Abstract
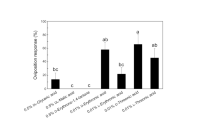
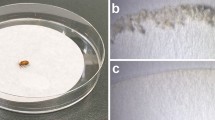
The chemical basis of oviposition elicitation in a generalist herbivore was determined by examination of oviposition responses in Ostrinia nubilalis to corn (Zea mays) chemicals in two-choice laboratory bioassays. A pentane extract of corn leaves stimulated oviposition and the activity persisted for three days, indicating that oviposition in O. nubilalis is elicited by low-volatility chemicals. Chemicals in the extract were fractionated by column chromatography on Florisil, using a sequence of solvents of increasing polarity. Bioassays of Florisil fractions indicated that the stimulants were eluted with nonpolar solvents. Positive bioassay results with an extract prepared by dipping corn leaves in pentane for 20 sec for extraction of leaf surface chemicals suggested that some of the active material was present in the leaf epicuticle. Gas chromatographic analyses and comparisons with retention times of standards suggested the presence of several n-alkanes in the dip extract. Five n-alkanes—hexacosane, heptacosane, octacosane, nonacosane, and tritriacontane—known to be present in the epicuticle of corn leaves were bioassayed, and all five elicited oviposition responses. These results suggest that oviposition elicitation in O. nubilalis is influenced by the presence of n-alkanes in the host plant epicuticle.
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
BAKER, E. A. 1982. Chemistry and morphology of plant epicuticular waxes, pp. 139–165, in D. F. Cutler, K. L. Alvin, and C. E. Price (eds.). The Plant Cuticle. Academic Press, London.
BIANCHI, G., and SALAMINI, F. 1975. Glossy mutants of maize IV. Chemical composition of normal epicuticular waxes. Maydica 20:1–3.
BINDER, B. F., ROBBINS, J. C., and WILSON, R. L. 1995. Chemically mediated ovipositional behaviors of the European corn borer, Ostrinia nubilalis (Lepidoptera: Pyralidae). J. Chem. Ecol. 21:1315–1327.
BLAKER, T. W., and GREYSON, R. I. 1988. Developmental variation of leaf surface wax of maize, Zea mays. Can. J. Bot. 66:839–846.
CANTELO, W. W., and JACOBSON, M. 1979. Corn silk volatiles attract many pest species of moths. J. Environ. Sci. Health Part A 14:695–707.
DERRIDJ, S., FIALA, V., and JOLIVET, E. 1986. Increase of European corn borer (Ostrinia nubilalis) oviposition induced by a treatment of maize plants with maleic hydrazide: Role of leaf carbohydrate content. Entomol. Exp. Appl. 41:305–310.
DERRIDJ, S., FIALA, V., BARRY, P., ROBERT, P., ROESSINGH, P., and STÄDLER, E. 1992. Role of nutrients found in the phylloplane, in the insect host-plant selection for oviposition, pp. 139–140, in S. B. J. Menken, J. H. Visser and P. Harrewijn (eds.). Proceedings of the 8th International Symposium of Insect-Plant Relationships. Kluwer Academic Publishers, Dordrecht.
EIGENBRODE, S. D., and ESPELIE, K. E. 1995. Effects of plant epicuticular lipids on insect herbivores. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 40:171–190.
FOSTER, S. P., and HARRIS, M. O. 1992. Foliar chemicals of wheat and related grasses influencing oviposition by Hessian fly, Mayetiola destructor (Say) (Diptera: Cecidomyiidae). J. Chem. Ecol. 18:1965–1980.
GRANT, G. G., and LANGEVIN, D. 1994. Oviposition responses of four Choristoneura (Lepidoptera: Tortricidae) species to chemical and physical stimuli associated with host and nonhost foliage. Environ. Entomol. 23:447–456.
GUTHRIE, W. D., ROBBINS, J. C., and JARVIS, J. L. 1985. Ostrinia nubilalis, pp. 407–413, in P. Singh and R. F. Moore (eds.). Handbook of Insect Rearing, Vol. 2. Elsevier, Amsterdam.
LUPOLI, R., MARION-POLL, F., PHAM-DELÈGUE, M. H., and MASSON, C. 1990. Effet d'émissions volatiles de feuilles de maïs sur les préférences de ponte chez Ostrinia nubilalis (Lepidoptera: Pyralidae). C.R. Acad. Sci. Ser. 3. Sci. Vie 311:225–230.
MASON, C. E., RICE, M. E., CALVIN, D. D., VANDUYN, J. W., SHOWERS, W. B., HUTCHISON, W. D., WITKOWSKI, J. F., HIGGINS, R. A., ONSTAD, D. W., and DIVELY, G. R. 1996. European corn borer ecology and management. North Central Regional Publication No. 327. Iowa State University, Ames, Iowa.
OTT, L. 1984. An Introduction to Statistical Methods and Data Analysis, 2nd ed. Duxbury Press, Boston.
RENWICK, J. A. A. 1989. Chemical ecology of oviposition in phytophagous insects. Experientia 45:223–228.
RENWICK, J. A. A., RADKE, C. D., SACHDEV-GUPTA, K., and STÄDLER, E. 1992. Leaf surface chemicals stimulating oviposition by Pieris rapae (Lepidoptera: Pieridae) on cabbage. Chemoecology 3:33–38.
SCHURR, K., and HOLDAWAY, F. G. 1970. Olfactory responses of female Ostrinia nubilalis (Lepidoptera: Pyraustinae). Entomol. Exp. Appl. 13:455–161.
STÄDLER, E. 1992. Behavioral responses of insects to plant secondary compounds, pp. 45–88, in G. A. Rosenthal and M. R. Berenbaum (eds.). Herbivores: Their Interactions with Secondary Plant Metabolites, Vol. 2. Academic Press, New York.
STÄDLER, E., and BUSER, H.-R. 1984. Defense chemicals in leaf surface wax synergistically stimulate oviposition by a phytophagous insect. Experientia 40:1157–1159.
STADLER, E., and SCHONI, R. 1990. Oviposition behavior of the cabbage root fly, Delia radicum (L.) influenced by host plant extracts. J. Insect Behav. 3:195–209.
THIERY, D., and LE QUÉRÉ, J. L. 1991. Identification of an oviposition-deterring pheromone in the eggs of the European corn borer. Naturwissenschaften 78:132–133.
UDAYAGIRI, S., and JONES, R. L. 1992. Role of plant odor in parasitism of European corn borer by braconid specialist parasitoid Macrocentrus grandii Goidanich: Isolation and characterization of plant synomones eliciting parasitoid flight response. J. Chem. Ecol. 18:1841–1855.
UDAYAGIRI, S., and MASON, C. E. 1995. Host plant constituents as oviposition stimulants for a generalist herbivore: European com borer. Entomol. Exp. Appl. 76:59–65.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Udayagiri, S., Mason, C.E. Epicuticular Wax Chemicals in Zea mays Influence Oviposition in Ostrinia nubilalis . J Chem Ecol 23, 1675–1687 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1023/B:JOEC.0000006443.72203.f7
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/B:JOEC.0000006443.72203.f7