Abstract
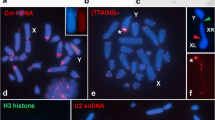
The status of an extra univalent, if it is a B chromosome or an achiasmatic Y chromosome, associating with the X chromosome in male meiosis of Cacopsylla peregrina (Frst.) (Homoptera, Psylloidea) was analysed. One extra univalent was present in all males collected from three geographically well separated populations, it was mitotically stable, and showed precise segregation from the X chromosome. These findings led us to propose that the univalent represents in fact a Y chromosome. The behaviour of the X and Y chromosomes during meiotic prophase suggested that their regular segregation was based on an achiasmatic segregation mechanism characterised by a ‘touch and go’ pairing of segregating chromosomes at metaphase I. To explain the formation of the achiasmatic Y within an insect group with X0 sex chromosome system, it was suggested that the Y chromosome has evolved from a mitotically stable B chromosome that was first integrated into an achiasmatic segregation system with the X chromosome, and has later become fixed in the karyotype as a Y chromosome.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Araujo, S.M.S.R., S.G. Pompolo, F. Perfectti & J.P.M. Camacho, 2001. Integration of a B chromosome into the A genome of a wasp. Proc. R. Soc. London B 268: 1127–1131.
Carvalho, A.B., 2002. Origin and evolution of the Drosophila Y chromosome. Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev. 12: 664–668.
Green, D.M., C.W. Zeyl & T.F. Sharbel, 1993. The evolution of hypervariable sex and supernumerary (B) chromosomes in the relict New Zealand frog, Leiopelma hochstetteri. J.Evol.Biol. 6: 417–441.
Grozeva, S. & A. Maryanska-Nadachowska, 1995. Meiosis of two species of Cacopsylla with polymorphic sex chromosomes in males (Homoptera: Psyllidae). Folia Biol. (Krakow) 43: 93–98.
Grozeva, S. & S. Nokkala, 1996. Chromosomes and their meiotic behaviour in two families of the primitive infraorder Dipsocoromorpha (Heteroptera). Hereditas 125: 31–36.
Hackstein, J.H.P., R. Hochstein, E. Hausteck-Jungen & L.W. Beukeboom, 1996. Is the Y chromosome of Drosophila an evolved supernumerary chromosome? BioEssays 18: 317–323.
Hewitt, G.W., 1973. The integration of supernumerary chromosomes into the Orthopteran genome. Cold Spring Harb. Symp. Quant. Biol. 38: 183–194.
Jande, S.S., 1960. Pre-reductional sex chromosomes in the family Tingidae (Gymnocerata-Heteroptera). Nucleus 3: 209–214.
Kimura, M. & H. Kayano, 1961. The maintenance of supernumerary chromosomes in wild populations of Lilium callosum by preferential segregation. Genetics 46: 1699–1712.
Kuznetsova, V.G., S. Nokkala & A. Maryanska-Nadachowska, 1997. Karyotypes, sex chromosome systems, and male meiosis in Finnish psyllids (Homoptera: Psylloidea). Folia Biol. (Krakow) 45: 143–152.
Maryanska-Nadachwoska, A., V.G. Kuznetsova & S. Nokkala, 2001. Standard and C-banded meiotic karyotypes of Psylloidea (Sternorrhyncha, Homoptera, Insecta). Folia Biol. (Krakow) 49: 53–62.
Maryanska-Nadachowska, A., G.S. Taylor & V.G. Kuznetsova, 2001. Meiotic karyotypes and structure of testes in males of 17 species of Psyllidae: Spondiliaspidinae (Hemiptera: Psylloidea) from Australia. Aust. J. Entomol. 40: 349–356.
Maryanska-Nadachowska, A., V.G. Kuznetsova, C.H.-T. Yang & I.H. Woudstra, 1996. New data on karyotypes and the number of testicular follicles in the psyllid families Aphalaridae, Psyllidae, Carsidaridae, and Triozidae (Homoptera: Psylloidea). Caryologia 49: 279–285.
Matcharashvili, I.D. & V.G. Kuznetsova, 1997. Karyotypes, spermatogenesis, and morphology of the internal reproductive system in males of some species of psyllids (Homoptera: Psylloidea) of fauna of Georgia. I. Karyotypes and spermatogonial meiosis. Entomol. Rev. 77: 12–20.
Nokkala, S., 1986a. The meiotic behaviour of B-chromosomes and their effect on the segregation of sex chromosomes in males of Hemerobius marginatus L. (Hemerobidae: Neuroptera). Hereditas 105: 221–227.
Nokkala, S., 1986b. The mechanism behind the regular segregation of the m-chromosomes in Coreus marginatus L. (Coreidae: Hemiptera). Hereditas 105: 73–85.
Nokkala, S., V. Kuznetsova & A. Maryanska-Nadachowska, 2000. Achiasmate segregation of a B chromosome from the X chromosome in two species of psyllids (Psylloidea: Homoptera). Genetica 108: 181–189.
Sharbel, T.F., D.M. Green & A. Houben, 1998. B-chromosome origin in the endemic New Zealand frog Leiopelma hochstetteri through sex chromosome evolution. Genome 41: 14–22.
Suomalainen, E. & O. Halkka, 1963. The mode of meiosis in the Psyllina. Chromosoma 14: 498–510.
White, M.J.D., 1973. Animal Cytology and Evolution. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nokkala, S., Grozeva, S., Kuznetsova, V. et al. The Origin of the Achiasmatic XY Sex Chromosome System in Cacopsylla peregrina (Frst.) (Psylloidea, Homoptera). Genetica 119, 327–332 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1023/B:GENE.0000003757.27521.4d
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/B:GENE.0000003757.27521.4d