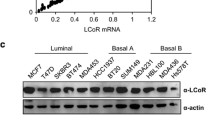
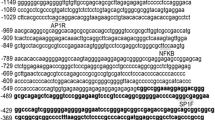
Abstract
The exact molecular mechanisms regulating estrogen receptor α (ERα) expression in breast tumors are unclear, but studies suggest that they are partly at the level of transcription. We have focused on the transcription factors that regulate the ERα minimal promoter, which we have previously shown to reside within the first 245 bp of the 5′-flanking region of the gene. Within this region are several elements essential for full ERα promoter transcriptional activity, including a GC box and an imperfect E box. In earlier studies we demonstrated an essential function for the Sp1 family of transcription factors in the regulation of ERα expression. We have now identified both USF-1 and ERα itself as components of a multi-protein complex of transcription factors that interacts at the ERα minimal promoter and is essential for its full transcriptional activity. Electrophoretic mobility shift assays demonstrated that Sp1 and USF-1, but not ERα, bind directly to the ERα minimal promoter. We showed by GST pull-down assays that ERα is able to interact in vitro with USF-1, suggesting, in addition to a possible interaction between ERα and Sp1, a mechanism whereby ERα is able to interact with the protein complex. Combined exogenous expression of the components of the complex in MCF-7 breast cancer cells resulted in a synergistic effect on transactivation of the ERα minimal promoter, suggesting that the importance of the protein complex is in the interactions among the components. Based upon these findings, we propose a possible model for transcription from the ERα minimal promoter.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
McGuire WL, Chamness GC: Studies on the estrogen receptor in breast cancer. Adv Exp Med Biol 36: 113–136, 1973
McGuire WL, Carbone PP, Vollmer EP: Estrogen Receptors in Human Breast Cancer. Raven Press, New York
Khan SA, Rogers MA, Obando JA, Tamsen A: Estrogen receptor expression of benign breast epithelium and its association with breast cancer. Cancer Res 54: 993–997, 1994
Khan SA, Rogers MA, Khurana KK, Meguid MM, Numann PJ: Estrogen receptor expression in benign breast epithelium and breast cancer risk [see comments]. J Natl Cancer Inst 90: 37–42, 1998
Fanelli MA, Vargas-Roig LM, Gago FE, Tello O, Lucero De Angelis R, Ciocca DR: Estrogen receptors, progesterone receptors, and cell proliferation in human breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat 37: 217–228, 1996
Netto GJ, Cheek JH, Zachariah NY, Romer JC, Lee CF, Schoenfeld R, Chakmakjian ZH: Steroid receptors in benign mastectomy tissue. Am J Clin Pathol 94: 14–27, 1990
Allegra JC, Lippman ME, Green L, Barlock A, Simon R, Thompson EB, Huff KK, Griffin W: Estrogen receptor values in patients with benign breast disease. Cancer 44: 228–231, 1979
van Agthoven T, Timmermans M, Dorssers LC, Henzen-Logmans SC: Expression of estrogen, progesterone and epidermal growth factor receptors in primary and metastatic breast cancer. Int J Cancer 63: 790–793, 1995
Martin MB, Saceda M, Garcia-Morales P, Gottardis MM: Regulation of estrogen receptor expression. Breast Cancer Res Treat 31: 183–189, 1994
Barrett-Lee PJ, Travers MT, McClelland RA, Luqmani Y, Coombes RC: Characterization of estrogen receptor messenger RNA in human breast cancer. Cancer Res 47: 6653–6659, 1987
Henry JA, Nicholson S, Farndon JR, Westley BR, May FE: Measurement of oestrogen receptor mRNA levels in human breast tumours. Br J Cancer 58: 600–605, 1988
Ricketts D, Turnbull L, Ryall G, Bakhshi R, Rawson NS, Gazet JC, Nolan C, Coombes RC: Estrogen and progesterone receptors in the normal female breast. Cancer Res 51: 1817–1822, 1991
Weigel RJ, deConinck EC: Transcriptional control of estrogen receptor in estrogen receptor-negative breast carcinoma. Cancer Res 53: 3472–3474, 1993
Saceda M, Lindsey RK, Solomon H, Angeloni SV, Martin MB: Estradiol regulates estrogen receptor mRNA stability. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol 66: 113–120, 1998
