Abstract
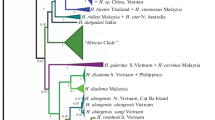
Snub-nosed monkeys (Rhinopithecus spp.) are confined to isolated mountainous regions in China and North Vietnam. Their systematic classification and phylogenetic relationship has been controversial. The structures of mitochondrial DNA cytochrome b and 12S rRNA show that the 4 species of Rhinopithecus are quite different from other colobines. It is reasonable to regard them as an independent genus, as determined by external features, morphometric characters and behavior. However, whether or not there should be a subdivision between the Vietnamese and Chinese species at the subgeneric level remains to be clarified; more evidence from a large range of Asian colobine species is needed. The Guizhou species, Rhinopithecus brelichi, is a valid species, which is more closely related to Pygathrix than the other species ( R. roxellana, R. bieti and R. avunculus) are. Results also indicate that 3 species—Rhinopithecus roxellana, R. bieti and R. avunculus—might have diverged from R. brelichi, but the phylogenetic relationship of R. avunculus is not clear.
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Allen, G. M. (1938) The Mammals of China and Mongolia, Part 1, American Museum of Natural History, New York, pp. 299-304.
Bernstein, I. S. (1968) Social status of two hybrids in a wild group of Macaca irus. Folia Primatol. 8: 121-131.
Bleisch, V. W., and Xie, J. H. (1998) Ecology and behavior of the Guizhou snub-nosed langur (Rhinopithecus [Rhinopithecus] brelichi), with a discussion of socioecology in the genus. In Jablonski, N. G. (ed.), The Natural of the Doucs and Snub-nosed Monkeys, World Scientific Publishing, Singapore, pp. 217-240.
Brandon-Jones, D. (1984) Colobus and leaf monkeys. In Macdonald, D. (ed), The Encyclopedia of Mammals, Vol. 1, Allen and Unwin, London, pp. 398-410.
Buettner-Janusch, J. (1963) A problem in evolutionary systematics: Nomenclature and classification of baboons. Folia Primatol. 4: 288-308.
Corbet, G. B., and Hill, J. E. (1980) A World List of Mammalian Species, British Museum (Natural History).
Ellerman, J. R., and Morrison-Scott, T. S. C. (1951) Checklist of Paratactic and Indian Mammals, British Museum (Natural History), London, pp. 1758-1946.
Elliot, D. C. (1913) A Review of the Primates, American Museum of Natural History, New York.
Goossens, B. L., Chikhi, S. S., Johannes de Ruiter, and Bruford, M. W. (2000) A multiple-samples, multiple-extracts approach for microsatellite analysis of faecal samples in an arboreal ape. Conserv. Genet. 1(2): 157-162.
Groves, C. P. (1970) The forgotten leaf-eaters, and the phylogeny of the colobinae. In Napier, J. R., and Napier, P. H. (eds.), Old World Monkeys, Academic Press, New York, pp. 555-587.
Groves, C. P. (1989) A Theory of Human and Primate Evolution, Oxford Science Publication, Oxford.
Groves, C. P. (2001) Primate Taxonomy, Smithsonian Institute Press, Washington, D. C.
Hill, W. C. O. (1974) Primates: Comparative Anatomy and Taxonomy. Vol. 7. Cynopithecinae, Wiley, New York.
Jablonski, N. G. (1996) A diverse anthropoid fauna of probable Late Pleistocene age from Luoding, Guangdong, P. R. China. Am. J. Phys. Anthropol. Suppl. 22: 130.
Jablonski, N. G. (1998a) The evolution of the doucs and snub-nosed monkeys and the question of the phyletic unity of the odd-nosed colobines. In Jablonski, N. G. (ed.), The Natural of the Doucs and Snub-nosed Monkeys, World Scientific Publishing, Singapore, pp. 13-52.
Jablonski, N. G. (1998b) The response of catarrhine primates to Pleistocene environmental fluctuations in East Asia. Primates 39: 29-37.
Jablonski, N. G., and Peng, Y. Z. (1993) The phylogenetic relationships and classification of the doucs and snub-nosed langurs of China and Vietnam. Folia Primatol. 60: 36-55.
Kimura, M. (1980) A simple method for estimating evolutionary rare of base substitutions through comparative studies of nucleotide sequences. J. Mol. Evol. 16: 111-120.
Kirkpatric, R. C. (1998) Ecology and behavior in snub-nosed and douc langurs. In Jablonski, N. G. (ed.), The Natural of the Doucs and Snub-nosed Monkeys, World Scientific Publishing, Singapore, pp. 155-190.
Kishino, H., and Hasagawa, M. (1989) Evaluation of the maximum likelihood estimate of evolutionary tree topologies from DNA sequences data, and the branching order in huminoidea. J. Mol. Evol. 29: 170-179.
Kocher, T. D., Thomas, W. K., Meyer, A., Edwards, S. V., Paabo, S., Villablanca, F. X., and Wilson, A. C. (1989) Dynamics of mitochondrial DNA evolution in animals: Amplification and sequencing with conserved primers. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 86: 6196-6200.
Kumar, S. K., Tamura, K., Jakobsen, I. B., and Nei, M. (2001) MEGA 2: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis Program, Pennsylvania State University, PA.
