, Air, & Soil Pollution 155, 205–221 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1023/B:WATE.0000026528.86641.5b
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/B:WATE.0000026528.86641.5b