Stoica A, Saceda M, Fakhro A, Solomon HB, Fenster BD, Martin, MB: The role of transforming growth factor-beta in the regulation of estrogen receptor expression in the MCF-7 breast cancer cell line. Endocrinology 138: 1498–1505, 1997
Read LD, Greene GL, Katzenellenbogen BS: Regulation of estrogen receptor messenger ribonucleic acid and protein levels in human breast cancer cell lines by sex steroid hormones, their antagonists, and growth factors. Mol Endocrinol 3: 295–304, 1989
Ferguson AT, Vertino PM, Spitzner JR, Baylin SB, Muller MT, Davidson NE: Role of estrogen receptor gene demethylation and DNA methyltransferase. DNA adduct formation in 5-aza-2_deoxycytidine-induced cytotoxicity in human breast cancer cells. J Biol Chem 272: 32260–32266, 1997
Ferguson AT, Lapidus RG, Baylin SB, Davidson NE: Demethylation of the estrogen receptor gene in estrogen receptornegative breast cancer cells can reactivate estrogen receptor gene expression. Cancer Res 55: 2279–2283, 1995
Chen Z, Ko A, Yang J, Jordan VC: Methylation of CpG island is not a ubiquitous mechanism for the loss of oestrogen receptor in breast cancer cells. Br J Cancer 77: 181–185, 1998
Piva R, Del Senno L: Analysis of a DNA sequence upstreama of the human estrogen receptor gene. Ann NY Acad Sci 684: 235–238, 1993
Green S, Walter P, Greene G, Krust A, Goffin C, Jensen E, Scrace G, Waterfield M, Chambon P: Cloning of the human oestrogen receptor cDNA. J Steroid Biochem 24: 77–83, 1986
Thompson DA, McPherson LA, Carmeci C, deConinck EC, Weigel RJ: Identification of two estrogen receptor transcripts with novel 5′ exons isolated from a MCF7 cDNA library. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol 62: 143–153, 1997
Grandien K: Determination of transcription start sites in the human estrogen receptor gene and identification of a novel, tissue-specific, estrogen receptor-mRNA isoform. Mol Cell Endocrinol 116: 207–212, 1996
Grandien K, Backdahl M, Ljunggren O, Gustafsson JA, Berkenstam A: Estrogen target tissue determines alternative promoter utilization of the human estrogen receptor gene in osteoblasts and tumor cell lines. Endocrinology 136: 2223–2229, 1995
Grandien K: Transcriptional Control of ER Expression. Department of Medical Nutrition and Novum, Stockholm, 1997, p. 57
Hayashi S, Imai K, Suga K, Kurihara T, Higashi Y, Nakachi K: Two promoters in expression of estrogen receptor messenger RNA in human breast cancer. Carcinogenesis 18: 459–464, 1997
Hayashi S, Yoshida T: [Regulation of ER(estrogen receptor) gene expression in the genesis and development of breast cancer]. Nippon Rinsho 58: 495–503, 2000
Donaghue C, Westley BR, May FE: Selective promoter usage of the human estrogen receptor-alpha gene and its regulation by estrogen. Mol Endocrinol 13: 1934–1950, 1999
Tang Z, Treilleux I, Brown M: A transcriptional enhancer required for the differential expression of the human estrogen receptor in breast cancers. Mol Cell Biol 17: 1274–1280, 1997
deConinck EC, McPherson LA, Weigel RJ: Transcriptional regulation of estrogen receptor in breast carcinomas. Mol Cell Biol 15: 2191–2196, 1995
McPherson LA, Baichwal VR, Weigel RJ: Identification of ERF-1 as a member of the AP2 transcription factor family. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 94: 4342–4347, 1997
deGraffenried LA, Hilsenbeck SG, Fuqua SA: Sp1 is essential for estrogen receptor alpha gene transcription. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol 82: 7–18, 2002
Bigger CB, Casanova EA, Gardner PD: Transcriptional regulation of neuronal nicotinic acetylcholine receptor genes. Functional interactions between Sp1 and the rat beta4 subunit gene promoter. J Biol Chem 271: 32842–32848, 1996
Fischer KD, Haese A, Nowock J: Cooperation of GATA-1 and Sp1 can result in synergistic transcriptional activation or interference. J Biol Chem 268: 23915–23923, 1993
