Abstract
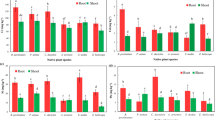
Antimony (Sb) and Copper (Cu) are two metals of major concern in sewage sludge. Antimony because its use in society is increasing and this might lead to increased Sb concentrations in sludge. Copper because its total volume in use in society is large and because of corrosion from water pipes it is most difficult to reduce the Cu concentrations in sludge. Fresh digested sewage sludge was spiked with Cu or Sb and the sludge was cultivated with oat (Avena sativa), lettuce (Lactuca sativa) or radish (Raphanus sativus). Elutriates from the cultivated sludge were tested for toxicity with Lemna minor (7-d growth) and Daphnia magna (48 h immobility). Before cultivation the elutriates were toxic to Lemna and Daphnia due to high concentrations of ammonia (NH3) and nitrite (NO2 -). Cultivation decreased the concentrations of both NH3 and NO2 -, thereby reducing the impact of these compounds in the toxicity tests. Cultivation also decreased the metal concentrations and pH. Daphnia magna was the most sensitive test organism in this study with a 48 h EC50 of 1130 mg Cu kg-1 dry wt and 5 mg Sb kg-1 dry wt in elutriates from sludge cultivated with oat. In sludge cultivated with radish the 48 h EC50 was 1700 mg Cu kg-1 dry wt and 22 mg Sb kg-1 dry wt. The effect of Cu could be predicted by pH and Cu concentrationin the elutriate, but the effect of Sb could not solely be explained by its concentration in the elutriate.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Antoniadis, V. and Alloway, B. J.: 2002, ‘The role of dissolved organic carbon in the mobility of Cd, Ni and Zn in sewage sludge-amended soils’, Envir. Pollut. 117, 515–521.
Chaudri, A. M., Lawlor, K., Preston, S., Paton, G. I., Killham, K. and McGrath, S. P.: 2000, ‘Response of a Rhizobium-based luminescence biosensor to Zn and Cu in solution from sewage sludge treated soils’, Soil Biol. Biochem. 32, 383–388.
Commission of the European Community.: 1986, ‘Council derivative (1986/278/EEC) on the protection of the environment and in particular of the soil, when sewage sludge is used in agriculture’.
Dahlin, S., Witter, E., Mårtensson, A., Turner, A. and Bååth, E.: 1997, ‘Where's the limit? Changes in microbiological properties of agricultural soils at low levels of metal contamination’, Soil Biol. Biochem. 29, 1405–1415.
De Schamphelaere, K. A. C., Heijerick, D. G. and Janssen, C. R.: 2002, ‘Refinement and field validation of a biotic ligand model predicting acute Cu toxicity to Daphnia magna’, Compar. Biochem. Physiol. 133c, 243–258.
Eriksson, J.: 2001, ‘Concentration of 61 trace elements in sewage sludge farm manure, mineral fertiliser, precipitation and in soil and crop’, Report 5159, Swedish Environmental Protection Agency, Stockholm 39 pp.
Filella, M., Belzile, N. and Chen, Y-W.: 2002, ‘Antimony in the environment: a review focused on natural waters, 1. Occurrence’, Earth Sci. Rev. 57, 125–176.
Fjällborg, B. and Dave, G.: 2003, ‘Toxicity of Copper in sewage sludge’, Envir. Inter. 28, 761–769.
Giller, K. E., Witter, E. and McGrath, S. P.: 1998, ‘Toxicity of heavy metals to microorganisms and microbial processes in agricultural soils: a review’, Soil Biol. Biochem. 30, 1389–1414.
Ginocchio, R., Rodriguez, P. H., Badilla-Ohlbaum, R., Allen, H. E. and Lagos, G. E.: 2002, ‘Effect of soil copper content and pH on copper uptake of selected vegetables grown under controlled conditions’, Envir. Toxicol. Chem., 21, 1736–1744.
Hammel, W., Debus, R., Steubing, L.: 1996, ‘Assessment of the ecotoxic potential of soil contaminants by using a soil-algae test’, Ecotoxicol. Envir. Safety 40, 173–176.
Hammel, W., Debus, R. and Steubing, L.: 2000, ‘Mobility of antimony in soil and its availability to plants’, Chemosphere 41, 1791–1798.
He, M. and Yang, J.: 1999, ‘Effects of different forms of antimony on rice during the period of germination and growth and antimony concentration in rice tissue’, Sci. Tot. Envir. 243/244, 149–155.
