Abstract
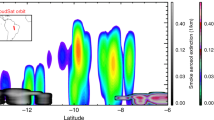
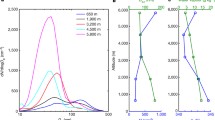
The temporal evolution and spatial structure of the aerosol layer (AL) height as observed with an airborne downlooking lidar over the Swiss Alps were investigated with a three-dimensional mesoscale numerical model and a particle dispersion model. Convective boundary-layer (CBL) heights were derived from the mesoscale model output, and the behaviour of surface-released particles was investigated with the particle dispersion model. While a previous investigation, using data from the same field study, equated the observed AL height with the CBL height, the results of the current investigation indicate that there is a considerable difference between AL and CBL heights caused by mixing and transport processes between the CBL and the free atmosphere. CBL heights show a more terrain-following behaviour and are lower than AL heights. We argue that processes causing the difference between AL and CBL heights are common over mountainous terrain and that the AL height is a length scale that needs to be considered in air pollution studies in mountainous terrain.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Braham, R. R. and Draginis, M.: 1960, ‘Roots of Orographic Cumuli’, J. Meteorol. 17, 214-224.
Ching, J. K. S., Shipley, S. T., and Browell, E. V.: 1988, “Evidence for Cloud Venting of Mixed Layer Ozone and Aerosols”, Atmos. Environ. 22, 225-242.
Cotton, W. R., Pielke, Sr., R. A., Walko, R. L., Liston, G. E., Tremback, C. J., Jiang, H., McAnelly, R. L., Harrington, J. Y., Nicholls, M. E., Carrio, G. G., and McFadden, J. P.: 2003, ‘RAMS 2001: Current Status and Future Directions’, Meteorol. Atmos. Phys. 82, 5-29.
Coulter, R. L.: 1979, ‘A Comparison of Three Methods for Measuring Mixing-Layer Height’, J. Appl. Meteorol. 8, 1495-1499.
Cramer, O. P.: 1972, ‘Potential Temperature Analysis for Mountainous Terrain’, J. Appl. Meteorol. 11, 44-50.
Cramer, O. P. and Lynott, R. E.: 1961, ‘Cross-section Analysis in the Study of Windflow over Mountainous Terrain’, Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 42, 693-702.
Dayan, U., Shenhav, R., and Graber, M.: 1988, ‘The Spatial and Temporal Behavior of the Mixed Layer in Israel’, J. Appl. Meteorol. 27, 1382-1394.
Deardorff, J. W., Willis, G. E., and Stockton, B. H.: 1980, ‘Laboratory Studies of the Entrainment Zone of a Convectively Mixed Layer’, J. Fluid Mech. 100, 41-64.
De Wekker, S. F. J.: 2002, Structure and Morphology of the Convective Boundary Layer in Mountainous Terrain, Ph.D. Dissertation, The University of British Columbia, BC, Canada, 191 pp.
De Wekker, S. F. J., Kossmann, M., and Fiedler, F.: 1997, ‘Observations of Daytime Mixed Layer Heights over Mountainous Terrain during the TRACT Field Campaign’, in Proceedings of the 12th AMS Symposium on Boundary Layers and Turbulence, Vancouver, BC, Canada, American Meteorological Society, 45 Beacon Street, Boston, MA, pp. 498-499.
Fast, J. D. and Zhong, S.: 1998, ‘Meteorological Factors Associated with Inhomogeneous Ozone Concentrations within the Mexico City Basin’, J. Geophys. Res. 103, 18927-18946.
Fiedler, F.: 1983, Einige Charakteristika der Strömung im Oberrheingraben, Wissenschaftliche Berichte des Meteorologischen Instituts der Universitä t Karlsruhe, Vol. 4, pp. 113-123.
Fiedler, F., Bischoff-Gauss, I., Kalthoff, N., and Adrian, G.: 2000, ‘Modeling of the Transport of a Tracer in the Freiburg-Schauinsland Area’, J. Geophys. Res. D 105, 1599-1610.
Hänel, G.: 1976, ‘The Properties of Atmospheric Aerosol Particles as Functions of the Relative Humidity at Thermodynamic Equilibrium with the Surrounding Moist Air’, Adv. Geophys. 19, 73-188.
Holzworth, G. C.: 1964, ‘Estimates of Mean Maximum Mixing Depths in the Contiguous U.S.’, Mon. Wea. Rev. 92, 235-242.
Kiemle, C., Kästner, M., and Ehret, G.: 1995, ‘The Convective Boundary Layer Structure from Lidar and Radiosonde Measurements during the EFEDA'91 Campaign’, J. Atmos. Ocean. Tech. 12, 771-782.
Kossmann, M., Corsmeier, U., De Wekker, S. F. J., Fiedler, F., Vögtlin, R., Kalthoff, N., Güsten, H., and Neininger, B.: 1999, ‘Observations of Handover Processes between the Atmospheric Boundary Layer and the Free Troposphere over Mountainous Terrain’, Contr. Atmos. Phys. 72, 329-350.
Kossmann, M., Vögtlin, R., Corsmeier, U., Vogel, B., Fiedler, F., Binder, H.-J., Kalthoff, N., and Beyrich, F.: 1998, ‘Aspects of the Convective Boundary Layer Structure over Complex Terrain’, Atmos. Environ. 32, 1323-1348.