Li, B. G., Pan, R. L., and Oxnard, C. E. (2002) Extinction of snub-nosed monkeys in China during the past 400 years. Int. J. Primatol. 23(6): 1227-1244.
Li, M., Liang, B., Tamate, H. B., and Feng, Z. (2001) Molecular phylogeny of Sichuan snub-nosed monkey (Rhinopithecus roxellae) with cytochrome b sequences. Primates 42: 153-160.
Li, Z. X., Ma, S. L., Ha, C. H., and Wang, Y. X. (1983) Classification and distribution of living primates in Yunnan. China. Zool. Res. 4: 113-120.
Napier, J. R., and Napier, P. H. (1967) A Handbook of Living Primates, Academic Press, London.
Napier, P. H. (1985) Catalogue of primates in the British Museum (Natural History) and Elsewhere in the British Isles. Part III: Family Cercopithecidae, subfamily Colobinae, British Museum (Natural History), London.
Pan, R. L., and Oxnard, C. (2001) Cranial morphology of the golden monkey (Rhinopithecus) and douc langur (Pygathrix nemaeus). Hum. Evol. 16: 199-223.
Peng, Y. Z., Pan, R. L., and Jablonski, N. G. (1993) Classification and evolution of Asian colobines. Folia Primatol. 60: 106-117.
Peng, Y. Z., Ye, Z. Z., Zhang, Y. P., and Pan, R. L. (1988) The classification and phylogeny of snub-nosed monkeys based on gross morphological characters. Zool. Res. 9: 239-248.
Pocock, R. L. (1924) A new genus of monkeys. Proc. Zool. Soc. Lond. 1924: 330-331.
Posada, D., and Crandall, K. A. (1998) MODELTEST: Testing the model of DNA substitution. Bioinformatics 14: 817-818.
Quan, G. Q., and Xie, J. H. (1981) Notes on Rhinopithecus roxellanae brelichi Thomas. Acta Theriol. Sinica 1(2): 113-116.
Sernstein, I. S. (1966) Natural occurring primate hybrid. Science, 154: 1559-1560.
Shotake, T. (1981) Population genetic study of natural hybridization between Papio anubis and P. hamdryas. Primates 23: 185-308.
Swindler, R. R. (1976) Dentition of Living Primates, Academic Press, London.
Swofford, D. L. (2000) PAUP: Phylogenetic Analysis Using Parsimony. Version 3.1.1, Illinois Natural History Survey, Champaign, IL.
Szalay, F. S., and Delson, E. (1979) Evolutionary History of the Primates, Academic Press, New York.
Tamura, K., and Nei, M. (1993) Estimation of the number of nucleotide substitutions in the control region of mitochondrial DNA in humans and chimpanzees. Mol. Biol. Evol. 10: 512-526.
Thomas, O. (1903) Notes on South American monkeys, bats, carnivores and rodents with descriptions of new species. Annals and Magazine of Natural history 12: 455-464.
Thompson, J. D., Gibson, T. J., Plewniak, F., Jeanmougin, F., and Higgins, D.G. (1997) The ClustalX windows interface: Flexible strategies for multiple sequence alignment aided by quality analysis tools. Nucleic Acids Research 25: 4876-4882.
van der Kuyl, A. C., Dekker, J. T., and Goudsmit, J. (2000) Primate genus Miopithecus: Evidence for the existence of species and subspecies of dwarf guenons based on cellular and endogenous viral sequences. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 14(3): 403-413.
van der Kuyl, A. C., Kuiken, C. L., Dekker, J. T., and Goudsmit, J. (1995) Phylogeny of African monkeys based upon mitochondrial 12S rRNA sequences. J. Mol. Evol. 40(2): 173-180.
Wang, W., Michaei, R. J. F., Zhang, Y. P., Liu, Z. M., Wei, Y., Huang, H. Q., Hu, H. G., Xie, Y. X., Wu, D. H., and Melnick, D. J. (1997) A phylogeny of Chinese leaf monkey using mitochondrial ND3-ND4 gene sequences. Int. J. Primatol. 18(3): 305-320.
Ye, Z. Z., Peng, Y. Z., Zhang, Y. P., and Liu, R. L. (1987) The Anatomy of the Golden Monkey, Yunnan Scientific Press, Kunming, China.
Zhang, R. Z., Quang, C. Q., Zhao, T. G., and Southwick, C. H. (1992) Distribution of primates (except Macaca) in China. Acta Theriol. Sin. 12(2): 81-95.
Zhang, Y. P., and Ryder, O. A. (1997) Mitochondrial DNA sequence evolution and conservation relevance of snub-nosed langurs. Acta Genet. Sin. 24(2): 116-121.
Zhang, Y. P., and Ryder, O. A. (1998) Mitochondrial cytochrome b gene sequences of old world monkeys: With special reference on evolution of Asia Colobines. Primates 39(1): 39-49.
Zhang, Y. P., and Shi, L. M. (1993) Phylogenetic relationships of macaques as inferred from restriction endonuclease analysis of mitochondrial DNA. Folia Primatol. 60: 7-17.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, M., Wei, F., Huang, C. et al. Phylogeny of Snub-Nosed Monkeys Inferred from Mitochondrial DNA, Cytochrome B, and 12S rRNA Sequences. International Journal of Primatology 25, 861–873 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1023/B:IJOP.0000029126.27618.88
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/B:IJOP.0000029126.27618.88