ISO: 1995, ‘Soil quality-Determination of the effects of pollutants on soil flora: Part 2: Effects of chemicals on the emergence and growth of higher plants’, ISO 11 269–2:1995, International Organisation for Standardisation, Geneva, Switzerland.
ISO: 1996, ‘Water quality-determination of the inhibition of the mobility of Daphnia magna Straus (Cladocera, Crustacea) — acute toxicity test’, ISO 66431, International Organisation for Standardisation, Geneva, Switzerland.
Khan, M. and Scullion, J.: 2000, ‘Effects of soil on microbial responses to metal contamination’, Envir. Pollut. 110, 115–125.
Krachler, M. and Emons, H.: 2000, ‘Potential of high performance liquid chromatography coupled to flow injection hydride generation atomic absorption spectrometry for the speciation of inorganic and organic antimony compounds’, J. Anal. Atomic Spectr. 15, 281–285.
Krachler, M., Emons, H. and Zheng, J.: 2001, ‘Speciation of antimony for the 21-st century: promises and pitfalls’, Trends Anal. Chem. 20, 79–90.
Lee, Y-W., Ong, S-K. and Sato, C.: 1997, ‘Effects of heavy metals on nitrifying bacteria’, Water Sci. Technol. 36, 69–74.
Lorenz, S. E., Hamon, R. E., Holm, P. E., Domingues, H. C., Sequeira, E. M., Christensen, T. H. and McGrath, S. P.: 1997, ‘Cadmium and zinc in plants and soil solutions from contaminated soils’, Plant and Soil 189, 21–31.
Martinez, C. E. and McBride, M. B.: 2000, ‘Copper phytotoxicity in a contaminated soil: remediation tests with adsorptive materials’, Envir. Sci. Technol. 34, 4386–4391.
Michalke, B. and Schramel, P.: 1999, ‘Antimony speciation in environmental samples by interfacing capillary electrophoresis on-line to an inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometer’, J. Chromat. A 834, 341–348.
Mount, D. I. and Andersson-Carnahan, L.: 1989, ‘Methods for aquatic toxicity identification evaluations: Phase 2 toxicity identification procedures’, EPA-600/3-88/035, U.S. Environmental Protection Agency, Duluth, MN.
Peltier, W. H. and Weber, C. I.: 1985, ‘Methods for measuring the acute toxicity of effluents to freshwater and marine organisms’, 3rd ed. U.S. Environmental Protection Agency, Cincinnati.
Santore, R. C., Di Toro, D. M., Paquin, P. R., Allen, H. E. and Meyer, J. S.: 2001, ‘Biotic ligand model of the acute toxicity of metals. 2. Application to copper toxicity in freshwater fish and Daphnia’, Envir. Toxicol. Chem. 20, 2397–2402.
SIS: 1995, ‘Water quality-Determination of growth inhibition (7-d) Lemna minor, duckweed’, SS 02 82 13, Swedish Standard Institution, Stockholm, Sweden.
Smith, L. M., Craig, P. J. and Jenkins, R. O.: 2002, ‘Formation of methyl antimony species by Clostridium spp’, Chemosphere 47, 401–407.
Spurgeon, D. J. and Hopkin, S. P.: 1999, ‘Comparison of metal accumulation and excretion kinetics in earthworms (Eisenia fetida) exposed to contaminated field and laboratory soils’, Appl. Soil Ecol. 11, 227–243.
Sternbeck, J. and Östlund, P.: 1999, ‘Nya metaller och metalloider i samhället (new metals and half metals in the society)’, IVL-rapport B1332, IVL publicationservice, Stockholm.
Swedish Environmental Protection Agency: 1997, www.environ.se
Takayanagi, K.: 2001, ‘Acute toxicity of waterborne Se (IV), Se (VI), Sb (III) and Sb (V) on red sea bream (Pargus major)’, Bull. Envir. Contam. Toxicol. 66, 808–813.
Trafas, M.: 1996, ‘Changes in the properties of post-flotation wastes due to vegetation introduced during process of reclamation’, Appl. Geochem. 11, 181–185.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fjällborg, B., Dave, G. Toxicity of Sb and Cu in Sewage Sludge to Terrestrial Plants (Lettuce, Oat, Radish), and of Sludge Elutriate to Aquatic Organisms (Daphnia and Lemna) and its Interaction. Water, Air, & Soil Pollution 155, 3–20 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1023/B:WATE.0000026520.81626.21
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/B:WATE.0000026520.81626.21