Abstract
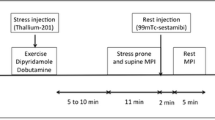
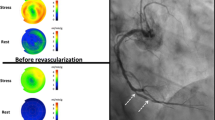
Background:A reverse redistribution pattern during myocardial perfusion imaging is most widely described using thallium (Tl-201), when stress images exhibit greater perfusion than rest. Technetium (Tc-99 m) radiopharmaceuticals may also yield a reverse perfusion (RP) pattern, but its significance is uncertain. This study tested the hypothesis that RP correlates with the presence and location of flow limiting coronary stenosis(es). Method:We reviewed 842 consecutive Tc-99 m tetrofosmin SP(age 32–79 mean 56, 17 female) had undergone cardiac catheterisation within 12 months of the scan. Correlation was sought between the presr; coronary stenosis(es); 5 single-vessel, 2 two-vessel and 3 three-vessel disease (3VD). Stenosis location correlated poorly with the RP territory (LAD/Anterior 5/17, RCA/Inferior 1/10, Cx/lateral 0/4 (p= 0.57)). Of the 6 patients with a lesion in the RP territory, 3 had 3VD; 2 of these had a simultaneous reversible defect. All 5 patients with previous myocardial infarction had a simultaneous fixed defect. However only 3/12 with co-existent reversible defects had significant disease. Conclusion:The reverse perfusion pattern is a poor predictor of flow limiting coronary disease, and does not correlate with stenosis location in those with significant lesions. Such patients should not undergo invasive investigation purely on the basis of this result.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Fintel DJ, Links JM, Brinker JA,et al.Improved diagnostic performance of exercise thallium-201 single photon emission computed tomography over planar imaging in the diagnosis of coronary artery disease:a receiver operating character-istic analysis.J Am Coll Cardiol 1989;13:600–612.
Maddahi J, Van Train K, Prigent F,et al.Quantitative single photon emission computed thallium-201 tomography for detection and localization of coronary artery disease: optimization and prospective validation of a new technique. J Am Coll Cardiol 1989;14:1689–1699.
Tamaki N, Yonekura Y, Mukai T,et al.Stress thallium-201 transaxial emission computed tomography:quantitative versus qualitative analysis for evaluation of coronary artery disease.J Am Coll Cardiol 1984;4:1213–1221.
Wackers FJ, Berman DS, Maddahi J,et al.Technetium-99m hexakis 2-methoxyisobutyl isonitrile:human biodistri-bution,dosimetry,safety,and preliminary comparison to thallium-201 for myocardial perfusion imaging.J Nucl Med 1989;30:301–311.
Zaret BL, Rigo P, Wackers FJ,et al.Myocardial perfusion imaging with 99mTc tetrofosmin.Comparison to 201Tl imaging and coronary angiography in a phase III multi-center trial.Tetrofosmin International Trial Study Group. Circulation 1995;91:313–319.
Hecht HS, Hopkins JM, Rose JG,et al.Reverse redis-tribution:worsening of thallium-201 myocardial images from exercise to redistribution.Radiology 1981;140:177–181.
Silberstein EB, DeVries DF.Reverse redistribution phenomenon in thallium-201 stress tests:angiographic cor-relation and clinical signi cance.J Nucl Med 1985;26:707–710.
Dudzic EM, Sridhara BS, Lahiri A.Reverse redistribution: fact or ction?Eur J Nucl Med 1994;21:449–453.
Maddahi J, Berman DS.Reverse redistribution of thallium-201.J Nucl Med 1995;36:1019–1021.
Koliakos G, Doumas A, Altas D,et al.The clinical signif-icance of reverse redistribution in Tl201 cardiac SPET.Int J Cardiovasc Imaging 2001;17:29–35.
Faraggi M.The continuing story of (201)Tl reverse redis-tribution:reverse redistribution is still alive,but is the myocardium still viable?J Nucl Med 2002;43:628–631.
Yamagishi H, Itagane H, Akioka K,et al.Clinical signi-cance of reverse redistribution on thallium-201 single-pho-ton emission computed tomography in patients with acute myocardial infarction.Jpn Circ J 1992;56:1095–1105.
Yamagishi H, Akioka K, Itagane H,et al.Relationship between insuficient redistribution in exercise thallium-201 myocardial single-photon emission computed tomography and reverse redistribution at rest.Jpn Circ J 1995;59:23–32.
De Sutter J, Van de WC, Dierckx R,et al.Reverse redis-tribution on thallium-201 single-photon emission tomogra-phy after primary angioplasty:a one-year follow-up study. Eur J Nucl Med 1999;26:633–639.
Popma JJ, Smitherman TC, Walker BS,et al.Reverse redistribution of thallium-201 detected by SPECT imaging after dipyridamole in angina pectoris.Am J Cardiol 1990; 65:1176–1180.
Lee JK, Kao CH.Reverse redistribution during dipyrid-amole thallium-201 myocardial single photon emission computed tomography in coronary artery disease.Ka-ohsiung J Med Sci 1996;12:630–633.
Fragasso G, Rossetti E, Dosio F,et al.High prevalence of the thallium-201 reverse redistribution phenomenon in pa-tients with syndrome X.Eur Heart J 1996;17:1482–1487.
Sugihara H, Nakagawa T, Yamashita E,et al.Reverse redistribution of Tc-99m-tetrofosmin in patients with acute myocardial infarction.Ann Nucl Med 1999;13:43–47.
Fujiwara S, Takeishi Y, Hirono O,et al.Reverse redistri-bution of 99m Tc-sestamibi after direct percutaneous transluminal coronary angioplasty in acute myocardial infarction:relationship with wall motion and functional response to dobutamine stimulation.Nucl Med Commun 2001;22:1223–1230.
Hirata Y, Takamiya M, Kinoshita N,et al.Interpretation of reverse redistribution of 99mTc-tetrofosmin in patients with acute myocardial infarction.Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 2002;29:1594–1599.
Fragasso G, Chierchia SL, Dosio F,et al.High prevalence of (99m)Tc-tetrofosmin reverse perfusion pattern in patients with myocardial infarction and angiographically smooth coronary arteries.Int J Cardiovasc Imaging 2002;18:31–40.
Kao CH, Wang SJ,Ting CT,et al.'Reverse redistribution pattern 'during myocardial perfusion imaging with 99Tcm-MIBI.Nucl Med Commun 1996;17:397–399.
Donovan P, Kieffer V, Shih WJ.Duodenogastric reflux on (99m)Tc-tetrofosmin myocardial SPECT mimics left ventricle inferior wall reverse redistribution and falsely decreases ejection fraction:a case report.J Nucl Med Technol 2001;29:193–196.
Shih WJ, Donovan P, Kiefer V.Signi cant enterogastric reflux secondary to Billroth II gastrectomy leads to reverse redistribution of the inferior wall of the left ventricle on dipyridamole Tc-99m tetrofosmin myocardial spect.Clin Nucl Med 2001;26:543–546.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Smith, E., Hussain, A., Manoharan, M. et al. A Reverse Perfusion Pattern During Technetium-99m Stress Myocardial Perfusion Imaging Does Not Predict Flow Limiting Coronary Artery Disease. Int J Cardiovasc Imaging 20, 321–326 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1023/B:CAIM.0000041951.48335.1a
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/B:CAIM.0000041951.48335.1a