Abstract
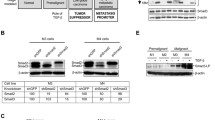
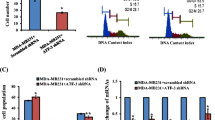
Cytokine oncostatin M (OM) strongly inhibits the growth of MCF-7 breast cancer cells through the STAT3 signaling pathway. We have performed cDNA microarray analyses to identify novel OM-regulated genes in MCF-7 cells that are downstream effectors of the STAT3 signaling cascade. We show that expression of the calcium-binding protein S100A9 is strongly induced by OM in MCF-7 cells and this induction is markedly reduced in MCF-7-dnStat3 cells that express a dominant negative mutant of STAT3. We further show the induction of S100A9 by OM in other breast cancer cell lines whose proliferations are inhibited by OM whereas S100A9 is not significantly induced in SKBR-3 or HepG2 cells that do not respond to OM with a growth repression. In addition, inhibition of S100A9 expression with siRNA decreased cell response to OM-induced growth repression. By analyzing a series of S100A9 promoter reporter constructs, we have defined two discrete regions in the S100A9 promoter responsible for OM-induced transcriptional activation. Together these studies identify S100A9 as a novel OM-regulated gene through the STAT3-signaling cascade and suggest its involvement in the growth regulation of breast cancer cells.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Liu J, Spence MJ, Wallace PM, Forcier K, Hellstrom I Vestal RE: Oncostatin M-specific receptor mediates inhibition of breast cancer cell growth and down-regulation of the c-myc proto-oncogene. Cell Growth Differ 8:667–676, 1997
Spence MJ, Vestal RE, Liu J: Oncostatin M-mediated transcriptional suppression of the c-myc gene in breast cancer cells. Cancer Res 57:2223–2228, 1997
Li C, Ahlborn TE, Kraemer FB, Liu J: Oncostatin Minduced growth inhibition and morphological changes of MDA-MB231 breast cancer cells are abolished by blocking the MEK/ERK signaling pathway. Breast Cancer Res Treat 66:111–121, 2001
Liu J, Hadjokas N, Mosley B, Estrov Z, Spence MJ, Vestal RE: Oncostatin M-speci c receptor expression and function in regulating cell proliferation of normal and malignant mammary epithelial cells. Cytokine 10:295–302,1998
Badache A, Hynes N: Interleukin 6 inhibits proliferation and, in cooperation with an epidermal growth factor receptor autocrine loop, increases migration of T47D breast cancer cells. Cancer Res 61:383–391, 2001
Zhang F, Li C, Halfter H, Liu J: Delineating an oncostatin M-activated STAT3 signaling pathway that coordinates the expression of genes involved in cell cycle regulation and extracellular matrix deposition of MCF-7 cells. Oncogene 22:894–905, 2003
Kiuchi N, Nakajima K, Ichiba M, Fukada T, Narimatsu M, Mizuno K, Hibi M, Hirano T:STAT3 is required for Activation of S100A9 gene expression by oncastatin M 133.the gp13–mediated full activation of the c-myc gene. J Exp Med 189:63–73, 1999
Matsui T, Kinoshita T, Hirano T, Yokota T, Miyajima A: STAT3 down-regulates the expression of cyclin D during liver development. J Biol Chem 277:36167–36173,2002
Kligman D, Hilt D: The S100 protein family. Trends Biochem Sci 13:437–443, 1988
Zimmer D, Cornwall EH, Landar A, Song W: The S100 protein family: history, function, and expression. Brain Res Bull 37:417–429, 1995.
Schäfer B, Heizmann C: The S100 family of EF-hand calcium binding protein: functions and pathology. TIBS 21: 134–140, 1996
Odink K, Cerletti N, Bruggen J, Clerc RC, Tarcsay L, Zwadlo G, Gerhards G, Schlegel R, Sorg C: Two calcium binding proteins in in ltrate macrophages of rheumatoid arthritis. Nature 330:82, 1987
Lagasse E, Clerk RG: Cloning and expression of two human genes encoding calcium-binding proteins that are regulated during myeloid differentiation. Mol Cell Biol 8: 2402–2410, 2002
Edgeworth J, Gorman M, Bennet R, Freemont P, Hogg N: Identification of p8,14 as a highly abundant heterodimericd calcium-binding protein complex of myeloid cells. J Biol Chem 266:7706–7713, 1991
Van Heyningen V, Dorin J: Possible role for two calcium-binding proteins of the S100 family, co-expressed in granulocytes and certain epithelia. Adv Exp Med Biol 269:139–143, 1990
Gupta A, Godwin AK, Vanderveer L, Lu A, Liu J: Hypomethylation of the synuclein c gene CpG island promotes its aberrant expression in breast carcinoma and ovarian carcinoma. Caner Res 63:664–673, 2003
Kerkhoff C, Hofmann H, Vormoor J, Melkonyan H, Roth J, Sorge CAKM: Binding of two nuclear complexes to a novel regulatory element within the human S100A9 promoter drives the S100A9 gene expression. J Biol Chem 277: 41879–41887, 2002
Klempt M, Melkonyan H, Hofmann H, Sorg C: Identification of epithelial and myeloid-specific DNA elements regulating MRP14 gene transcription. J Biol Chem 73:49–55, 1999
Liu J, Streiff R, Zhang YL, Vestal RE, Spence MJ, Briggs MR: Novel mechanism of transcriptional activation of hepatic LDL receptor by oncostatin M. J Lipid Res 38: 2035–2048, 1997
Kuruto-Niwa R, Nakamura M, Takeishi K, Nuorva K: Transcriptional regulation by C/EBP alpha and-beta in the expression of the gene for the MRP14 myeloid calcium binding protein. Cell Struc Funct 23:109–118, 1998
Gebhardt C, Breitenbach U, Tuckermann JP, Dittrich BT, Richter KH, Angel P: Calgranulins S100A8 and S100A9 are negatively regulated by glucocorticoids in a c-Fos-dependent manner and overexpressed throughout skin carcinogenesis. Oncogene 21:4266–4276,2002
Stulik J, Koupilova K, Osterreicher J, Knizek J, Macela A, Bures J, Jandik P, Langnr F: Protein abundance alterations in matched sets of macroscopically normal colon mucosa and colorectal carcinoma. Electrophoresis 20:3638–3646, 1999
Arai K, Teratani T, Nozawa R, Yamada T:Immunohistochemical investigation of S100A9 expression in pulmonary adenocarcinoma:S100A9 expression is associated with tumor differentiation. Oncol Rep 8:591–596, 2001
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, C., Zhang, F., Lin, M. et al. Induction of S100A9 Gene Expression by Cytokine Oncostatin M in Breast Cancer Cells Through the STAT3 Signaling Cascade. Breast Cancer Res Treat 87, 123–134 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1023/B:BREA.0000041594.36418.f6
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/B:BREA.0000041594.36418.f6