Abstract
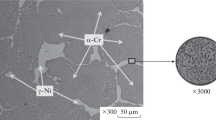
The methods of electron microscopy, metallography, and determination of impact toughness and resistivity are used to investigate the structural and phase stability of nickel-chromium alloys after aging at 350, 400, and 450°C for up to 40,000 h. The chromium content is shown to be correlated with the susceptibility of the alloys to ordering. It is established that the alloy with about 41 wt.% Cr has the highest stability of the structure and properties in the studied temperature range.
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
M. I. Solonin, V. P. Kondrat'ev, S. N. Votinov, et al., “Alloy KhNM-1 as a promising material for elements of the structure of nuclear and thermonuclear reactors with water coolant,” VANT, Ser. Materialoved. Nov. Mater., Issue 1(52), 13–20 (1995).
V. P. Kondrat'ev, M. I. Solonin, V. N. Rechitskii, et al., “Alloy KhNM-1 as an alternative material for VVÉR reactor bodies,” VANT, Ser. Materialoved. Nov. Mater., Issue 1(58), 79–85 (2001).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kolotushkin, V.P., Kondrat'ev, V.P., Laushkin, A.V. et al. Effect of Long-Term Aging on the Structural and Phase Stability and Properties of Nickel-Chromium Alloys. Metal Science and Heat Treatment 45, 411–414 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1023/B:MSAT.0000019192.49582.25
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/B:MSAT.0000019192.49582.25