Abstract
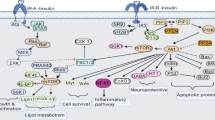
We have previously reported that thiazolidinediones (TZDs) are able to restore the tyrosine phosphorylation of insulin receptor and insulin receptor substrate-1, activation of phosphatidyl inositol 3-kinase and glucose uptake in insulin resistant skeletal muscle cells [21]. In this study, we investigated the effects of insulin stimulation and TZDs on the role of mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) in insulin resistant skeletal muscle cells. All the three MAPKs [extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK), c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK) and p38 MAPK] were activated by insulin in the sensitive skeletal muscle cells. In contrast, activation of p38 MAPK was impaired in insulin resistant cells, where as ERK and JNK were activated by insulin. Treatment with TZDs resulted in the restoration of p38 MAPK activity in insulin resistant cells. The treatment of cells with p38 MAPK inhibitor, SB203580, blocked the insulin stimulated glucose uptake in sensitive as well as resistant cells and it also prevented the activation of p38 by insulin. These results suggest the potential involvement of p38 as well as the mechanistic role of TZDs in insulin resistance.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lewis TS, Shapiro PS, Ahn NG: Signal transduction through MAP kinase cascades. Adv Cancer Res 74: 49-139, 1998
Ludwig S, Hoffmeyer A, Goebeler M, Kilian K, Hafner H, Neufeld B, Han J, Rapp UR: The stress inducer arsenite activates mitogen-activated protein kinases extracellular signal-regulated kinases 1 and 2 via a MAPK kinase 6/p38-dependent pathway. J Biol Chem 273: 1917-1922, 1998
Ishrath A, Kumar N, Dey CS: Differential activation of ERK and JNK by arsenite in mouse muscle cells. Comp Biochem Physiol 132C: 375-384, 2002
Recio JA, Merlino G: Hepatocyte growth factor/scatter factor activates proliferation in melanoma cells through p38 MAPK, ATF-2 and cyclin D1. Oncogene 21: 1000-1008, 2002
Zentrich E, Han SY, Pessoa-Brandao L, Butterfield L, Heasley LE: Collaboration of JNKs and ERKs in nerve growth factor regulation of the neurofilament light chain promoter in PC12 cells. J Biol Chem 277: 4110-4118, 2002
Guo JH, Wang H, Malbon CC: Conditional, tissue-specific expression of Q205L Gαi2 in vivo mimics insulin activation of c-Jun N-terminal kinase and p38 kinase. J Biol Chem 273: 16487-16493, 1998
Somwar R, Perreault M, Kapur S, Taha C, Sweenet G, Ramlal T, Kim DY, Keen J, Cote CH, Klip A, Marette A: Activation of p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase α and β by insulin and contraction in rat skeletal muscle. Diabetes 49: 1794-1800, 2000
Farese RV: Insulin-sensitive phospholipid signaling systems and glucose transport. Update II. Exp Biol Med 226: 283-295, 2001
Cefalu WT: Insulin resistance: Cellular and clinical concepts. Exp Biol Med 226: 13-26, 2001
Somwar R, Kim DY, Sweeney G, uang C, Niu W, Lador C, Ramlal T, Klip A: GLUT4 translocation precedes the stimulation of glucose uptake by insulin in muscle cells: Potential activation of GLUT4 via p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase. Biochem J 359: 639-649, 2001
Konrad D, Somwar R, Sweeney G, Yaworsky K, Hayashi M, Ramlal T, Klip A: The antihyperglycemic drug α-lipoic acid stimulates glucose uptake via both GLUT4 translocation and GLUT4 activation. Diabetes 50: 1464-1471, 2001
Sweeney G, Somwar R, Ramlal T, Volchuk A, Ueyama A, Klip A: An inhibitor of p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase prevents insulin-stimulated glucose transport but not glucose transporter translocation in 3T3-L1 adipocytes and L6 myotubes. J Biol Chem 274: 10071-10078, 1999
Clancy BM, Harrison SA, Buxton JM, Czech MP: Protein synthesis inhibitors activate glucose transport without increasing plasma membrane glucose transporters in 3T3-L1 adipocytes. J Biol Chem 266: 10122-10130, 1991
Cusi K, Maezono K, Osman A, Pendergrass M, Patti ME, Pratipanawatr T, DeFronzo RA, Kahn CR, Mandarino LJ: Insulin resistance differentially affects the PI 3-kinase-and MAP kinase-mediated signaling in human muscle. J Clin Invest 105: 311-320, 2000
Aguirre V, Uchida T, Yenush L, Davis R, White MF: The c-Jun NH2-terminal kinase promotes insulin resistance during association with insulin receptor substrate-1 and phosphorylation of Ser307. J Biol Chem 275: 9047-9054, 2000
Huang C, Somwar R, Patel N, Niu W, Torok D, Klip A: Sustained exposure of L6 myotubes to high glucose and insulin decreases insulin-stimulated GLUT4 translocation but upregulates GLUT4 actiivty. Diabetes 51: 2090-2098, 2002
Olefsky JM: Treatment of insulin resistance with peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ agonists. J Clin Invest 106: 467-472, 2000
Arakawa K, Ishihara T, Aoto M, Inamasu M, Saito A, Ikezawa K: Actions of novel antidiabetic thiazolidinediones, T-174, in animal models of non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus (NIDDM) and in cultured muscle cells. Br J Pharmacol 125: 429-436, 1998
