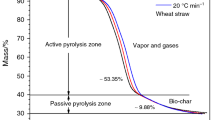
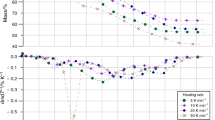
Abstract
Sewage sludge disposal is a difficult task owing to increasingly restrictive re-use policies. Its final destination will obviously depend on its nature and composition but the generation of energy is a significant option. The thermochemical conversion requires exhaustive gas emission controls. In this regard, this paper offers the results of the use of mass spectrometry together with a thermogravimetric analysis system used to study the thermal conversion processes of two kinds of sewage sludge under different atmospheres simulating pyrolysis, gasification and combustion. This TG-MS combination indicates that gasification is the best process for one kind of sludge while a co-combustion process is more suitable for the other.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Renner 2000; European Environment Agency Indicator Fact Sheet Signals 2001-Chapter Waste.
J. Werther and T. Ogada, Prog. Energy Combus. Sci., 25 (1999)55.
M. Otero, L. F. Calvo, B. Estrada, A. I. García and A. Morán, Thermochim. Acta, 389 (2002)121.
J. Rodríguez-Añón, J. Proupin, M. González-Añón and L. Núñez-Regueira, J. Therm. Anal. Cal., 52 (1998)1005.
P. J. Matthews, European progress on the political and economic concerns of sludge disposal-is the future biosolids or ash? In: Proceedings of the EWPCA-NVA Conference on Future of Water Quality Management in Europe, Aquatech, Amsterdam, September,1996
L. F. Calvo, M. Otero, B. M. Jenkins, A. I. García and A. Morán, Thermochim. Acta, 409 (2004)127.
C. Díez, O. Martínez, L. F. Calvo, J. Cara and A. Morán, Waste Management, 24 (2004)463.
A. Napoli, Ph.D. Thesis, Université Paul Sabatier de Toulouse, France1998.
B. Pacewska, A. Klepariska, P. Stefaniak and D. Szychowski, J. Therm. Anal. Cal., 60 (2000)229.
J. Heikinen and H. Spliethoff, J. Therm. Anal. Cal., 72 (2003)1031.
J. H. Ferrase, S. Chávez, P. Arlabosse and N. Dupuy, Thermochim. Acta, 404 (2003)97.
A. Arenillas, F. Rubiera and J. J. Pis, J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis, 50 (1999)31.
M. C. M. Alvim-Ferraz and S. A. V. Afonso, Atmos. Environ., 37 (2003)5415.
V. I. Kouprianov and W. Permchart, Appl. Energy, 74 (2003)383.
A. M. Henihan, M. J. Leahy, J. J. Leahy, E. Cummins and B. P. Lelleher, Bioresource Technol., 87 (2003)289.
H. Liu and B. M. Gibbs, Fuel, 82 (2003)1591.
C. Díez, O. Martínez, L. F. Calvo, J. Cara and A. Morán, Waste Management, 24 (2004)463.
L. Zhang, A. Sato, Y. Ninomiya and E. Sasaoka, Fuel, 83 (2004)1039.
P. J. Hatton and B. W. Southward, J. Therm. Anal. Cal., 72 (2003)83.
A. Arenillas, F. Rubiera and J. J. Pis, J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis, 50 (1999)31.
J. Werther and T. Ogada, Prog. Energy Combust. Sci., 25 (1999)55.
M. Otero, L. F. Calvo, B. Estrada, A. I. García and A. Morán, Thermochim. Acta, 389 (2002)121.
M. Otero, L. F. Calvo, B. Estrada, A. I. García and A. Morán, Thermochim. Acta, 389 (2002)121.
A. B. Singh, Ph.D. Thesis, University of California, Davis1996.
J. T. Shaw, J. Inst. Fuel, 64 (1973)170.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Calvo, L.F., Sánchez, M.E., Morán, A. et al. TG-MS as a technique for a better monitoring of the pyrolysis, gasification and combustion of two kinds of sewage sludge. Journal of Thermal Analysis and Calorimetry 78, 587–598 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1023/B:JTAN.0000046121.14253.38
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/B:JTAN.0000046121.14253.38