Abstract
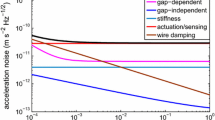
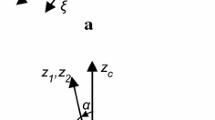
By using a novel free-flying, rotating, optical bench aboard the International Space Station (ISS) as the basis for a measurement of differential acceleration between two gravitating bodies, in principle the Newtonian inverse-square law and the constant of gravitation, G, can be determined at the parts in 106 level.
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Committee on Data for Science and Technology (CODATA) (1998). http://physics.nist.gov/cgi-bin/cuu/Value?bg; Mohr, P. J. and Taylor, B. N. (2000). Rev. Mod. Phys. 72, 351.
Baldi, P., Compari, E. G., Casula, G., Focardi, S., and Palmonari, F. (2001). Phys. Rev. D. 68, 082001.
Adelberger, E., Heckel, B.-R., and Nelson, A. E. (2003). Annu. Rev. Nucl. Particle Sci. 53, 77-121. (http://www.annualreviews.org/catalog/pub_dates.asp).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lockerbie, N.A. ISLAND—Inverse Square Law Acceleration Measurement Using iNertial Drift. General Relativity and Gravitation 36, 593–600 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1023/B:GERG.0000010732.01651.a4
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/B:GERG.0000010732.01651.a4