El-Kebbi IM, Roser S, Pollet RJ: Regulation of glucose transport by pioglitazone in cultured muscle cells. Metabolism 43: 953-958, 1994
Ciaraldi TP, Huber-Knudsen K, Hickman M, Olefsky JM: Regulation of glucose transport in cultured muscle cells by novel hypoglycemic agents. Metabolism 44: 976-982, 1995
Kumar N, Dey CS: Development of insulin resistance and reversal by thiazolidinediones in C2C12 skeletal muscle cells. Biochem Pharmacol 65: 249-257, 2003
Tsiani E, Ramlal T, Leiter LA, Klip A, Fantus IG: Stimulation of glucose uptake and increased plasma membrane content of glucose transporters in L6 skeletal muscle cells by sulfonylureas gliclazide and glyburide. Endocrinology 136: 2505-2512, 1995
Ricort JM, Tanti JF, Obberghen EV, Le Marchand-Brustel Y: Alterations in insulin signaling pathway induced by prolonged insulin treatment of 3T3-L1 adipocytes. Diabetologia 38: 1148-1156, 1995
Chang PY, Le Marchand-Brustel Y, Cheatham LA, Moller DE: Insulin stimulation of mitogen-activated protein kinase, p90rsk, and p70 S6 kinase in skeletal muscle of normal and insulin-resistant mice. Implications for the regulation of glycogen synthase. J Biol Chem 270: 29928-29935, 1995
Engelman JA, Berg AH, Lewis RY, Lisanti MP, Scherer PE: Tumor necrosis factor α-mediated insulin resistance, but not dedifferentiation, is abrogated by MEK 1/2 inhibitors in 3T3-L1 adipocytes. Mol Endocrinol 14: 1557-1569, 2000
Jain RG, Meredith MJ, Pekala PH: Tumor necrosis factor-α mediated activation of signal transduction cascades and transcription factors in 3T3-L1 adipocytes. Adv Enzyme Regul 38: 333-347, 1998
Lennon AM, Ramauge M, Dessouroux A, Pierre M: MAP kinase cascades are activated in astrocytes and preadipocytes by dPGJ2 and the thiazolidinedione ciglitazone through PPAR γ independent mechanisms involving ROS. J Biol Chem 277: 29681-29685, 2002
Napoli R, Gibson L, Hirshman MF, Boppart MD, Dufresne SD, Horton ES, Goodyear LJ: Epinephrine and insulin stimulate different mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling pathways in rat skeletal muscle. Diabetes 47: 1549-1554, 1998
Kayali AG, Austin DA, Webster NJG. Stimulation of MAPK cascades by insulin and osmotic shock. Diabetes 49: 1783-1793, 2000
Fujishiro M, Gotoh Y, Katagiri H, Sakoda H, Ogihara T, Anai M, Onishi Y, Ono H, Funaki M, Inukai K, Fukushima Y, Kikuchi M, Oka Y, Asano T: MKK6/3 and p38 MAPK pathway activation is not necessary for insulin-induced glucose uptake but regulates glucose transporter expression. J Biol Chem 276: 19800-19806, 2001
Moyers JS, Bilan PJ, Reynet C, Kahn CR: Overexpression of rad inhibits glucose uptake in cultured muscle and fat cells. J Biol Chem 271: 23111-23116, 1996
Palmer RM, Thompson MG, Knott RM, Campbell GP, Thom A, Morrison KS: Insulin and insulin-like growth factor-I responsiveness and signalling mechanisms in C2C12 satellite cells: Effect of differentiation and fusion. Biochim Biophys Acta 1355: 167-176, 1997
Sarabia V, Lam L, Burdett E, Leiter LA, Klip A. Glucose transport in human skeletal muscle cells in culture: stimulation by insulin and metformin. J Clin Invest 90: 1386-1395, 1992
Lawson MA, Purslow PP: Differentiation of myoblasts in serum-free media: effects of modified media are cell line-specific. Cells Tissues Organs 167: 130-137, 2000
Pinset C, Gros F, Whalen R: Proliferation and differentiation of a myogenic line in synthetic media. CR Sean Acad Sci 295: 727-732, 1982
Conejo R, Lorenzo M: Insulin signaling leading to proliferation, survival, and membrane ruffling in C2C12 myoblasts. J Cell Physiol 187: 96-108, 2001
Goto S, Miyazaki K, Funabiki T, Yasumitsu H: Serum-free culture conditions for the analysis of secretory proteinases during myogenic differentiation of mouse C2C12 myoblasts. Anal Biochem 272: 135-142, 1999
Cabrero À, Alegret M, Sánchez RM, Adzet T, Laguna JC, Manuel V: Down-regulation of uncoupling protein-3 and-2 by thiazolidinediones in C2C12 myotubes. FEBS Lett 484: 37-42, 2000
Nagase I, Yoshida S, Canas X, I Yukiko, Kimura K, Yoshida T, Saito M: Up-regulation of uncoupling protein 3 by thyroid hormone, peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor ligands and 9-cis retinoic acid in L6 myotubes. FEBS Lett 461
Yonemitsu S, Nishimura H, Shintani M, Inoue R, Yamamoto Y, Masuzaki H, Ogawa Y, Hosoda K, Inoue G, Hayashi T, Nakao K: Troglitazone induces GLUT 4 4 translocation in L6 myotubes. Diabetes 50: 1093-1101, 2001
Raingeaud J, Gupta S, Rogers JS, Dickens M, Han J, Ulevitch RJ, Davis RJ: Pro-inflammatory cytokines and environmental stress cause p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase activation by dual phosphorylation on tyrosine and threonine. J Biol Chem 270: 7420-7426, 1995
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kumar, N., Dey, C.S. Restoration of impaired p38 activation by insulin in insulin resistant skeletal muscle cells treated with thiazolidinediones. Mol Cell Biochem 260, 55–64 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1023/B:MCBI.0000026054.60072.48
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/B:MCBI.0000026054.60072.48