Lagouvardos, K., Kotroni, V., and Kallos, G.: 1996, ‘Exploring the Effects of Different Types of Model Initialisation: Simulation of a Severe Air-Pollution Episode in Athens, Greece’, Meteorol. Appl. 3, 147-155.
Lenschow, D. H., Stankov, B. B., and Mahrt, L.: 1979, ‘The Rapid Morning Boundary-Layer Transition’, J. Atmos. Sci. 36, 2108-2124.
Lu, R. and Turco, R. P.: 1994, ‘Air Pollutant Transport in a Coastal Environment. Part 1: Two Dimensional Simulations of Sea-Breeze and Mountain Effects’, J. Atmos. Sci. 51, 2285-2308.
Lugauer, M.: 1998, Vertical Transport of Atmospheric Trace Species in the Alps, Ph.D. Dissertation, University of Bern, Switzerland, 91 pp.
Lyons, W. A., Pielke, R. A., Cotton, W. R., Tremback, C. J., Walko, R. L., Uliasz, M., and Ibarra, J. I.: 1994, ‘Recent Applications of the RAMS Meteorological and the HYPACT Dispersion Models’, in S.-E. Gryning and M. M. Millan (eds.), Proceedings of the 20th ITM of NATO/CCMS on Air Pollution Modeling and its Application. Plenum Press, New York, pp. 19-26.
Marsik, F. J., Fischer, K. W., McDonald, T. D., and Samson, P. J.: 1995, ‘Comparison of Methods for Estimating Mixing Height Used during the 1992 Atlanta Field Intensive’, J. Appl. Meteorol. 34, 1802-1814.
McKendry, I. G. and Lundgren, J.: 2000, ‘Tropospheric Layering of Ozone in Regions of Urbanized Complex and/or Coastal Terrain: A Review’, Progr. Phys. Geog. 24, 329-354.
McKendry, I. G., Steyn, D. G., Lundgren, J., Hoff, R. M., Strapp, W., Anlauf, K., Froude, F., Martin, B. A., Banta, R. M., and Olivier, L. D.: 1997, ‘Elevated Pollution Layers and Vertical Downmixing over the Lower Fraser Valley, B. C.’, Atmos. Environ. 31, 2135-2146.
Nyeki, S., Kalberer, M., Colbeck, I., De Wekker, S. F. J., Furger, M., Gäggeler, H. W., Kossmann, M., Lugauer, M., Steyn, D., Weingartner, E., Wirth, M., and Baltensperger, U.: 2000, ‘Convective Boundary Layer Evolution to 4 km asl over High-Alpine Terrain: Airborne Lidar Observations in the Alps’, Geophys. Res. Lett. 27, 689-692.
Pielke, R. A.: 2002, Mesoscale Meteorological Modeling, 2nd edn., Academic Press, San Diego, CA, 676 pp.
Raymond, D. and Wilkening, M.: 1980, ‘Mountain Induced Convection under Fair Weather Conditions’, J. Atmos. Sci. 37, 2693-2706.
Schwiesow, R. L., 1984, ‘Lidar Measurements of Boundary-Layer Variables’, in D. H. Lenschow (ed.), Probing the Atmospheric Boundary Layer, Amer. Meteorol. Soc., pp. 139-162.
Seibert, P., Beyrich, F., Gryning, S.E., Joffre, S., Rasmussen, A., and Tercier, P.: 2000, ‘Review and Intercomparison of Operational Methods for the Determination of the Mixing Height’, Atmos. Environ. 34, 1001-1027.
Sullivan, P. P., Moeng, C-H., Stevens, B., Lenschow, D. H., and Mayor, S. D.: 1998, ‘Structure of the Entrainment Zone Capping the Convective Atmospheric Boundary-Layer’, J. Atmos. Sci. 55, 3042-3064.
Troen, I. and Mahrt, L.: 1986, ‘A Simple Model of the Atmospheric Boundary-Layer: Sensitivity to Surface Evaporation’, Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 37, 129-148.
Van Pul, W. A. J., Holtslag, A. A. M., and Swart, D. P. J.: 1994, ‘A Comparison of ABLheights Inferred Routinely from Lidar and Radiosondes at Noontime’, Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 68, 173-191.
Vogelezang, D. H. P. and Holtslag, A. A. M.: 1996, ‘Evaluation and Model Impacts of Alternative Boundary-Layer Height Formulations’, Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 81, 245-269.
Walko,R.L.,Tremback,C.J.,and Bell,M.J.:2001,HYPACT.Hybrid Particle and Concentration Transport Model.User's Guide ,35 pp. [Available from ASTER Division, Mission Research Corporation, P. O. Box 466, Fort Collins, CO 80525-0466].
Whiteman, C. D.: 1990, ‘Observations of Thermally Developed Wind Systems in Mountainous Terrain’, in W. Blumen (ed.), Atmospheric Processes over Complex Terrain, Meteorol. Monogr., 23 (no. 45), Amer. Meteorol. Soc., Boston, MA, pp. 5-42.
WMO (World Meteorological Organization): 1993, Handbook of Meteorological Forecasting for Soaring Flights, 2nd edn., Technical Note No. 158, WMO No. 495, Geneva, Switzerland, 84 pp.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
De Wekker, S.F.J., Steyn, D.G. & Nyeki, S. A Comparison Of Aerosol-Layer And Convective Boundary-Layer Structure Over A Mountain Range During Staaarte '97. Boundary-Layer Meteorology 113, 249–271 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1023/B:BOUN.0000039371.41823.37
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/B:BOUN.0000039371.41823.37