Dang CV, Dolde C, Gillison ML, Kato GJ: Discrimination between related DNA sites by a single amino acid residue of Myc-related basic-helix-loop-helix proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 89: 599–602, 1992
Rippe RA, Umezawa A, Kimball JP, Breindl M, Brenner DA: Binding of upstream stimulatory factor to an E-box in the 3′-flanking region stimulates alpha1(I) collagen gene transcription. J Biol Chem 272: 1753–1760, 1997
Castles CG, Oesterreich S, Hansen R, Fuqua SA: Autoregulation of the estrogen receptor promoter. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol 62: 155–163, 1997
Vyhlidal C, Samudio I, Kladde MP, Safe S: Transcriptional activation of transforming growth factor alpha by estradiol: requirement for both a GC-rich site and an estrogen response element half-site. J Mol Endocrinol 24: 329–338, 2000
Wang F, Duan R, Chirgwin J, Safe SH: Transcriptional activation of cathepsin D gene expression by growth factors. J Mol Endocrinol 24: 193–202, 2000
Salvatori L, Ravenna L, Felli MP, Cardillo MR, Russo MA, Frati L, Gulino A, Petrangeli E: Identification of an estrogenmediated deoxyribonucleic acid-binding independent transactivation pathway on the epidermal growth factor receptor gene promoter. Endocrinology 141: 2266–2274, 2000
Duan R, Porter W, Safe S: Estrogen-induced c-fos protooncogene expression in MCF-7 human breast cancer cells: role of estrogen receptor Sp1 complex formation. Endocrinology 139: 1981–1990, 1998
Xing W, Archer TK: Upstream stimulatory factors mediate estrogen receptor activation of the cathepsin D promoter. Mol Endocrinol 12: 1310–1321, 1998
Treilleux, Peloux N, Brown M, Sergeant A: Human estrogen receptor (ER) gene promoter-P1: estradiol-independent activity and estradiol inducibility in ER+ and ER-cells. Mol Endocrinol 11: 1319–1331, 1997
Hori M, Iwasaki M, Shimazaki J, Inagawa S, Itabashi M: Assessment of hypermethylated DNA in two promoter regions of the estrogen receptor alpha gene in human endometrial diseases. Gynecol Oncol 76: 89–96, 2000
Weigel RJ, Crooks DL, Iglehart JD, deConinck EC: Quantitative analysis of the transcriptional start sites of estrogen receptor in breast carcinoma. Cell Growth Differ 6: 707–711, 1995
Grandien K, Berkenstam A, Gustafsson JA: The estrogen receptor gene: promoter organization and expression. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 29: 1343–1369, 1997
Flouriot G, Griffin C, Kenealy M, Sonntag-Buck V, Gannon F: Differentially expressed messenger RNA isoforms of the human estrogen receptor-alpha gene are generated by alternative splicing and promoter usage. Mol Endocrinol 12: 1939–1954, 1998
Kadonaga JT, Courey AJ, Ladika J, Tjian R: Distinct regions of Sp1 modulate DNA binding and transcriptional activation. Science 242: 1566–1570, 1988
Jackson SP, MacDonald JJ, Lees-Miller S, Tjian R: GC box binding induces phosphorylation of Sp1 by a DNA-dependent protein kinase. Cell 63: 155–165, 1990
Dynan WS, Sazer S, Tjian R, Schimke RT: Transcription factor Sp1 recognizes a DNA sequence in the mouse dihydrofolate reductase promoter. Nature 319: 246–248, 1986
Wright KL, Moore TL, Vilen BJ, Brown AM, Ting JP: Major histocompatibility complex class II-associated invariant chain gene expression is up-regulated by cooperative interactions of Sp1 and NF-Y. J Biol Chem 270: 20978–20986, 1995
Rohr O, Aunis D, Schaeffer E: COUP-TF and Sp1 interact and cooperate in the transcriptional activation of the human immunodeficiency virus type 1 long terminal repeat in human microglial cells. J Biol Chem 272: 31149–31155, 1997
Schanke JT, Durning M, Johnson KJ, Bennett LK, Golos TG: SP1/SP3-binding sites and adjacent elements contribute to basal and cyclic adenosine 3′,5′-monophosphatestimulated transcriptional activation of the rhesus growth hormone-variant gene in trophoblasts [In Process Citation]. Mol Endocrinol 12: 405–417, 1998
Carrasco-Serrano C, Campos-Caro A, Viniegra S, Ballesta JJ, Criado M: GC-and E-box motifs as regulatory elements in the proximal promoter region of the neuronal nicotinic receptor alpha7 subunit gene. J Biol Chem 273: 20021–20028, 1998
