Abstract
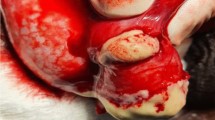
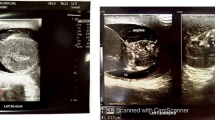
Symptoms of tuberculous orchiepididymitis in a39-year-old male started with swelling of leftscrotum, followed by fistula formation withsuppurative discharge. There was no anyimprovement produced by antibiotics. Surgicalextirpation of inflammatory destroyed testicleand epidydimis was performed. Presence oftubercle bacilli was not shown bybacteriological analysis of testicle tissue.Tuberculous etiology was suggested afterhistopathological examination of testis andepididymis. Exudate from surgical wound wasexamined on presence of Mycobacteriumtuberculosis DNA. Etiology oforchiepididymitis was proved by positive assayand inflammatory process was completely curedby antituberculotics therapy. By this report itwas clearly shown that sometimes only molecularmethods could confirm etiology of inflammatoryprocess.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Fanning AE. Globalization of tuberculosis. Can Med Assoc J 1998; 158: 611-612.
Murray PR, Rosenthal KS, Kobayashi GS, Pfaller MA, eds. Medical Microbiology, 3rd edn. St. Louis: Mosby Inc., 1998: 319-330.
Fanning A. Tuberculosis: 6. Extrapulmonary disease. Can Med Assoc J 1999; 160: 1597-1603.
Pereira Arias JG, Gallego Sanchez JA, Larrinaga Simon J et al. Advanced tubercular disease of urogenital tract. Arch Esp Urol 1997; 50: 396-399.
Gupta P, Singh K, Singh R, Sharma C, Kukreti R. Unusual case of scrotal swellings. Indian Pediatr 2000; 37: 1013-1016.
Ehlers S, Ignatius R, Regnath T et al. Diagnosis of extrapulmonary tuberculosis by Gen-Probe Amplified Mycobacterium cobacterium tuberculosis direct test. J Clin Microbiol 1996; 34: 2275-2279.
Lenk S, Schroeder J. Genitourinary tuberculosis. Curr Opin Urol 2001; 11: 93-96.
Gamboa F, Donomguez J, Padilla E et al. Rapid diagnosis of extrapulmonary tuberculosis by ligase chain reaction amplifi-cation. J Clin Microbiol 1998; 36: 1324-1329.
Laszlo A.Tuberculosis: 7. Laboratory aspect of diagnosis. Can Med Assoc J 1999; 160: 1725-1729.
Ausina V, Gamboa F, Gazapo E et al. Evaluation of the semiautomated Abbott LCx Mycobacterium tuberculosis assay for direct detection of Mycobacterium tuberculosis in respiratory specimens. J Clin Microbiol 1997; 35: 1996-2002.
Tortoli E, Lavinia F, Saimonetti MT. Evaluation of a comercial ligase chain reaction kit (Abbott LCx) for direct detection of Mycobacterium tuberculosis in pulmonary and extrapulmonary specimens. J Clin Microbiol 1997; 35: 2424-2426.
Urlić V. Development of microbiology in the city of Split. Retrospection on the 50th anniversary of the beginning of work of the Bacteriological Station. Lijec Vjesn 1972; 94: 636-638.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Barišić, Z., Vrsalović-Carević, N., Milostić, K. et al. Tuberculous orchiepididymitis diagnosed by nucleic acid amplification test: A case report. Int Urol Nephrol 35, 203–205 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1023/B:UROL.0000020296.88425.57
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/B:UROL.0000020296.88425.57