Abstract
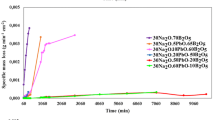
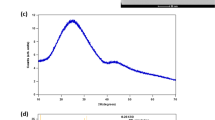
This study deals with durable borosilicate glasses for the immobilizing of radioisotopes from nuclear waste streams generated by a radiopharmaceutical production unit. In this regard, different boron frits (glasses) and waste-loaded glasses were prepared under various experimental conditions. The effects of some parameters such as melting temperature, cooling procedure and various raw materials were investigated. The best composition of the frits as well as the best glass/waste ratio was determined to optimize the immobilization process. All experiments were performed in non-active bench scale.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
W. Baehr, IAES Bulletin, 4 (1989) 43.
K. M. Armstrong, L. M. Klingler, Evaluation of a Unique System for the Thermal Processing of Radioactive and Mixed Wastes, MLM-3340, EG&G Mound Applied Technologies, Miamisburg, Ohio, 1985.
D. Clery, New Scientist, 16 (1990) 34.
D. F. Bickford, P. Hrma, B. W. Bowan, J. Amer. Ceram. Soc., 73 (1990) 2903.
W. J. Bjorklund, G. B. Mellinge, J. M. Pope, Vitrification of simulated West Valley waste using a liquid-fed ceramic melter, in: Advances in Ceramics, Vol. 8, G. G. Wicks, W. A. Ross (Eds), Nuclear Waste Management, The American Ceramic Society, Inc., Columbus, Ohio, 1984.
E. Berkey, Hazardous Mater. Managem. Magazine, (1989) 42.
International Atomic Energy Agency, Management of Radioactive Waste from 99Mo Production, IAEA-TECDOC-1051, 1998, p. 42.
Wu-Long Cheng, Process Study on the Separation of 99Mo from Utilization of Research Reactors, 1989, p. 562.
R. Sayareh, M. Ghannadi Maragheh, M. Shamsaie, Annals Nucl. Energy, 30 (2003) 883.
A. A. Sameh, J. A. Hans, Radiochim. Acta, 41 (1987) 65.
R. Munze, O. Hladik, G. Bernhard, W. Bossert, R. Schwarzback, Intern. J. Appl. Radiation Isotopes, 35 (1984) 749.
R. C. Ewing, W. J. Weber, F. W. Clinard, Progr. Nucl. Energy, An International Review Journal, 29 (1995) No. 2, 63.
D. M. Strachan, B. O. Barnes, R. P. Turcotte, MCC-1 Standard Leach Test for Nuclear Waste Forms, PNL-SA-8737, Pacific Northwest Laboratory, Richland, Washington, 1980.
Encyclopedia of Chemical Technology, Vol. 12, John Wiley and Sons, Inc., 4 th ed., 1996, p. 555.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kazemian, H., Mallah, M.H. & Maragheh, M.G. Vitrification of HLW generated by a production unit for radiopharmaceuticals using simulated waste solutions. Journal of Radioanalytical and Nuclear Chemistry 261, 619–623 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1023/B:JRNC.0000037104.03675.7f
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/B:JRNC.0000037104.03675.7f