Pagliuca A, Cannada-Bartoli P, Lania L: A role for Sp and helix-loop-helix transcription factors in the regulation of the human Id4 gene promoter activity. J Biol Chem 273: 7668–7674, 1998
Ulgiati D, Subrata LS, Abraham LJ: The role of Sp family members, basic Kruppel-like factor, and E box factors in the basal and IFN-gamma regulated expression of the human complement C4 promoter. J Immunol 164: 300–307, 2000
Liu HC, Shen JT, Augustin LB, Ko JL, Loh HH: Transcriptional regulation of mouse delta-opioid receptor gene. J Biol Chem 274: 23617–23626, 1999
Gobin SJ, van Zutphen M, Woltman AM, van den Elsen PJ: Transactivation of classical and nonclassical HLA class I genes through the IFN-stimulated response element. J Immunol 163: 1428–1434, 1999
Li Q, Hu N, Daggett MA, Chu WA, Bittel D, Johnson JA, Andrews GK: Participation of upstream stimulator factor (USF) in cadmium-induction of the mouse metallothionein-I gene. Nucl Acids Res 26: 5182–5189, 1998
Takahashi Y, Nakayama K, Itoh S, Kamataki T: Upstream stimulatory factor 1 (USF1) suppresses induction of CYP1A1 mRNA by 3-methylcholanthrene (MC) in HepG2 cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 240: 293–297, 1997
Ferre-D’Amare AR, Pognonec P, Roeder RG, Burley SK: Structure and function of the b/HLH/Z domain of USF. Embo J 13: 180–189, 1994
Lefrancois-Martinez AM, Martinez A, Antoine B, Raymondjean M, Kahn A: Upstream stimulatory factor proteins are major components of the glucose response complex of the L-type pyruvate kinase gene promoter. J Biol Chem 270: 2640–2643, 1995
Scholz A, Truss M, Beato M: Hormone-induced recruitment of Sp1 mediates estrogen activation of the rabbit uteroglobin gene in endometrial epithelium. J Biol Chem 273: 4360–4366, 1998
Krishnan V, Wang X, Safe S: Estrogen receptor-Sp1 complexes mediate estrogen-induced cathepsin D gene expression in MCF-7 human breast cancer cells. J Biol Chem 269: 15912–15917, 1994
Porter W, Saville B, Hoivik D, Safe S: Functional synergy between the transcription factor Sp1 and the estrogen receptor. Mol Endocrinol 11: 1569–1580, 1997
Roy AL, Du H, Gregor PD, Novina CD, Martinez E, Roeder RG: Cloning of an inr-and E-box-binding protein, TFII-I, that interacts physically and functionally with USF1. Embo J 16: 7091–7104, 1997
Oesterreich S, Zhang Q, Hopp T, Fuqua SA, Michaelis M, Zhao HH, Davie JR, Osborne CK, Lee AV: Tamoxifenbound estrogen receptor (ER) strongly interacts with the nuclear matrix protein HET/SAF-B, a novel inhibitor of ER-mediated transactivation. Mol Endocrinol 14: 369–381, 2000
Fuqua SA, Benedix MG, Krieg S, Weng CN, Chamness GC, Oesterreich S: Constitutive overexpression of the 27,000 dalton heat shock protein in late passage human breast cancer cells. Breast Cancer Res Treat 32: 177–186, 1994
Tandon AK, Clark GM, Chamness GC, Ullrich A, McGuire WL: HER-2/neu oncogene protein and prognosis in breast Cancer. J Clin Oncol 7: 1120–1128, 1989
Dynan WS, Tjian R: The promoter-specific transcription factor Sp1 binds to upstream sequences in the SV40 early promoter. Cell 35: 79–87, 1983
Hough PV, Mastrangelo IA, Wall JS, Hainfeld JF, Sawadogo M, Roeder RG: The gene-specific initiation factor USF (upstream stimulatory factor) bound at the adenovirus type 2 major late promoter: mass and three-dimensional structure. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 84: 4826–4830, 1987
Kreider BL, Benezra R, Rovera G, Kadesch T: Inhibition of myeloid differentiation by the helix-loop-helix protein Id. Science 255: 1700–1702, 1992
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
deGraffenried, L.A., Hopp, T.A., Valente, A.J. et al. Regulation of the Estrogen Receptor α Minimal Promoter by Sp1, USF-1 and ERα. Breast Cancer Res Treat 85, 111–120 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1023/B:BREA.0000025398.93829.78
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/B:BREA.0000025398.93829.78