Abstract
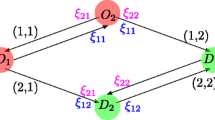
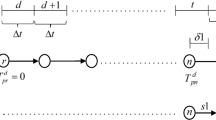
In this paper, we propose a model of dynamic traffic assignment where strategic choices are an integral part of user behaviour. The model is based on a discrete-time description of flow variation through a road network involving arcs with rigid capacities. In such network, a driver's strategy consists in a rule that assigns to each node of the network a set of arcs in the forward star of that node, sorted according to some preference order. The main element of the model is a ‘within-day’ submodel where strategic volumes are loaded onto the network in accordance with the first-in first-out discipline and user preferences. An equilibrium assignment is achieved when expected delays of active strategies are minimal, for every origin-destination pair. We prove the existence of such an assignment and provide numerical results on test networks.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Astarita, V. (1996). "A Continuous Time Link Model for Dynamic Network Loading Based on Travel Time Function," In J.B. Lesort (ed.), Proc. 13th International Symposium on Transportation and Traffic Theory Pergamon-Elsevier, pp. 79–102.
Carey, M. (1992). "Non Convexity of the Dynamic Traffic Assignment Problem." Transportation Research B26, 127–133.
Chriqui, C. and P. Robillard. (1975). "Common Bus Line." Transportation Science 9, 115–121.
Drissi-Kaïtouni, O. and A. Hamada-Benchekroun. (1992). "A Dynamic Traffic Assignment Model and a Solution Algorithm." Transportation Science 26, 119–128.
Drissi-Kaitouni, O. and M. Gendreau. (1992). "A NewDynamic Traffic Assignment Model." PublicationCRT-854, Centre de recherche sur les transports, Université de Montréal.
Friesz, T.L., D. Bernstein, T.E. Smith, R. Tobin, and B.W. Wie. (1993). "A Variational Inequality Formulation of the Dynamic Network User Equilibrium Problem." Operations Research 41, 179–191.
Gao, S. and I. Chabini. (2003). "A Policy-Based Approach to Stochastic Dynamic Traffic Assignment." Preprint, Massachusetts Institute of Technology.
Hamdouch,Y. (2002). Affectation Statique et Dynamique des Usagers Dans unRéseau de TransportAvec Capacités Rigides, Ph.D dissertation, Département d'informatique et de recherche opérationnelle, Université de Montréal.
Hamdouch, Y., P. Marcotte, and S. Nguyen. (2002). "Capacitated Traffic Assignment with Priority Rules." Report CRT-2002-41, Centre de recherche sur les transports, Université de Montréal.
Marcotte, P. and S. Nguyen. (1998). "Hyperpath Formulations of Traffic Assignment Problems." In P. Marcotte and S. Nguyen (eds.), Equilibrium and Advanced Transportation Modelling Kluwer Academic Publisher, pp. 175–199.
Marcotte, P., S. Nguyen, and A. Schoeb. (2000). A Strategic Flow Model of Traffic Assignment in Capacitated Networks, Publication 2000-10, Centre de recherche sur les transports, Université de Montréal.
Merchant, D. and G. Nemhauser. (1978). "A Model and an Algorithm for the Dynamic Traffic Assignment Problems." Transportation Science 12, 183–199.
Moore, E.F. (1959). "The Shortest Path Through a Maze." In Proc. International Symposium on Theory of Switching, Part 2, Harvard University Press, pp. 285–292.
Nguyen, S. and S. Pallottino. (1988). "Equilibrium Traffic Assignment for Large Scale Transit Networks." European Journal of Operational Research 37, 176–186.
Nguyen, S. and S. Pallottino. (1989). "Hyperpaths and Shortest Hyperpaths." In B. Simeone (ed.), Combinatorial Optimization, vol. 1403 of Lecture Notes in Mathematics, Berlin: Springer-Verlag, pp. 258–271.
Spiess, H. et M. Florian. (1989). "Optimal Strategies: A New Assignment Model for Transit Networks." Transportation Research B 23, 83–102.
Suwansirikul, C., T.L. Friesz, and R.L. Tobin. (1987). "Equilibrium Decomposition Optimization: A Heuristic for the Continuous Equilibrium Network Design Problem." Transportation Science 21, 254–263.
Wardrop, J.G. (1952). "Some Theoretical Aspects of Road Traffic Research." In Proceedings of the Institution of Civil Engineers, Part II, pp. 325–378.
Zawack, D. and G. Thompson. (1987). "A Dynamic Space-Time Network FlowModel for CityTraffic Congestion." Transportation Science 21, 153–162.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hamdouch, Y., Marcotte, P. & Nguyen, S. A Strategic Model for Dynamic Traffic Assignment. Networks and Spatial Economics 4, 291–315 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1023/B:NETS.0000039784.00352.66
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/B:NETS.0000039784.00352.66