Abstract
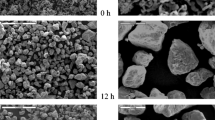
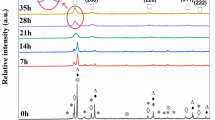
The phase composition and structure of Co60Ge40 prepared by mechanical alloying followed by heat treatment are studied by x-ray diffraction, x-ray microanalysis, differential scanning calorimetry, and scanning electron microscopy. The results indicate that milling a 60 : 40 mixture of Co and Ge for 2 h leads to the formation of phase-pure, nanocrystalline β-Co5Ge3 (B82 structure). This phase is chemically inhomogeneous and metastable. On heating to 720°C, it transforms into a homogeneous, equilibrium phase of β-Co5Ge3. The transformation into the stable β phase occurs through a two-phase state, involving the formation of the orthorhombic phase Co2Ge. At t ≥ 630°C, Co2Ge dissolves in β-Co5Ge3.
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Albertini, F., Paoluzi, A., Pareti, L., et al., Thermomag-netic Analysis of the Phase Formation in Fe–Ge Com-pounds Obtained by Mechanical Alloying, Mater. Sci. Forum, 1995, vol. 195, pp. 167–172.
Chen, Q.Z., Ngan, A.H., and Duggan, B.J., The L 1 2 DO 19 Transformation in the Intermetallic Compound Fe 3 Ge, J. Mater. Sci., 1998, vol. 33, pp. 5405–5414.
Carera, A.F., Sánchez, F.H., and Mendoza, L., Mechani-cal Alloying of Fe 1 – x M x (M = Si, Ge, Sn): A Compara-tive Study, J. Metastable Nanocryst. Mater., 1999, vols. 2–6, pp. 85–90.
Gerasimov, K.V. and Pavlov, S.V., New Equilibrium Phase in the Fe–Ge System Obtained by Mechanical Alloying, Intermetallics, 2000, vol. 8, pp. 451–452.
Elsukov, E.P., Dorofeev, G.A., Ul'yanov, A.L., and Zagainov, A.V., Mechanical-Alloying-Induced Struc-tural Phase Transitions of Fe 50 Ge 50, Fiz. Met. Metall-oved., 2003, vol. 95, pp. 1–8.
PAULING FILE Binaries Edition, Version 1.0, Villars, P., Ed., JST–MPDS, 2002.
Gel'd, P.V., Levin, E.S., Zagryazhskii, V.L., and Zamaraev, V.N., Physicochemical Properties and Structure of Solid and Liquid Co 5 Ge 3 and Ni 5 Ge 3, Izv. Akad. Nauk SSSR, Neorg. Mater., 1979, vol. 15, pp. 21–24.
Shelekhov, E.V. and Sviridova, T.A., Modeling of Motion and Heating Processes in Planetary Mills, Mate-rialovedenie, 1999, no. 10, pp. 13–21.
De Lima, J.C., Santos, V.H.F., Crandi, T.A., et al., Ther-modynamic Considerations about the Formation of Alloys by Mechanical Alloying, Phys. Rev. B: Condens. Matter, 2000, vol. 62, pp. 8871–8877.
Panday, P.K. and Schubert, K., Strukturuntersuchugen in einigen Mischungen T–B 3 –B 4 (T = Mn, Fe, Co, Ir, Ni, Pd; B 3 = Al, Ga, Tl; B 4 = Si, Ge), J. Less-Common. Met., 1969, vol. 18, pp. 175–202.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fadeeva, V.I., Kubalova, L.M. & Sviridov, I.A. Structure and Thermal Stability of Co60Ge40 Prepared by Mechanical Alloying. Inorganic Materials 40, 1032–1034 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1023/B:INMA.0000046463.69625.b1
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/B:INMA.0000046463.69625.b1