Abstract
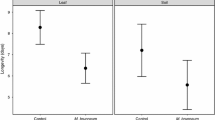
Host plant acceptance behavior of redlegged earth mites (Halotydeus destructor) on cotyledons of subterranean clover (subclover) lines was investigated in the laboratory. Sustained feeding consisted of a series of short bouts of feeding; rather than one long period of feeding. H. destructor preferred to feed at mite-damaged rather than undamaged sites on cotyledons. With time the numbers of mites feeding in aggregations increased, as mites were attracted to damaged patches. Most feeding occurred in aggregations, and mites in such groups benefited by greater weight gain. The sequence of foraging leading to feeding was similar between subclover lines, however, feeding and aggregation activities were markedly reduced on a resistant line. Host plant acceptance occurred during probing but only after some feeding had occurred.
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Adams, J. B., and van Emden, H. F. (1972). The biological properties of aphids and their host plant relationships. In van Emden, H. F. (ed.), Aphid Technology, Academic Press, New York, pp. 47–104.
Annells, A., and Ridsdill-Smith, T. J. (1994). Host plant species and carbohydrate supplements affecting rate of multiplication of redlegged earth mite. Exp. Appl. Acarol. 18: 521–530.
Bernays, E. A., and Chapman, R. F. (1994). Host-Plant Selection by Phytophagous Insects, Chapman and Hall, London.
Blackwell, A. (1988). The disruption of aggregation behaviour in Pieris brassicae larvae by chlordimeform. Entomol. Exp. Appl. 48: 141–147.
Blaney, W. M., and Simmonds, M. S. J. (1985). Food selection by locusts: The role of learning in rejection behaviour. Entomol. Exp. Appl. 39: 273–278.
Domek, J. M., and Johnson, D. T. (1988). Demonstration of semiochemically induced aggregation in the green june beetle, Cotinis nitida (L.) (Coleoptera: Scarabaeidae). Environ. Entomol. 17: 147–149.
Eigenbrode, S. D., Espelie, K. E., and Shelton, A. M. (1991). Behavior of neonate diamondback moth larvae (Plutella xylostella (L.)) on leaves and on extracted leaf waxes of resistant and susceptible cabbages. J. Chem. Ecol. 17: 1691–1704.
Gaull, K. R., and Ridsdill-Smith, T. J. (1996). The foraging behaviour of redlegged earth mite, Halotydeus destructor (Acarina: Penthaleidae), in an annual subterranean clover pasture. Bull. Entomol. Res. 86: 247–252.
Gillespie, D. J. (1991). Identification of resistance to redlegged earth mite (Halotydeus destructor) in pasture legumes. Plant Protect. Q. 6: 170–171.
Jiang, Y., and Ridsdill-Smith, T. J. (1996a). Antixenotic resistance of subterranean clover cotyledons to redlegged earth mite, Halotydeus destructor. Entomol. Exp. Appl. 79: 161–169.
Jiang, Y., and Ridsdill-Smith, T. J. (1996b). Examination of the involvement of mechanical strength in antixenotic resistance of subterranean clover cotyledons to the redlegged earth mite (Halotydeus destructor) (Acarina: Penthaleidae). Bull. Entomol. Res. 86: 263–270.
Jiang, Y., Ghisalberti, E. L., and Ridsdill-Smith, T. J. (1996). Correlation of 1-octen-3-one with antixenotic resistance in subterranean clover cotyledons to redlegged earth mite, Halotydeus destructor (Acarina: Penthaleidae). J. Chem. Ecol. 22: 369–382.
Jiang, Y., Ridsdill-Smith, T. J., and Ghisalberti, E. L. (1997). The effect of volatile metabolites of lipid peroxidation on the aggregation of redlegged earth mites Halotydeus destructor (Acarina: Penthaleidae) on damaged cotyledons of subterranean clover. J. Chem. Ecol. 23: 163–174.
Klinghauf, F. A. (1987). Host plant finding and acceptance. In Minks, A. K., and Harrewijn, P. (eds.), Aphids. Their Biology, Natural Enemies and Control, Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp. 209–223.
Martin, P., and Bateson, P. (1993). Measuring Behaviour—An Introductory Guide, 2nd ed., Cambridge University Press, Cambridge.
Miller, J. R., and Strickler, K. L. (1984). Finding and accepting host plants. In Bell, W. J., and Cardé, R. T. (eds.), Chemical Ecology of Insects, Chapman and Hall, London, pp. 127–157.
Piper, R. G. (1988). Larval aggregation in Aedes vigilax (Skuse) (Diptera: Culicidae). Aust. Entomol. Mag. 15: 119–121.
Ridsdill-Smith, T. J. (1995). Responses and feeding damage of redlegged earth mite (Acarina: Penthaleidae) to seedlings of resistant and susceptible subterranean clover varieties. Aust. J. Agr. Res. 46: 1091–1099.
Ridsdill-Smith, T. J. (1997). Biology and control of Halotydeus destructor (Tucker) (Acarina: Penthaleidae): A review. Exp. Appl. Acarol. 21: 195–224.
Ridsdill-Smith, T. J., Jiang, Y., and Ghisalberti, E. L. (1995). A method to test compounds for feeding deterrence towards redlegged earth mite (Acarina: Penthaleidae). Ann. Appl. Biol. 127: 593–600.
Sabelis, M. W. (1985). Reproductive strategies. In Helle, W., and Sabelis, W. M. (eds.), Spider Mites. Their Biology, Natural Enemies and Control, Vol. 1A, Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp. 265–278.
Swan, D. C. (1934). The red-legged earth mite Halotydeus destructor (Tucker) in South Australia: With remarks upon Penthaleus major. J. Dept. Agr. South. Aust. 38: 353–367.
Way, M. J., and Cammell, M. (1970). Aggregation behaviour in relation to food utilization by aphids. In Watson, A. (ed.), Animal Populations in Relation to Their Food Resources, Blackwell Scientific, Oxford, pp. 229–247.
Woodhead, S. (1983). Surface chemistry of Sorghum bicolor and its importance in feeding by Locusta migratoria. Physiol. Entomol. 8: 345–352.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gaull, K.R., Ridsdill-Smith, J. Host Plant Acceptance by Redlegged Earth Mite, Halotydeus destructor (Tucker) (Acarina: Penthaleidae). Journal of Insect Behavior 10, 859–869 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1023/B:JOIR.0000010418.06585.94
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/B:JOIR.0000010418.06585.94